Credit: Burcu Kepsutlu/HZB
Today, nanoparticles are not only in cosmetic products, but everywhere, in the air, in water, in the soil and in food. Because they are so tiny, they easily enter into the cells in our body. This is also of interest for medical applications: Nanoparticles coated with active ingredients could be specifically introduced into cells, for example to destroy cancer cells. However, there is still much to be learned about how nanoparticles are distributed in the cells, what they do there, and how these effects depend on their size and coating.
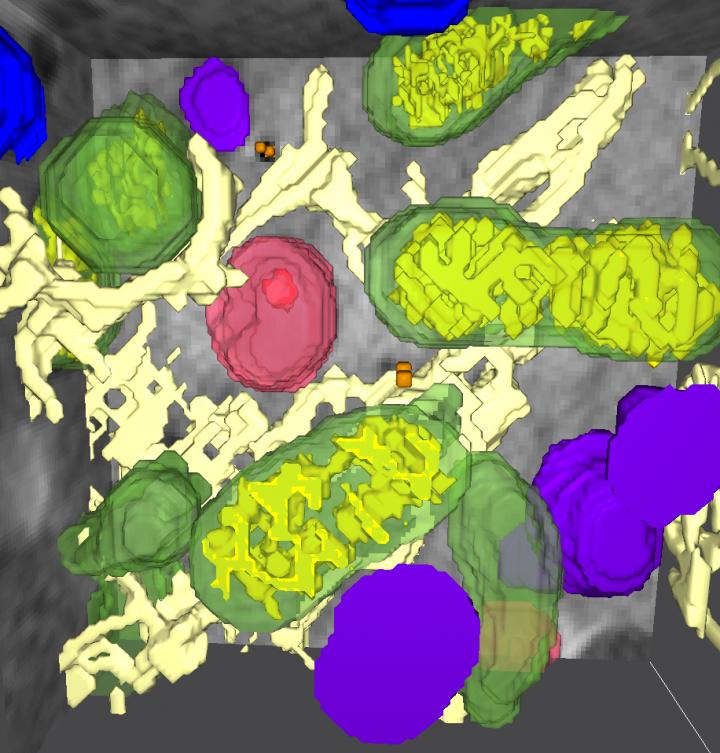
New insights have come from a study at BESSY II, where Prof. Gerd Schneider’s team can take X-ray microscopy images with soft, intensive X-rays. Researchers from the X-ray microscopy group led by HZB biophysicist Dr. James McNally investigated cells with differently coated nanoparticles. The nanoparticles were exactly the same size, but were coated with different active ingredients.
“X-ray microscopy offers significantly better resolution than light microscopy, and a much better overview than electron microscopy,” emphasizes Schneider. For the first time, the team obtained complete, three-dimensional, high-resolution images of the nanoparticle-treated cells with the organelles contained therein: including lipid droplets, mitochondria, multivesicular bodies and endosomes. Lipid droplets act as energy stores in the cell, while mitochondria metabolize this energy.
The analysis of the images showed: The nanoparticles accumulate preferentially in a subset of the cell organelles and also change the number of certain organelles at the expense of other organelles. The changes in organelle numbers were similar regardless of the nanoparticle coating, suggesting that many different kinds of nanoparticle coatings may induce a similar effect. To evaluate how general this effect is, further studies with other nanoparticle coatings and with other cell types must be performed.
“X-ray microscopy allows us to see the cell as a whole, so we were able to observe this behavior for the first time,” explains McNally. “We found that the absorption of such nanoparticles increases the number of mitochondria and endosomes, while other organelles, namely lipid droplets and multivesicular bodies, decrease,” says Burcu Kepsutlu, who carried out the experiments for her doctorate.”When we go on a starvation diet or run a marathon, we see similar changes in the cell – namely an increase in mitochondria and a decrease in lipid droplets,” says McNally. “Apparently it takes energy for the cell to absorb the nanoparticles, and the cell feels like it has just run a marathon.”
###
Media Contact
Antonia Roetger
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




