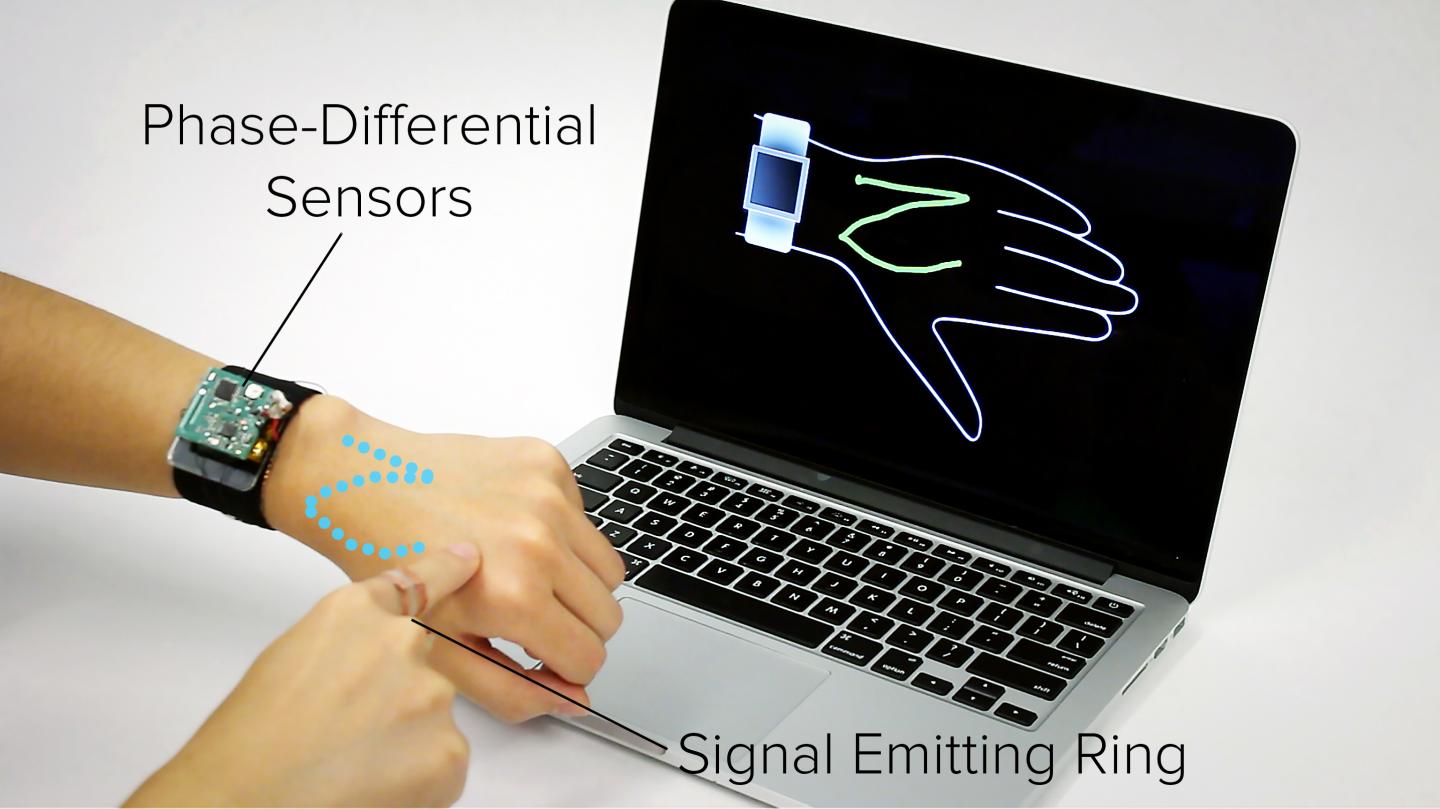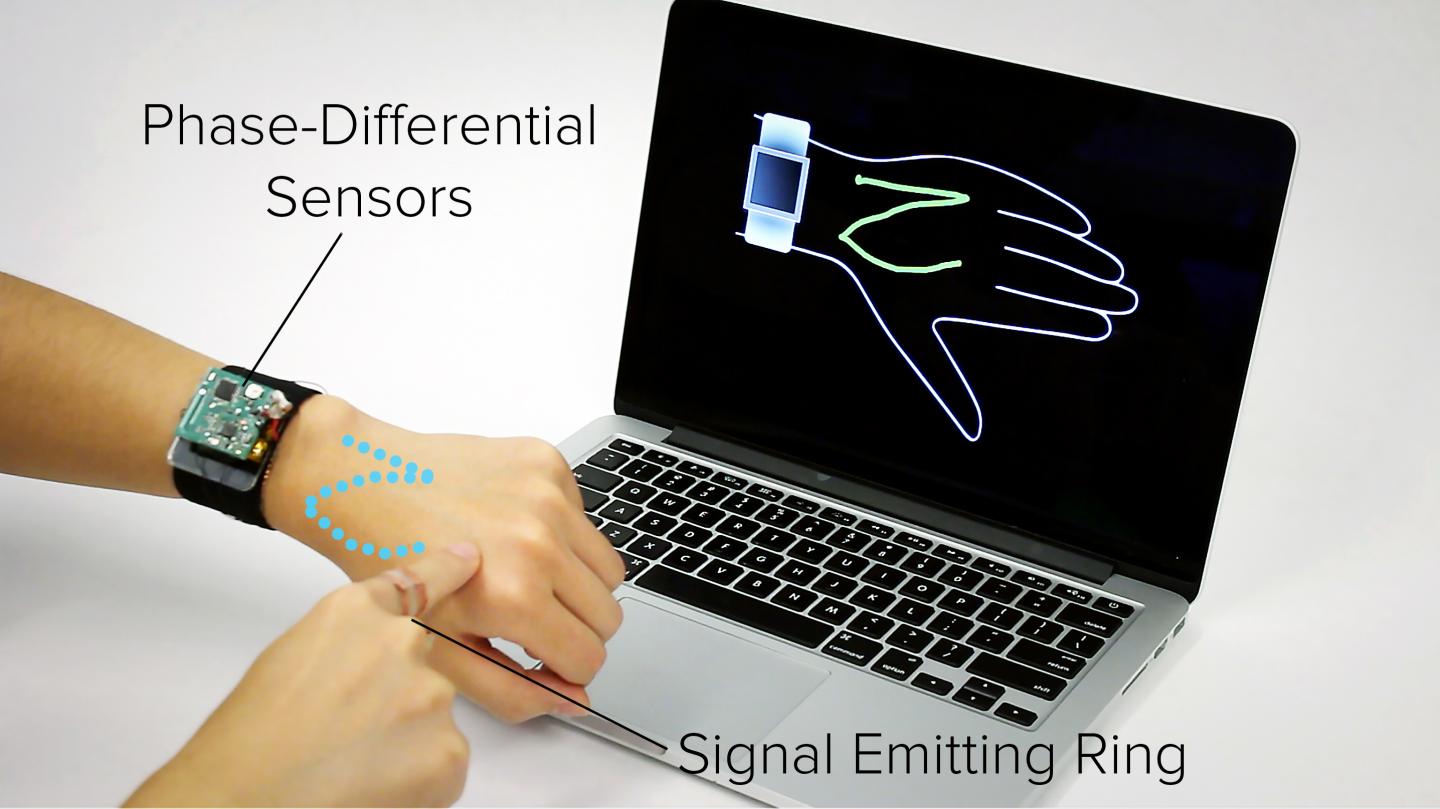
PITTSBURGH — Ever since the advent of smartwatches, technologists have been looking to expand interactions beyond the confines of the small watch face. A new wearable technology developed at Carnegie Mellon University suggests turning the entire lower arm into a touchpad.
Called SkinTrack and developed by the Human-Computer Interaction Institute’s Future Interfaces Group, the new system allows for continuous touch tracking on the hands and arms. It also can detect touches at discrete locations on the skin, enabling functionality similar to buttons or slider controls.
Previous “skin to screen” approaches have employed flexible overlays, interactive textiles and projector/camera combinations that can be cumbersome. SkinTrack, by contrast, requires only that the user wear a special ring, which propagates a low-energy, high-frequency signal through the skin when the finger touches or nears the skin surface.
“The great thing about SkinTrack is that it’s not obtrusive; watches and rings are items that people already wear every day,” said Yang Zhang, a first-year Ph.D. student in HCII. He will present details of the technology May 10, 2016 at CHI 2016, the Association for Computing Machinery’s Conference on Human Factors in Computing, in San Jose, Calif. A video explaining the technology can be viewed on YouTube.
“A major problem with smartwatches and other digital jewelry is that their screens are so tiny,” said Gierad Laput, a Ph.D. student in HCII and part of the research team. “Not only is the interaction area small, but your finger actually blocks much of the screen when you’re using it. Input tends to be pretty basic, confined to a few buttons or some directional swipes.”
“SkinTrack makes it possible to move interactions from the screen onto the arm, providing much larger interface,” said Chris Harrison, assistant professor in the HCII and adviser to the research. The user wears a ring that produces a high-frequency electrical signal. When the finger gets near to the skin or touches the skin, that signal propagates through the skin.
By using electrodes integrated into the watch’s strap, it’s possible to pinpoint the source of those electromagnetic waves because the phase of the waves will vary. Electrodes corresponding to the 12 o’clock and 6 o’clock positions on the watch, for instance, can detect phase differences that can determine the position of the finger along the width of the arm; electrodes at the 3 o’clock and 9 o’clock positions can determine the finger’s position along the length of the arm.
The researchers found that they could determine when the finger was touching the skin with 99 percent accuracy and they could resolve the location of the touches with a mean error of 7.6 millimeters. That compares well with other on-body finger-tracking systems and approaches touchscreen-like accuracy.
The researchers showed that SkinTrack could be used as a game controller, to scroll through lists on the smartwatch, to zoom in and out of onscreen maps, and to draw. A number pad application enabled users to use the back of the hand as a dial pad for the onscreen number pad; hovering a finger over the hand acts as a cursor, highlighting numbers on the screen to aid in targeting touch points. The system has some limitations. Keeping the ring powered up is a challenge. Signals also tend to change as the device is worn for long periods, thanks to factors such as sweat and hydration and the fact the body is in constant motion.
The technology is safe. No evidence suggests that the radio frequency signals used by SkinTrack have any health effects. The body is commonly excited by daily appliances — everything from the tiny amounts of current drawn from the finger by touchscreens to the electromagnetic noise emanating from fluorescent lights — with no ill effects.
###
About Carnegie Mellon University: Carnegie Mellon is a private, internationally ranked research university with programs in areas ranging from science, technology and business, to public policy, the humanities and the arts. More than 13,000 students in the university’s seven schools and colleges benefit from a small student-to-faculty ratio and an education characterized by its focus on creating and implementing solutions for real problems, interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation.
Media Contact
Byron Spice
[email protected]
412-268-9068
@CMUScience
http://www.cmu.edu
The post SkinTrack technology turns arm into smartwatch touchpad appeared first on Scienmag.