Earth and environmental scientists reported that as human socio-economic activities increase, greenhouse gas emissions will rise, leading to more frequent extreme weather events such as droughts and floods. However, a research team from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has published a study suggesting that anthropogenic greenhouse gases might actually mitigate droughts, offering a new perspective on the impact of human activities on nature.
Credit: POSTECH
Earth and environmental scientists reported that as human socio-economic activities increase, greenhouse gas emissions will rise, leading to more frequent extreme weather events such as droughts and floods. However, a research team from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has published a study suggesting that anthropogenic greenhouse gases might actually mitigate droughts, offering a new perspective on the impact of human activities on nature.
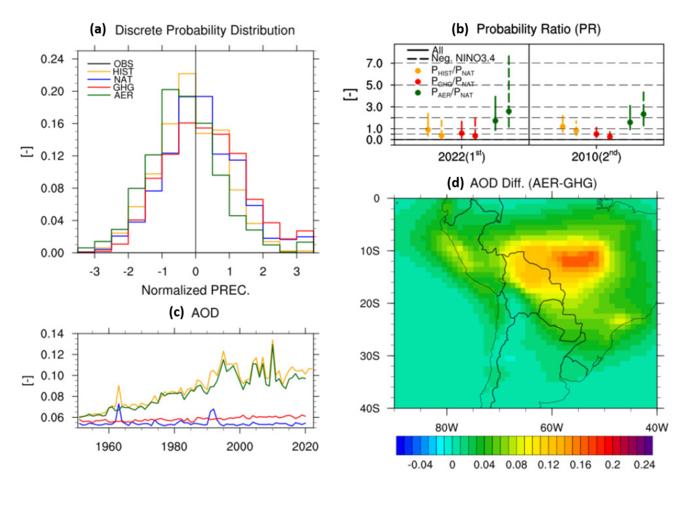
Professor Jonghun Kam from the Division of Environmental Science and Engineering at POSTECH used climate model simulations to examine individual effects of aerosols and greenhouse gases produced by human activities, focusing on the spring drought in 2022 that caused severe agricultural damage in the central Andes mountainous region. This research was recently published in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, one of international journals in atmospheric science and meteorology.
Drought occurs when there is a prolonged absence of rainfall, leading to a lack of precipitation. It begins as a meteorological drought and progresses to an agricultural drought where the soil loses moisture. More severe droughts can escalate to hydrological droughts, characterized by reduced stream flows. When droughts significantly impact society and the economy, they are termed “socioeconomic droughts”.
The socioeconomic impact of drought is especially severe in societies and countries heavily dependent on agriculture. During the globally severe spring drought of 2022, the central Andean mountainous region of South America (including southern Peru, western Bolivia, and northern Chile), where agriculture is a major industry, experienced greater economic hardship than other regions. However, at that time, a shortage of human resources and funding limited an opportunity to better understand the causes of the 2022 drought.
In the study, Professor Jonghun Kam from POSTECH used 11 different climate models to analyze the impact of human activities on the spring drought that struck the Central Andean region in 2022, the most severe since 1951.
Climate model experiments revealed that human socio-economic activities have increased anthropogenic aerosols in the atmosphere, affecting its chemical composition and worsening the spring drought in the Central Andes. Conversely, the rise in greenhouse gases due to human activities has led to increased precipitation in the region, mitigating extreme spring droughts and reducing the likelihood of such events. Thus, aerosols and greenhouse gases from human activities have had opposite effects on atmospheric chemical composition and precipitation mechanisms.
The study is significant because it challenges previous conclusions that greenhouse gases are the primary cause of drought in South Africa and Iran, highlighting the need for more comprehensive research on the effects of human socio-economic activities.
Professor Jonghun Kam stated, “Some countries are disproportionately affected by extreme weather events due to the climate crisis, yet they often face the lacking of not only human but also financial resources to respond proactively.” He added, “Our goal is to address the global climate crisis by conducting research that supports these countries and thoroughly analyzing the impact of human activities on nature.”
The research was conducted with the support from the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Journal
Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society
DOI
10.1175/BAMS-D-23-0241.1
Article Title
Climate Models Indicate Compensating Effects between Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols on the 2022 Central Andes Spring Drought
Article Publication Date
6-May-2024




