UCLA researchers study the disease’s systemic effects
Credit: JCI Insight/UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center
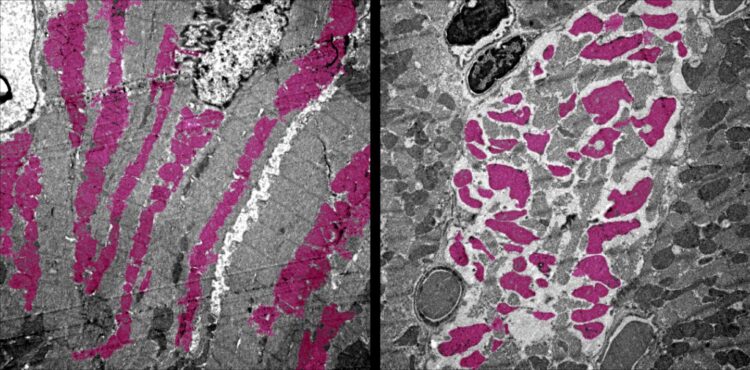
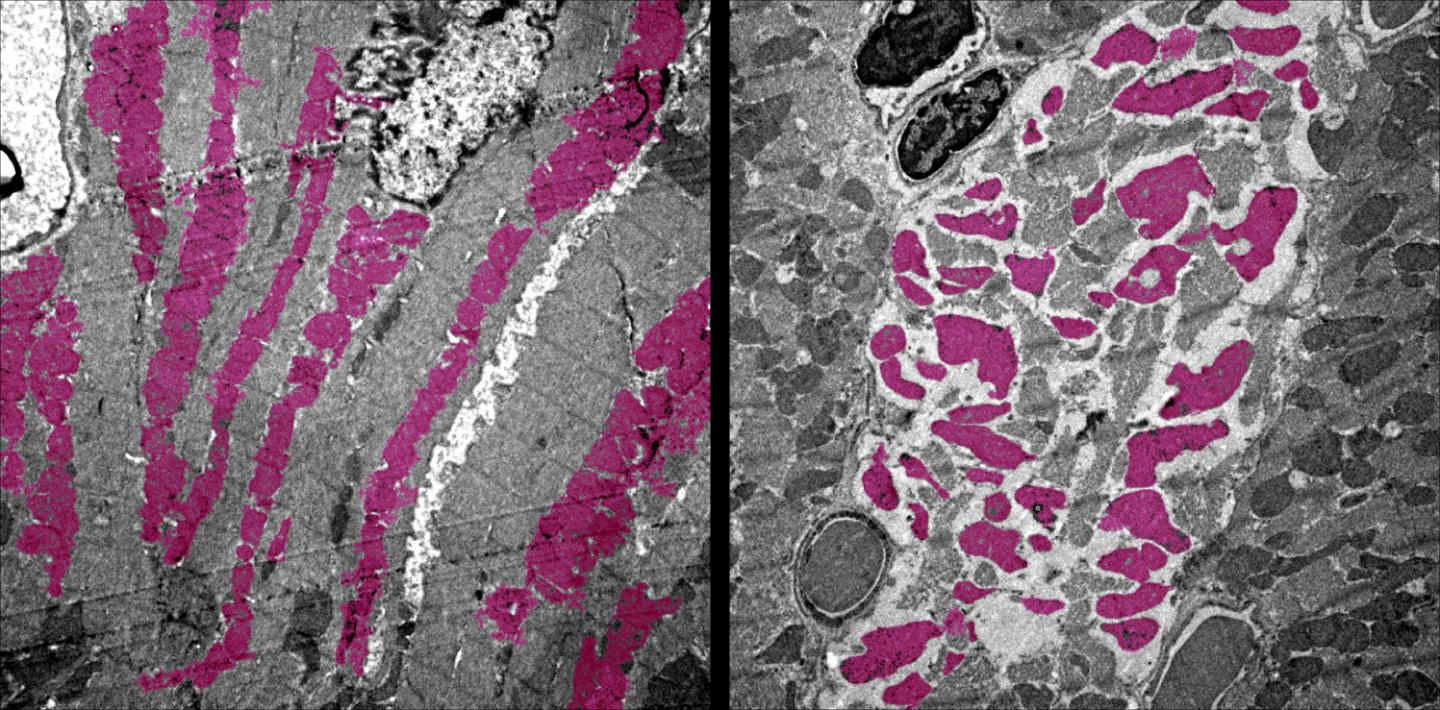
UCLA researchers are the first to create a version of COVID-19 in mice that shows how the disease damages organs other than the lungs. Using their model, the scientists discovered that the SARS-CoV-2 virus can shut down energy production in cells of the heart, kidneys, spleen and other organs.
“This mouse model is a really powerful tool for studying SARS-CoV-2 in a living system,” said Dr. Arjun Deb, a co-senior author of a paper about the study and a member of the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA. “Understanding how this virus can hijack our cells might eventually lead to new ways to prevent or treat the organ failure that can accompany COVID-19 in humans.”
Deb said the same model could also help researchers learn more about other similar viruses that might emerge in the future, and it could be useful for testing eventual treatments.
The paper, published in the journal JCI Insight, was co-led by Vaithilingaraja Arumugaswami, an associate professor of molecular and medical pharmacology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA and a member of the Broad Stem Cell Research Center.
Researchers often study mice to understand the fundamentals of human disease, but translating human health conditions to animal models can be tricky. SARS-CoV-2, for instance, relies on the ACE2 protein to infect humans. But the virus doesn’t recognize the mouse version of ACE2, so healthy mice exposed to the SARS-CoV-2 virus don’t get sick.
In previous experiments by other research teams around the world, mice have been genetically engineered to have the human version of ACE2 in their lungs and then been infected — through their noses — with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Although that enables the virus to infect the mice and cause pneumonia, animals in those experiments don’t get as broad a range of other symptoms as humans do.
“Among COVID-19 patients, those who have organs involved other than the lungs are most at risk of a bad outcome,” said Deb, who is also a cardiologist and professor of molecular cell and developmental biology. “So we felt it was really important to understand how the virus affects those other organs.”
Research in humans has suggested that SARS-CoV-2 can circulate through the bloodstream to reach multiple organs. So in the UCLA experiment, the researchers first engineered mice to have the human version of ACE2 in the heart and other vital organs. Then, they infected half of the animals by injecting SARS-CoV-2 into their bloodstreams. Over the following days, the researchers tracked the animals’ overall health and analyzed how levels of certain genes and proteins in their bodies changed.
Within seven days, all of the mice with COVID-19 had stopped eating and were completely inactive, and had lost, on average, about 20% of their body weight. Animals that had been engineered to carry the human ACE2 protein but had not been infected with the virus, on the other hand, did not lose a significant amount of weight.
Moreover, the COVID-19 infected animals had altered levels of immune cells, swelling of the heart tissue and wasting away of the spleen — all symptoms that have been observed in people who are critically ill with COVID-19.
Deb’s team also looked at which genes were turned on and off in the mice infected with SARS-CoV-2, and they discovered other signs of disease. Common molecular processes that help cells generate energy — through mechanisms known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle, or TCA cycle, and electron transport chain — were shut off in the heart, kidney, spleen and lungs.
“If a virus snuffs out the energy-generating pathways in multiple organs of the body, that’s going to really wreak havoc,” Deb said.
Finally, the study also revealed that some changes were long-lasting throughout the organs in mice with COVID-19. In addition to temporarily altering which genes were turned on and off in some cells, the virus made epigenetic changes — chemical alterations to the structure of DNA that cause more lasting effects. Deb said that could explain why, in some people with COVID-19, symptoms persist for weeks or months after their bodies are rid of the virus.
Although the findings don’t have immediate implications for treating COVID-19, Deb said the mouse model will be useful for ongoing studies on how the virus infects vital organs other than the lungs, and for trials of new drugs to treat the disease.
###
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine and two UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine-Broad Stem Cell Research Center COVID-19 research awards.
Media Contact
Tiare Dunlap
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.
https://scienmag.com/scientists-discover-how-covid-19-virus-causes-multiple-organ-failure-in-mice/