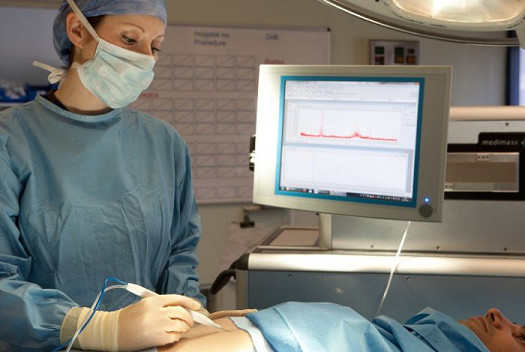
Researchers have developed an “intelligent knife” that can tell surgeons immediately whether the tissue they are cutting is cancerous or not.
In the first study to test the invention in the operating theatre, the “iKnife” diagnosed tissue samples from 91 patients with 100 per cent accuracy, instantly providing information that normally takes up to half an hour to reveal using laboratory tests.
The findings, by researchers at Imperial College London, are published today in the journal Science Translational Medicine. The study was funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Imperial Biomedical Research Centre, the European Research Council and the Hungarian National Office for Research and Technology.
In cancers involving solid tumours, removal of the cancer in surgery is generally the best hope for treatment. The surgeon normally takes out the tumour with a margin of healthy tissue. However, it is often impossible to tell by sight which tissue is cancerous. One in five breast cancer patients who have surgery require a second operation to fully remove the cancer. In cases of uncertainty, the removed tissue is sent to a lab for examination while the patient remains under general anaesthetic.
The iKnife is based on electrosurgery, a technology invented in the 1920s that is commonly used today. Electrosurgical knives use an electrical current to rapidly heat tissue, cutting through it while minimising blood loss. In doing so, they vaporise the tissue, creating smoke that is normally sucked away by extraction systems.
The inventor of the iKnife, Dr Zoltan Takats of Imperial College London, realised that this smoke would be a rich source of biological information. To create the iKnife, he connected an electrosurgical knife to a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument used to identify what chemicals are present in a sample. Different types of cell produce thousands of metabolites in different concentrations, so the profile of chemicals in a biological sample can reveal information about the state of that tissue.
In the new study, the researchers first used the iKnife to analyse tissue samples collected from 302 surgery patients, recording the characteristics of thousands of cancerous and non-cancerous tissues, including brain, lung, breast, stomach, colon and liver tumours to create a reference library. The iKnife works by matching its readings during surgery to the reference library to determine what type of tissue is being cut, giving a result in less than three seconds.
The technology was then transferred to the operating theatre to perform real-time analysis during surgery. In all 91 tests, the tissue type identified by the iKnife matched the post-operative diagnosis based on traditional methods.
While the iKnife was being tested, surgeons were unable to see the results of its readings. The researchers hope to carry out a clinical trial to see whether giving surgeons access to the iKnife’s analysis can improve patients’ outcomes.
“These results provide compelling evidence that the iKnife can be applied in a wide range of cancer surgery procedures,” Dr Takats said. “It provides a result almost instantly, allowing surgeons to carry out procedures with a level of accuracy that hasn’t been possible before. We believe it has the potential to reduce tumour recurrence rates and enable more patients to survive.”
Although the current study focussed on cancer diagnosis, Dr Takats says the iKnife can identify many other features, such as tissue with an inadequate blood supply, or types of bacteria present in the tissue. He has also carried out experiments using it to distinguish horsemeat from beef.
Professor Jeremy Nicholson, Head of the Department of Surgery and Cancer at Imperial College London, who co-authored the study, said: “The iKnife is one manifestation of several advanced chemical profiling technologies developed in labs our that are contributing to surgical decision-making and real-time diagnostics. These methods are part of a new framework of patient journey optimisation that we are building at Imperial to help doctors diagnose disease, select the best treatments, and monitor individual patients’ progress as part our personalised healthcare plan.”
Lord Darzi, Professor of Surgery at Imperial College London, who also co-authored the study, said: “In cancer surgery, you want to take out as little healthy tissue as possible, but you have to ensure that you remove all of the cancer. There is a real need for technology that can help the surgeon determine which tissue to cut out and which to leave in. This study shows that the iKnife has the potential to do this, and the impact on cancer surgery could be enormous.”
Lord Howe, Health Minister, said: “We want to be among the best countries in the world at treating cancer and know that new technologies have the potential to save lives. The iKnife could reduce the need for people needing secondary operations for cancer and improve accuracy, and I’m delighted we could support the work of researchers at Imperial College London. This project shows once again how Government funding is putting the UK at the forefront of world-leading health research.”
J. Balog et al. ‘Intraoperative tissue identification using rapid evaporative ionization mass spectrometry.’ Sci. Transl. Med. 5, 194ra93 (2013).
Story Source:
The above story is reprinted from materials provided by Imperial College London, Sam Wong.