Credit: JIA Xiuquan
A research group led by Prof. XU Jie from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a surface acidity- and selectivity-tunable manganese oxide catalyst using a surface modification technique. Their findings were published in Nature Communications.
Surface properties of transition metal oxides play a pivotal role in their catalytic applications. Despite numerous reports investigating the surface chemisorption of organic molecules on metal oxides, it is not clear how adsorption of organic modifiers can be exploited to optimize the catalytic properties of metal oxides.
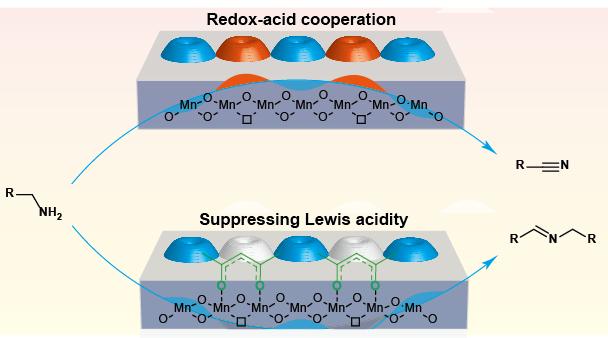
The researchers used enolic acetylacetones to modify the surface Lewis acid properties of manganese oxide catalysts. This enabled rational control of the oxidation selectivities of structurally diverse arylmethyl amines so they could switch from nitriles to imines.
The stable modification of acetylacetones strongly influenced the redox-acid cooperative catalysis of MnOx by suppressing the surface Lewis acidity of the catalysts. In the aerobic oxidation reaction of benzylamine, using unmodified MnOx as catalyst, nitrile was obtained with a yield of 86.5%. In contrast, the MnOx modified by acetylacetones produced imine with a yield of 90.6% under identical conditions.
The current study demonstrates an example of a selectivity-switchable metal oxide catalyst with an organic switch to tune its surface properties. This may contribute to future insights into the surface structure-activity relationships of metal oxide catalysts.
###
Media Contact
Wang Yongji
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




