This article by Dr. Jihong Guan et al. is published in Current Bioinformatics, Volume 13, Issue 6, 2018
Credit: Bentham Science Publishers, Jihong Guan
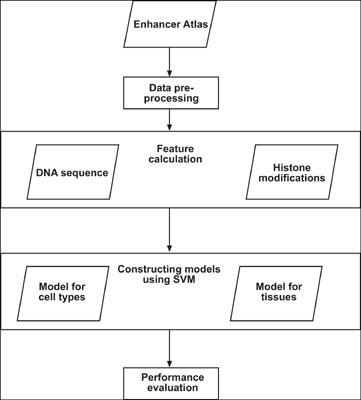
In genetics, an enhancer is a short region of DNA that can be bound by proteins to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These proteins are usually referred to as transcription factors. Enhancers allow researchers to understand the process of gene expression. An enhancer’s functioning does not depend upon the distance and the orientation of targeted gene. However, it is difficult to locate enhancers. New technologies (ChIP-seq (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation sequencing)) are emerging, through which enhancers can be predicted.
Most of the methods are based upon p300 binding sites and/or DNAase I hypersensitive sites (DHSs) for the sake of collecting positive training samples which are sometimes imprecise and lead to unsatisfactory prediction performance. In this article, the method based on support vector machines is proposed to investigate the presence of the enhancers on cell lines and tissues by using EnhancerAtlas. Enhancer prediction has been performed in models of diseases related to heart and lung tissues.
Experimental results have shown that the proposed methods performed even better than other state-of-the-art methods proposed earlier on the specific cell lines. The findings also indicate that predicting enhancers is much easier in adult or young tissue samples rather than in experiments on fetal samples.
###
This article is Open Access. To obtain the article please visit http://www.
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




