International research team investigates the binding kinetics of kinase inhibitors
Credit: Knapp Laboratory, Goethe University Frankfurt
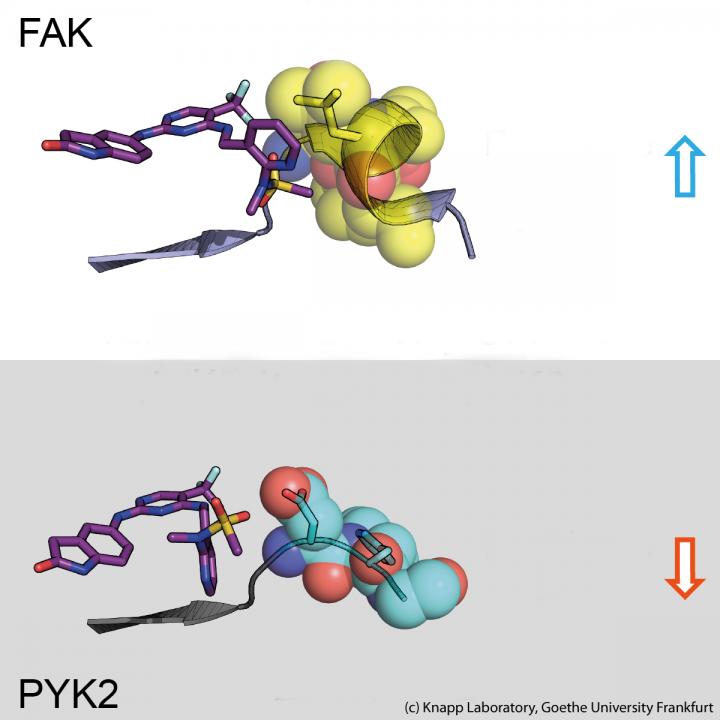
FRANKFURT. Many anti-cancer drugs block signals in cancer cells that help degenerated cells to multiply uncontrollably and detach from tissue. For example, blocking the signalling protein FAK, a so-called kinase, causes breast cancer cells to become less mobile and thus less likely to metastasise. The problem is that when FAK is blocked by an inhibitor, the closely related signalling protein PYK2 becomes much more active and thus takes over some of FAK’s tasks. The ideal would therefore be an inhibitor that inhibits both FAK and PYK2 in the same way for as long as possible.
An international team led by the pharmaceutical chemist Prof. Stefan Knapp from Goethe University has investigated a series of specially synthesised FAK inhibitors. All inhibitors bound to the FAK protein at about the same rate. However, they differed in the duration of binding: The most effective inhibitor remained bound to the FAK signalling protein the longest.
Using structural and molecular biological analyses as well as computer simulations, the research team discovered that binding of inhibitors that remain in the FAK binding pocket for a long time induce a structural change. Thus, through binding of these inhibitors, FAK changes its shape and forms a specific, water-repellent structure at contact sites with the inhibitor, comparable to an intimate embrace.
The closely related protein PYK2, on the other hand, remained comparatively rigid, and although the most effective FAK inhibitor also blocked PYK2, its effect was significantly weaker due to quickly dissociating inhibitors from the binding site. Interestingly, computer simulations were able to predict the kinetics of binding very well, providing a method for accurate simulation of drug dissociation rates for future optimisation of drug candidates.
Prof. Stefan Knapp explains: “Because we now have a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the interaction of potent inhibitors of these two kinases, we hope to be able to use computer simulations to better predict drug residence times of inhibitors and drugs candidates in the future. So far, little attention has been paid to the kinetic properties of drug binding. However, this property has now emerged as an important parameter for the development of more effective drugs that are designed to inhibit their target proteins – as in the case of FAK and PYK2 – not only potently but also for a long time.”
###
This work was carried out within the framework of the public-private partnership K4DD (Kinetics for Drug Discovery) of the Innovative Medicinces Initiatives (IMI). https:/
Media Contact
Dr. Markus Bernards
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




