Scientists at Osaka University develop a test to measure the quality of nanofibrillation for wood pulp using its natural optical birefringence, which may lead to clear definition and sophisticated utilization of wooden cellulose nanofibers
Credit: Osaka University
Osaka, Japan – Researchers from the Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research at Osaka University have devised a new method to determine the degree of fibrillation in wood pulp. By taking advantage of the intrinsic optical birefringence of cellulose, they were able to measure the morphology change through optical retardation distribution. This work may lead to clear grading and smart utilization of renewable biomass, cellulose nanofibers.
Cellulose, the primary structural component of most plants, has been harvested by humanity for millennia as an important biomaterial for clothing, paper, and wooden structures. More recently, cellulose nanofibers have been produced, which have the advantage of various functionalities derived from the extended chain crystals that make up cellulose, including optical birefringence. Birefringence occurs when the effective speed of light inside a material depends on its polarization; in this case, whether the light is polarized parallel or perpendicular to the polymer chains.
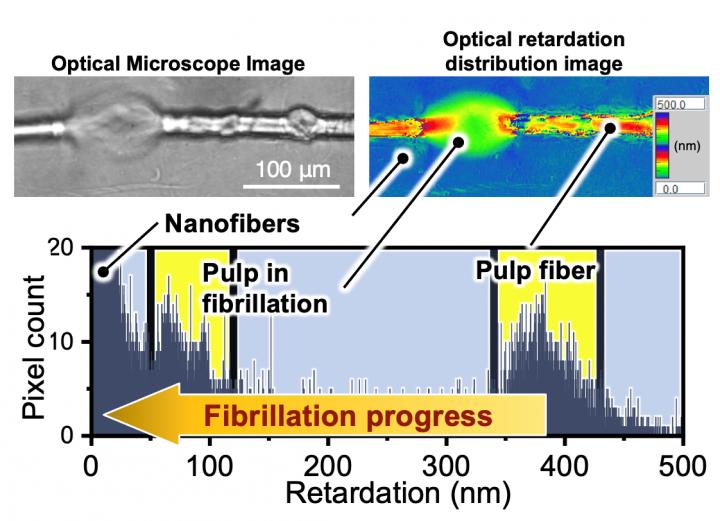
Now, a team of scientists at Osaka University has developed an optical analysis system that can directly quantify the degree of fibrillation of wood pulps. Fibrillation is the process of decreasing the bundling of cellulose molecules in micro-scale pulp fibers to form nanoscale fibers. Compared with painstakingly measuring fiber widths with an electron microscope, this technique quickly and easily determines if the cellulose fibers are aligned or dispersed in random orientations. “Our system offers clear and quantifiable criteria for grading the quality of cellulose nanofibers,” says first author Kojiro Uetani.
This is accomplished by observing cellulose fibers in a quartz flow cell with a birefringence microscope. The sample is illuminated from below with circularly polarized light, which has an electrical field orientation that rotates in space like a helix. Regions of the fibers with large birefringence will cause a larger optical retardation in the phase of the light. Using a birefringence microscope, the researchers were able to record this value pixel-by-pixel. They found that both the average optical retardation and its standard deviation were correlated with the degree of fibrillation. Large retardation values were associated with intact pulp fibers, while smaller values were seen with balloon-like structure in fibrillating pulps, and very small values occurred with dispersed nanofibers.
“We hope to promote the precise structure control and advanced use of wood pulps and cellulose nanofibers,” says senior author Masaya Nogi. In addition to the results of the article described above, the team has also confirmed that it is possible to automatically determine the degree of fibrillation of unknown pulp samples by deep learning of retardation images. This system is expected to lead to a clearer and more automatic definition of the degree of fibrillation by artificial intelligence (AI) in the future and will become a key analysis technology for indicating the quality of pulp materials and cellulose nanofibers.
###
The article, “Direct determination of the degree of fibrillation of wood pulps by distribution analysis of pixel-resolved optical retardation,” was published in Carbohydrate Polymers at DOI:
https:/
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan’s most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




