Most native species are going locally extinct, while introduced tropical species thrive
Credit: © Paolo Albano
The coastline of Israel is one of the warmest areas in the Mediterranean Sea. Here, most marine species have been at the limits of their tolerance to high temperatures for a long time – and now they are already beyond those limits. Global warming has led to an increase in sea temperatures beyond those temperatures that Mediterranean species can sustain. Consequently, many of them are going locally extinct.
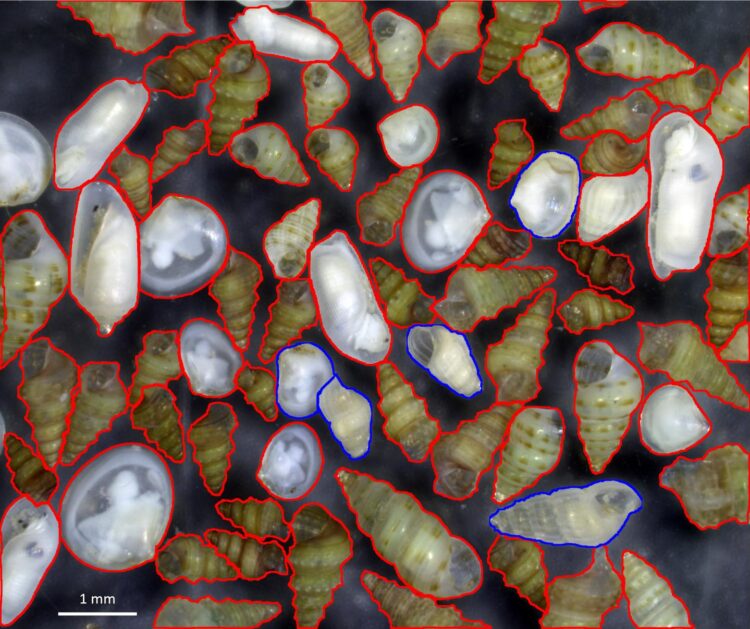
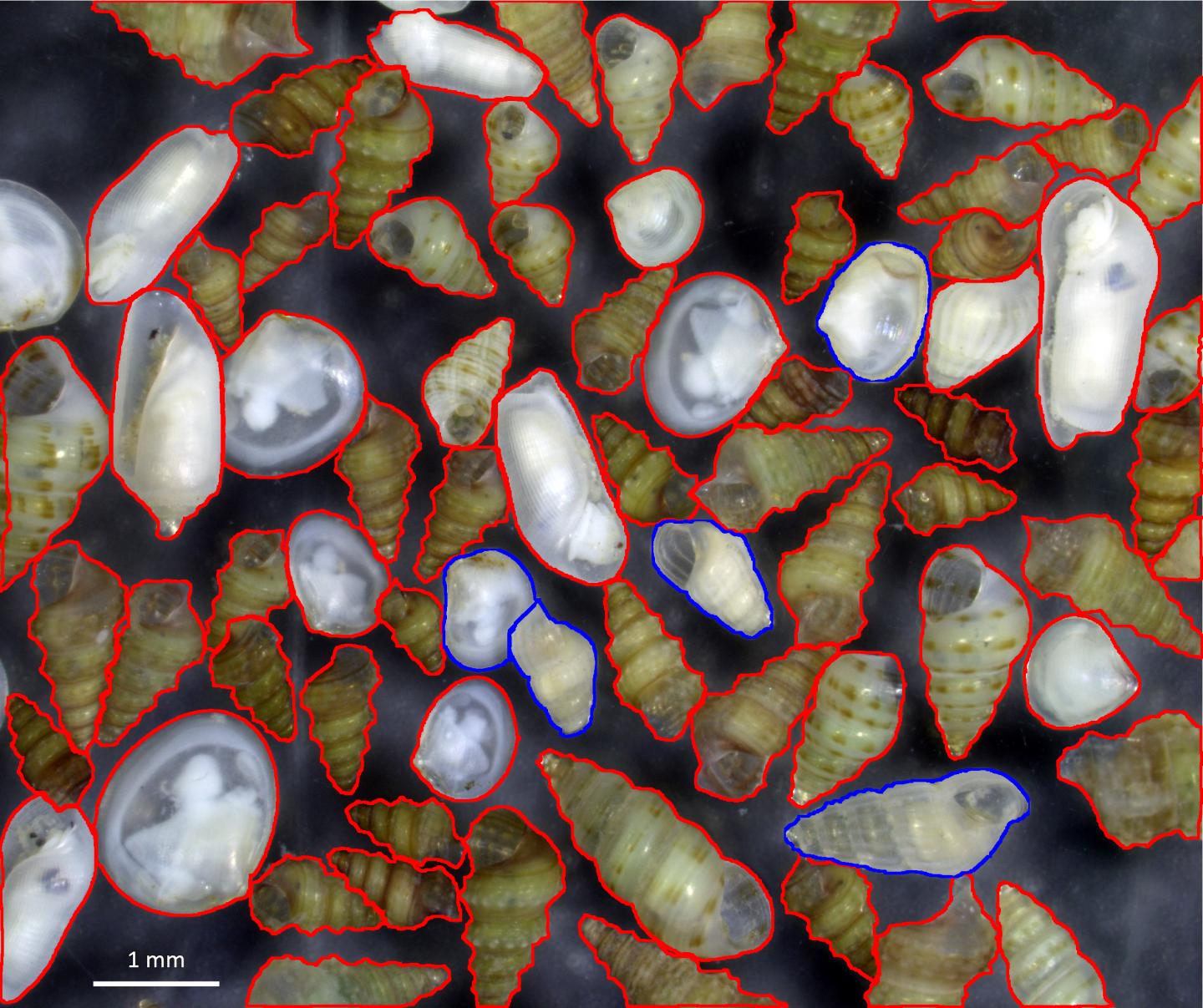
Paolo Albano’s team quantified this local extinction for marine molluscs, an invertebrate group encompassing snails, clams and mussels. They thoroughly surveyed the Israeli coastline and reconstructed the historical species diversity using the accumulations of empty shells on the sea bottom.
Biodiversity loss in the last few decades
The shallow habitats at scuba diving depths are affected most. Here, the researchers were not able to find living individuals of up to 95 per cent of the species whose shells were found in the sediments. The study suggests that most of this loss has occurred recently, presumably in just the last few decades.
Additionally, most of the species still found alive cannot grow enough to reproduce, “a clear sign that the biodiversity collapse will further continue,” says Albano. In contrast, the tropical species that enter from the Suez Canal thrive. The warm waters in the Eastern Mediterranean are very suitable habitats for them. Indeed, they occur in large populations and their individuals are fully fit to reproduce.
“For anyone accustomed to snorkel or dive in the Mediterranean,” explains the researcher, “the underwater scenario in Israel is unrecognisable: The most common species are missing, while in contrast tropical species are everywhere”.
The future perspectives for the Mediterranean are not good. The sea will continue to warm even if we would stop carbon dioxide emissions today. This is due to the inertia of the system, the long braking distance, so to speak.
It is thus likely that the biodiversity collapse will continue to spread. It may already be occurring in other eastern Mediterranean areas not surveyed yet, and it will expand to the West and intensify. Only intertidal organisms, which are to some extent pre-adapted to temperature extremes, and habitats in deeper water, where the temperature is markedly lower, will continue to persist – at least for some time.
“But the future is dim unless we immediately act to reduce our carbon emissions and to protect marine habitats from other pressures which contribute to biodiversity loss,” says Paolo Albano, “The changes that already occurred in the warmest areas of the Mediterranean may not be reversible, but we would be able to save large parts of the rest of the basin.”
Methodologically, the study was also interesting due to its interdisciplinary character: “These results came from the cooperation of scientists with very different backgrounds,” says Martin Zuschin, Head of the Department of Palaeontology and co-author of the study – “In particular, the cooperation between ecologists and palaeontologists is providing unique new views on how humankind is impacting biodiversity”.
###
Publication in Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences:
Albano P.G., Steger J., Bošnjak M., Dunne B., Guifarro Z., Turapova E., Hua Q., Kaufman D.S., Rilov G., Zuschin M.: Native biodiversity collapse in the Eastern Mediterranean. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 2021.
DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2020.2469
Media Contact
Dr. Paolo Albano
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.