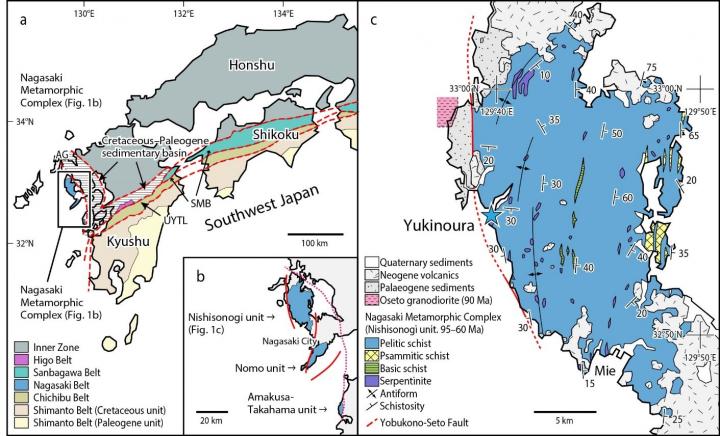
a: Geological zone in western Japan. The blue-green part is the Sanbagawa belt that crosses mainland Japan. The Nishisonogi metamorphic rock was thought to belong to the same geological formation…
view more
A collaboration of researchers based in Kumamoto University, Japan have discovered microdiamonds in the Nishisonogi metamorphic rock formation in Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. Microdiamonds in metamorphic rocks are important minerals because they form in continental collision zones and show that the crust has penetrated deeper than 120 km below the surface. This is the second area in the world, after the Italian Alps, that shows microdiamonds can form in metamorphic rock through subduction of oceanic plates.
In recent years, microdiamonds have received a great deal of attention because they have been discovered in metamorphic rocks around the world and it has become clear that they are formed in collisions between continents. It was thought that Japan would not produce such microdiamonds because it is not a continental collision zone, but an oceanic plate subduction zone. However, the first microdiamonds from metamorphic rocks in Japan were found in the Nishisonogi metamorphic rock formation in the west coast of Nagasaki Prefecture.
The area where the microdiamonds were discovered is an approximately 100-million-year-old Cretaceous metamorphic rock formation. On the west coast of Saikai City in Nagasaki Prefecture, blocks of pelitic and basic schist are scattered amongst serpentinite that was created from mantle material. Such rocks are called a serpentinite mélange and indicate that they have risen from deep in the subduction zone. Researchers found microdiamonds here, in the serpentinite mélange. Their formation conditions have been estimated to be a temperature of about 450 °C and a pressure of about 2.8 GPa, which makes them the coldest diamonds ever formed. It has been thought that the Nishisonogi metamorphic rock was formed under a pressure of about 1 GPa, but it is now clear that they were ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks that rose after subducting to 120 km–a very unexpected discovery.
“The discovery of microdiamonds from Japan’s first metamorphic rocks will rewrite Japan’s geological history,” said Professor Tadao Nishiyama, the leader of this study. “Until now, the Nagasaki metamorphic rocks were said to belong to a low-temperature, high-pressure-type metamorphic rock belt, the “Sanbagawa Belt,” which crosses the Japanese mainland. It has become clear, however, that they are independently-formed ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks. I expect that there will be many discussions about what kind of plate movement created this formation.”
###
This research was posted online in Scientific Reports on 15 July 2020.
Source: Nishiyama, T., Ohfuji, H., Fukuba, K., Terauchi, M., Nishi, U., Harada, K., … Arai, S. (2020). Microdiamond in a low-grade metapelite from a Cretaceous subduction complex, western Kyushu, Japan. Scientific Reports, 10(1). doi:10.1038/s41598-020-68599-7
Media Contact
J. Sanderson, N. Fukuda
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




