New research published in The American Journal of Pathology suggests that aged African green monkeys may be suitable models for the study of severe forms of COVID-19
Credit: The American Journal of Pathology
Philadelphia, January 19, 2021 – Aged, wild-caught African green monkeys exposed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus developed acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) with clinical symptoms similar to those observed in the most serious human cases of COVID-19, report researchers in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier. This is the first study to show that African green monkeys can develop severe clinical disease after SARS-CoV-2 infection, suggesting that they may be useful models for the study of COVID-19 in humans.
“Animal models greatly enhance our understanding of diseases. The lack of an animal model for severe manifestations of COVID-19 has hampered our understanding of this form of the disease,” explained lead investigator Robert V. Blair, DVM, PhD, Dip ACVP, Tulane National Primate Research Center, Covington, LA, USA. “If aged green monkeys prove to be a consistent model of severe COVID-19, studying the disease pathobiology in them would improve our understanding of the disease and allow testing treatment options.”
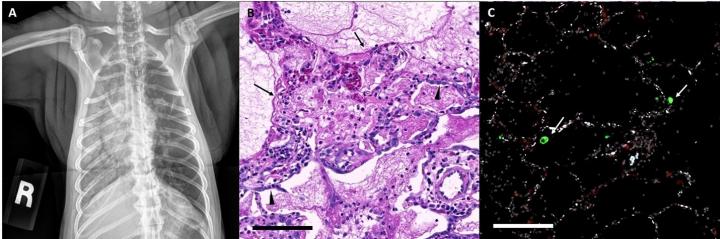
The researchers exposed four aged rhesus macaques and four aged African green monkeys to SARS-CoV-2. Older animals (13-16 years of age) were specifically chosen to see if they would develop the severe form of the disease that is observed more frequently in elderly individuals. All of the monkeys developed a spectrum of disease from mild to severe COVID-19. A day after routine screening found no remarkable symptoms, two of the African green monkeys developed rapid breathing that quickly progressed to severe respiratory distress. Radiographic studies found the two African green monkeys had widespread opacities in the lungs, in stark contrast to images taken the day before, highlighting the rapid development of the disease. Such opacities are a hallmark of ARDS in humans.
The African green monkeys that progressed to severe disease had notable increases in plasma cytokines that are compatible with cytokine storm, which is thought to underlie the development of ARDS in some patients. All four African green monkeys had elevated levels of interferon gamma; the two that had progressed to ARDS had the highest plasma concentration. Plasma cytokines were not increased in the rhesus macaques. Dr. Blair suggested that elevated interferon gamma could be explored as a potential predictive biomarker for advanced disease in patients and a possible therapeutic target.
Dr. Blair said, “Our data suggest that both rhesus monkeys and African green monkeys are capable of modeling mild manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and aged African green monkeys may additionally be capable of modeling severe disease manifestations, including ARDS.”
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




