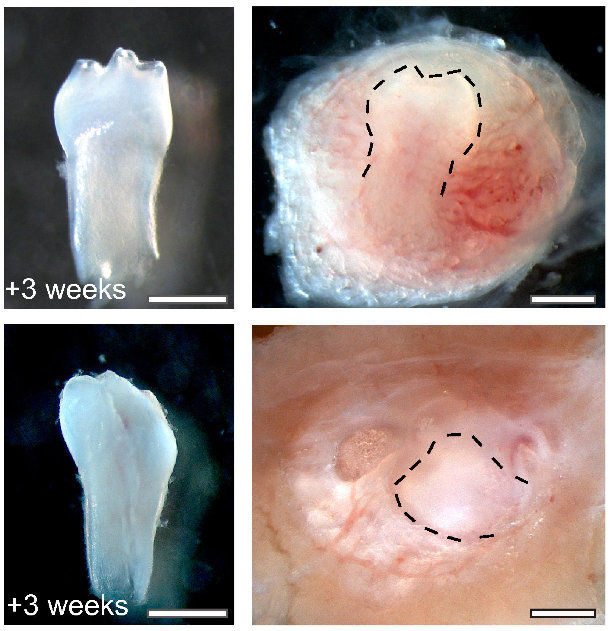
Researchers have grown rudimentary teeth out of the most unlikely of sources, human urine.The results, published in Cell Regeneration Journal, showed that urine could be used as a source of stem cells that in turn could be grown into tiny tooth-like structures.
The team from China hopes the technique could be developed into a way of replacing lost teeth. Other stem cell researchers caution that that goal faces many challenges. Teams of researchers around the world are looking for ways of growing new teeth to replace those lost with age and poor dental hygiene.
Stem cells – the master cells which can grow into any type of tissue – are a popular area of research. The group at the Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health used urine as the starting point.
Cells which are normally passed from the body, such as those from the lining of the body’s waterworks, are harvested in the laboratory. These collected cells are then coaxed into becoming stem cells.
A mix of these cells and other material from a mouse was implanted into the animals.
Continue reading the main story
“
Start Quote
You just wouldn’t do it in this way”
Prof Chris Mason
University College London
The researchers said that after three weeks the bundle of cells started to resemble a tooth: “The tooth-like structure contained dental pulp, dentin, enamel space and enamel organ.”
However, the “teeth” were not as hard as natural teeth.
This piece of research is not immediately going to lead to new options for the dentist, but the researchers say it could lead to further studies towards “the final dream of total regeneration of human teeth for clinical therapy”.
‘Worst source’
Prof Chris Mason, a stem cell scientist at University College London, said urine was a poor starting point.
“It is probably one of the worst sources, there are very few cells in the first place and the efficiency of turning them into stem cells is very low.
“You just wouldn’t do it in this way.”
He also warned that the risk of contamination, such as through bacteria, was much higher than with other sources of cells.
Prof Mason added: “The big challenge here is the teeth have got a pulp with nerve and blood vessels which have to make sure they integrate to get permanent teeth.”
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by BBC News, James Gallagher.
Photo Credit: Screenshot by Amanda Kooser/CNET