Researchers studied the fabrication of polymeric fibers for use in advanced health care
Credit: Hussain Alenezi, Muhammet Emin Cam and Mohan Edirisinghe
WASHINGTON, D.C., October 15, 2019 — “Polymers are very, very useful materials when it comes to modern applications.”
Mohan Edirisinghe leads a team of researchers at University College London studying the fabrication of polymeric nanofibers and microfibers — very thin fibers made up of polymers. The group describes a study comparing fabrication techniques for these fibers without the use of electric fields in Applied Physics Reviews, from AIP Publishing.
For applications ranging from scaffolding for tissue engineering and drug delivery to bacterial and viral air filtration, polymeric fibers can be woven into textilelike structures with the characteristics required for the task. Depending on the use, different fiber thicknesses may be necessary. But the ability to fabricate thin fibers with consistent characteristics is important.
“When you have thinner fibers, you use lesser material, and you can weave a web — whether it’s a tissue engineering scaffold or a filtration scaffold — much better,” said Edirisinghe. “You can put more fiber strands in what you weave.”
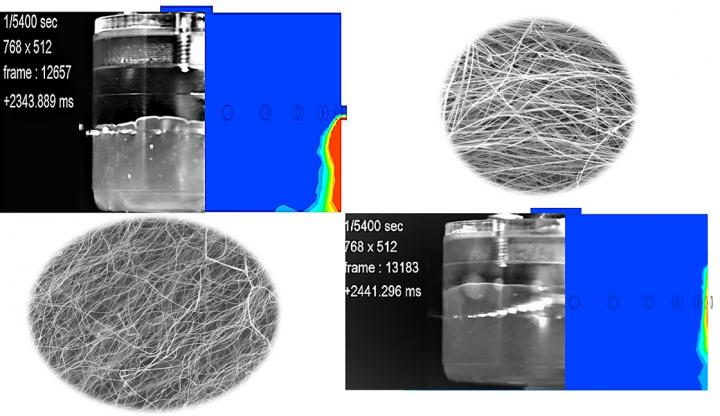
To study the effects of various parameters on fiber fabrication, the researchers compared the characteristics of fibers created in different ways. The conventional way of making fibers is by a process called centrifugal spinning. In centrifugal spinning, the polymer solution is placed in a reservoir. When the reservoir is rotated at high speeds, the polymer solution jets out in the form of fine fibers.
Edirisinghe and his team compared this to a method they invented and developed called pressure gyration. It functions broadly the same as centrifugal spinning, but with one key difference. High-pressure gas is applied inside the rotating vessel during the fabrication process.
They found increasing the rotational speed in both techniques and increasing the applied pressure in the pressure gyration technique both lead to thinner, more consistent fibers.
“The pressure makes a hell of a lot of difference,” Edirisinghe said.
For industrial applications, polymeric fibers need to be fabricated in larger quantities and in a way that ensures uniformity from pot to pot. To address these concerns, the researchers were also interested in seeing how the polymer was behaving inside the vessel while the fibers were being fabricated. For the first time, they fabricated the fibers in a transparent pot and used a high-speed camera to capture images during the process. They also compared the behavior to theoretical predictions.
In the future, the group plans to automate the fabrication process to make these nanofibers with optimal thickness and minimal waste. In addition, they are working on finding ways to make the material stronger and more suitable for biomedical applications by making fibers with a different interior and a bioactive exterior.
“If you take this technology to textiles where you can coat the fiber with some other smart sensing material, you can do miracles with them,” Edirisinghe said. “There are lots of possibilities!”
###
The article, “Experimental and theoretical investigation of the fluid behavior during polymeric fiber formation,” is authored by Hussain Alenezi, Muhammet Emin Cam and Mohan Edirisinghe. The article will appear in Applied Physics Reviews on Oct. 15, 2019 (DOI: 10.1063/1.5110965). After that date, it can be accessed at http://aip.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Reviews features articles on significant and current topics in experimental or theoretical research in applied physics, or in applications of physics to other branches of science and engineering. The journal publishes both original research on pioneering studies of broad interest to the applied physics community, and reviews on established or emerging areas of applied physics. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
301-209-3090
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




