Calcium ion batteries (CIBs) have attracted much attention as next-generation batteries to replace lithium ion batteries (LIBs) because the theoretical capacity of CIBs is twice that of LIBs. This doubled capacity can be explained by the difference between monovalent and divalent ions. In addition, CIBs possess advantages such as a lower cost and higher safety because calcium is more abundant than lithium and because CIBs have a higher melting point than LIBs. However, there is one major obstacle to the application in CIBs. There is no suitable electrode material in which calcium ions can be inserted and extracted reversibly because of the relatively large ionic radius of calcium ions (112 pm) as compared to that of lithium ions (76 pm).
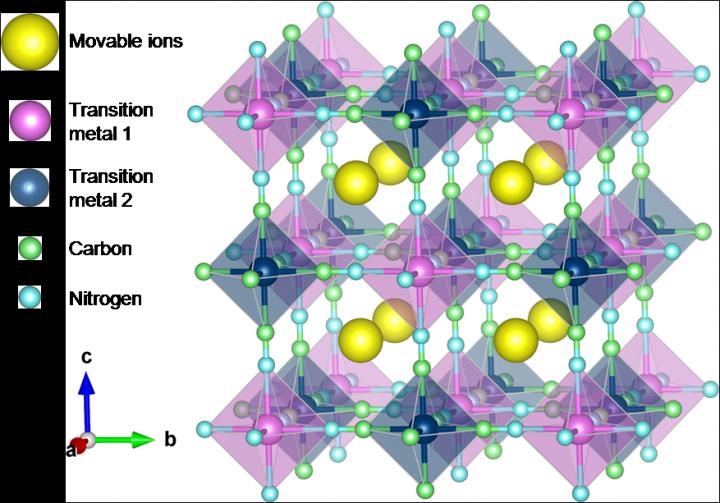
In this study, Tomohiro Tojo and his colleagues at the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology, employed Prussian blue (PB) and Prussian blue analogues (PBAs) as CIB electrodes because they possess large sites for inserting and extracting large-sized ions, as shown in Fig. 1. Up to now, using PBAs as an electrode material, the electrochemical behaviors of sodium ions corresponding to the radius of calcium ions have been examined in organic and inorganic electrolytes. These reports have shown reversible insertion and extraction of sodium ions into and from PBA structures.
The research team investigated the electrochemical performance of several PBA electrodes in order to determine whether calcium ions in an organic electrolyte exhibit either reversible or irreversible insertion and extraction into and from the crystal structure. We found reversible capacities of 40-50 mAh/g at a low current density, as shown in Fig. 2(a). In Fig. 2(b), the Coulombic efficiencies, which are defined as the ratio of the amount of insertion (discharge) and extraction (charge) of calcium ions, were observed to have a constant value of 90% after the 3rd cycle.
The results shown in Fig. 2 demonstrate the excellent cyclability of the PBA electrodes, even though the reversible capacities were half the theoretical capacity. The researchers investigated the reason for the high reversibility using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The reversibility is explained by the durable structure of the PBAs and their excellent charge balance during the insertion and extraction of calcium ions.
We propose Prussian blue (PB) and Prussian blue analogues (PBAs) as feasible electrode materials for CIBs, even though additional investigation is needed in order to enhance the reversible capacities still further. The researchers have carried out the further study to utilize CIBs beyond LIBs.
###
Funding agency:
Tomohiro Tojo acknowledges the partial support through a Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research (No. 15K13947). Yoji Sakurai acknowledges support from a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B), No. 24360109 from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Reference:
Authors: Tomohiro Tojo, Yosuke Sugiura, Ryoji Inada, and Yoji Sakurai.
Title of original paper: Reversible Calcium Ion Batteries Using a Dehydrated Prussian Blue Analogue Cathode.
Journal, volume, pages and year: Electrochimica Acta, 207, 22-27 (2016).
Digital Object Identifier (DOI): 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.04.159
Affiliation: Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology.
Information about the first author: http://researchmap.jp/tj1010/?lang=english
Further information
Toyohashi University of Technology
1-1 Hibarigaoka, Tempaku
Toyohashi, Aichi Prefecture, 441-8580, JAPAN
Inquiries: Committee for Public Relations
E-mail: [email protected]
Toyohashi University of Technology, which was founded in 1976 as a National University of Japan, is a leading research institute in the fields of mechanical engineering, advanced electronics, information sciences, life sciences, and architecture.
Website: http://www.tut.ac.jp/english/
Media Contact
Ryoji Inada
[email protected]
The post Towards building next-generation batteries using a pigment electrode appeared first on Scienmag.