It sounds like something from the scene in Star Wars where Master Yoda instructs the young Luke Skywalker to use the force to release his stricken X-Wing from the swamp: Marc Folcher and other researchers from the group led by Martin Fussenegger, Professor of Biotechnology and Bioengineering at the Department of Biosystems (D-BSSE) in Basel, have developed a novel gene regulation method that enables thought-specific brainwaves to control the conversion of genes into proteins – called gene expression in technical terms.
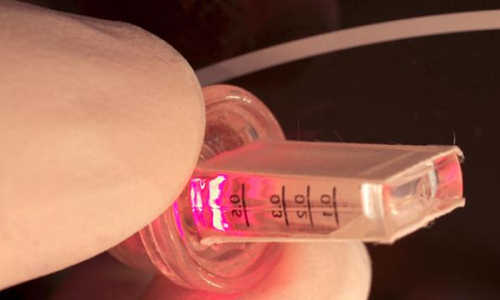
Thoughts control a near-infrared LED, which starts the production of a molecule in a reaction chamber.
“For the first time, we have been able to tap into human brainwaves, transfer them wirelessly to a gene network and regulate the expression of a gene depending on the type of thought. Being able to control gene expression via the power of thought is a dream that we’ve been chasing for over a decade,” says Fussenegger.
A source of inspiration for the new thought-controlled gene regulation system was the game Mindflex, where the player wears a special headset with a sensor on the forehead that records brainwaves. The registered electroencephalogram (EEG) is then transferred into the playing environment. The EEG controls a fan that enables a small ball to be thought-guided through an obstacle course.
Wireless Transmission to Implant
The system, which the Basel-based bioengineers recently presented in the journal Nature Communications, also makes use of an EEG headset. The recorded brainwaves are analysed and wirelessly transmitted via Bluetooth to a controller, which in turn controls a field generator that generates an electromagnetic field; this supplies an implant with an induction current.
A light then literally goes on in the implant: an integrated LED lamp that emits light in the near-infrared range turns on and illuminates a culture chamber containing genetically modified cells. When the near-infrared light illuminates the cells, they start to produce the desired protein.
Thoughts Control Protein Quantity
The implant was initially tested in cell cultures and mice, and controlled by the thoughts of various test subjects. The researchers used SEAP for the tests, an easy-to-detect human model protein which diffuses from the culture chamber of the implant into the mouse’s bloodstream.
To regulate the quantity of released protein, the test subjects were categorised according to three states of mind: bio-feedback, meditation and concentration. Test subjects who played Minecraft on the computer, i.e. who were concentrating, induced average SEAP values in the bloodstream of the mice. When completely relaxed (meditation), the researchers recorded very high SEAP values in the test animals. For bio-feedback, the test subjects observed the LED light of the implant in the body of the mouse and were able to consciously switch the LED light on or off via the visual feedback. This in turn was reflected by the varying amounts of SEAP in the bloodstream of the mice.
New Light-sensitive Gene Construct
“Controlling genes in this way is completely new and is unique in its simplicity,” explains Fussenegger. The light-sensitive optogenetic module that reacts to near-infrared light is a particular advancement. The light shines on a modified light-sensitive protein within the gene-modified cells and triggers an artificial signal cascade, resulting in the production of SEAP. Near-infrared light was used because it is generally not harmful to human cells, can penetrate deep into the tissue and enables the function of the implant to be visually tracked.
The system functions efficiently and effectively in the human-cell culture and human-mouse system. Fussenegger hopes that a thought-controlled implant could one day help to combat neurological diseases, such as chronic headaches, back pain and epilepsy, by detecting specific brainwaves at an early stage and triggering and controlling the creation of certain agents in the implant at exactly the right time.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by ETH Zurich, Martin Fussenegger.