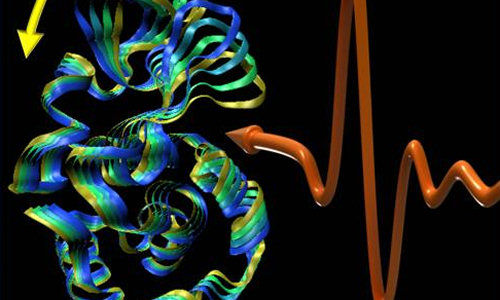
Like the strings on a violin or the pipes of an organ, the proteins in the human body vibrate in different patterns, scientists have long suspected.
Now, a new study provides what researchers say is the first conclusive evidence that this is true.
Using a technique they developed based on terahertz near-field microscopy, scientists from the University at Buffalo and Hauptman-Woodward Medical Research Institute (HWI) have for the first time observed in detail the vibrations of lysozyme, an antibacterial protein found in many animals.
The team found that the vibrations, which were previously thought to dissipate quickly, actually persist in molecules like the “ringing of a bell,” said UB physics professor Andrea Markelz, PhD, wh0 led the study.
These tiny motions enable proteins to change shape quickly so they can readily bind to other proteins, a process that is necessary for the body to perform critical biological functions like absorbing oxygen, repairing cells and replicating DNA, Markelz said.
The research opens the door to a whole new way of studying the basic cellular processes that enable life.
“People have been trying to measure these vibrations in proteins for many, many years, since the 1960s,” Markelz said. “In the past, to look at these large-scale, correlated motions in proteins was a challenge that required extremely dry and cold environments and expensive facilities.”
“Our technique is easier and much faster,” she said. “You don’t need to cool the proteins to below freezing or use a synchrotron light source or a nuclear reactor—all things people have used previously to try and examine these vibrations.”
The findings will appear in Nature Communications on Jan. 16, and publication of information on the research is prohibited until 5 a.m. U.S. Eastern Time on that day.
To observe the protein vibrations, Markelz’ team relied on an interesting characteristic of proteins: The fact that they vibrate at the same frequency as the light they absorb.
This is analogous to the way wine glasses tremble and shatter when a singer hits exactly the right note. Markelz explained: Wine glasses vibrate because they are absorbing the energy of sound waves, and the shape of a glass determines what pitches of sound it can absorb. Similarly, proteins with different structures will absorb and vibrate in response to light of different frequencies.
So, to study vibrations in lysozyme, Markelz and her colleagues exposed a sample to light of different frequencies and polarizations, and measured the types of light the protein absorbed.
This technique, developed with Edward Snell, a senior research scientist at HWI and assistant professor of structural biology at UB, allowed the team to identify which sections of the protein vibrated under normal biological conditions. The researchers were also able to see that the vibrations endured over time, challenging existing assumptions.
“If you tap on a bell, it rings for some time, and with a sound that is specific to the bell. This is how the proteins behave,” Markelz said. “Many scientists have previously thought a protein is more like a wet sponge than a bell: If you tap on a wet sponge, you don’t get any sustained sound.”
Markelz said the team’s technique for studying vibrations could be used in the future to document how natural and artificial inhibitors stop proteins from performing vital functions by blocking desired vibrations.
“We can now try to understand the actual structural mechanisms behind these biological processes and how they are controlled,” Markelz said.
“The cellular system is just amazing,” she said. “You can think of a cell as a little machine that does lots of different things—it senses, it makes more of itself, it reads and replicates DNA, and for all of these things to occur, proteins have to vibrate and interact with one another.”
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by University of Buffalo.