Four promising antiviral drug candidates identified and analyzed by a University of Arizona-University of South Florida team in the preclinical study
Credit: Image generated by Yu Chen, University of South Florida Health, using X-ray crystallography
TAMPA, Fla. (July 6, 2020) — As the death toll from the COVID-19 pandemic mounts, scientists worldwide continue their push to develop effective treatments and a vaccine for the highly contagious respiratory virus.
University of South Florida Health (USF Health) Morsani College of Medicine scientists recently worked with colleagues at the University of Arizona College of Pharmacy to identify several existing compounds that block replication of the COVID-19 virus (SARS-CoV-2) within human cells grown in the laboratory. The inhibitors all demonstrated potent chemical and structural interactions with a viral protein critical to the virus’s ability to proliferate.
The research team’s drug discovery study appeared June 15 in Cell Research, a high-impact Nature journal.
The most promising drug candidates – including the FDA-approved hepatitis C medication boceprevir and an investigational veterinary antiviral drug known as GC-376 – target the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), an enzyme that cuts out proteins from a long strand that the virus produces when it invades a human cell. Without Mpro, the virus cannot replicate and infect new cells. This enzyme had already been validated as an antiviral drug target for the original SARS and MERS, both genetically similar to SARS-CoV-2.
“With a rapidly emerging infectious disease like COVID-19, we don’t have time to develop new antiviral drugs from scratch,” said Yu Chen, PhD, USF Health associate professor of molecular medicine and a coauthor of the Cell Research paper. “A lot of good drug candidates are already out there as a starting point. But, with new information from studies like ours and current technology, we can help design even better (repurposed) drugs much faster.”
Before the pandemic, Dr. Chen applied his expertise in structure-based drug design to help develop inhibitors (drug compounds) that target bacterial enzymes causing resistance to certain commonly prescribed antibiotics such as penicillin. Now his laboratory focuses its advanced techniques, including X-ray crystallography and molecular docking, on looking for ways to stop SARS-CoV-2.
Mpro represents an attractive target for drug development against COVID-19 because of the enzyme’s essential role in the life cycle of the coronavirus and the absence of a similar protease in humans, Dr. Chen said. Since people do not have the enzyme, drugs targeting this protein are less likely to cause side effects, he explained.
The four leading drug candidates identified by the University of Arizona-USF Health team as the best (most potent and specific) for fighting COVID-19 are described below. These inhibitors rose to the top after screening more than 50 existing protease compounds for potential repurposing:
- Boceprevir, a drug to treat Hepatitis C, is the only one of the four compounds already approved by the FDA. Its effective dose, safety profile, formulation and how the body processes the drug (pharmacokinetics) are already known, which would greatly speed up the steps needed to get boceprevir to clinical trials for COVID-19, Dr. Chen said.
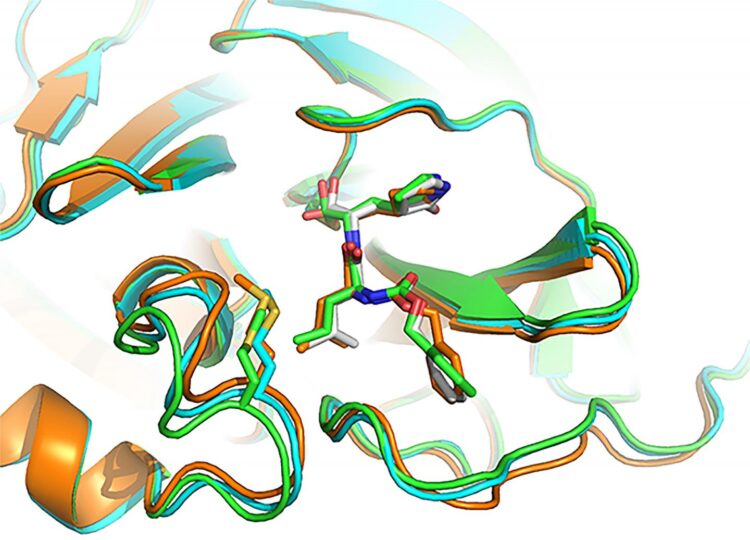
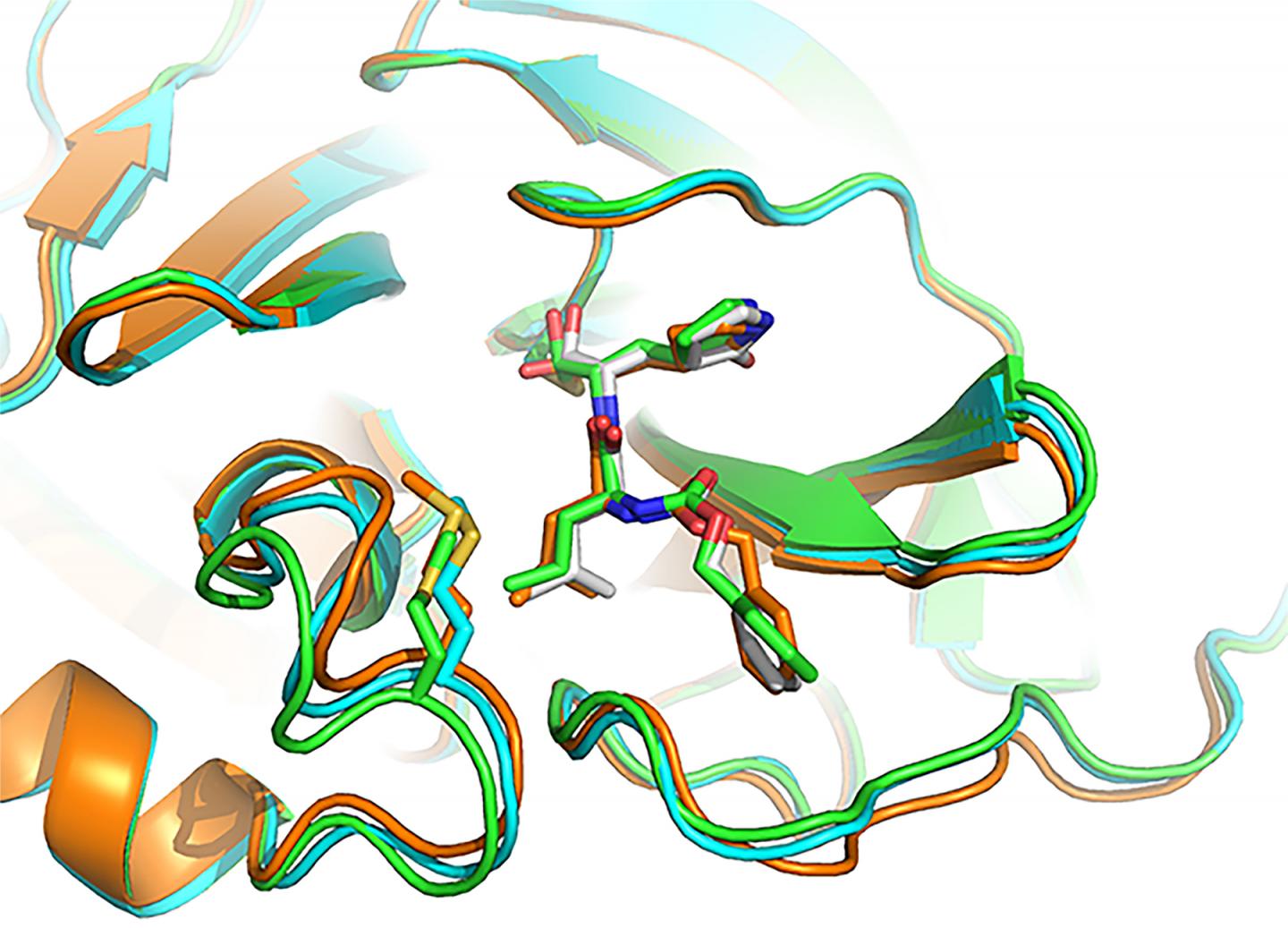
- GC-376, an investigational veterinary drug for a deadly strain of coronavirus in cats, which causes feline infectious peritonitis. This agent was the most potent inhibitor of the Mpro enzyme in biochemical tests, Dr. Chen said, but before human trials could begin it would need to be tested in animal models of SARS-CoV-2. Dr. Chen and his doctoral student Michael Sacco determined the X-ray crystal structure of GC-376 bound by Mpro, and characterized molecular interactions between the compound and viral enzyme using 3D computer modeling.
- Calpain inhibitors II and XII, cysteine inhibitors investigated in the past for cancer, neurodegenerative diseases and other conditions, also showed strong antiviral activity. Their ability to dually inhibit both Mpro and calpain/cathepsin protease suggests these compounds may include the added benefit of suppressing drug resistance, the researchers report.
All four compounds were superior to other Mpro inhibitors previously identified as suitable to clinically evaluate for treating SARS-CoV-2, Dr. Chen said.
A promising drug candidate – one that kills or impairs the virus without destroying healthy cells — fits snugly, into the unique shape of viral protein receptor’s “binding pocket.” GC-376 worked particularly well at conforming to (complementing) the shape of targeted Mpro enzyme binding sites, Dr. Chen said. Using a lock (binding pocket, or receptor) and key (drug) analogy, “GC-376 was by far the key with the best, or tightest, fit,” he added. “Our modeling shows how the inhibitor can mimic the original peptide substrate when it binds to the active site on the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease.”
Instead of promoting the activity of viral enzyme, like the substrate normally does, the inhibitor significantly decreases the activity of the enzyme that helps SARS-CoV-2 make copies of itself.
Visualizing 3-D interactions between the antiviral compounds and the viral protein provides a clearer understanding of how the Mpro complex works and, in the long-term, can lead to the design of new COVID-19 drugs, Dr. Chen said. In the meantime, he added, researchers focus on getting targeted antiviral treatments to the frontlines more quickly by tweaking existing coronavirus drug candidates to improve their stability and performance.
Dr. Chen worked with lead investigator Jun Wang, PhD, UA assistant professor of pharmacology and toxicology, on the study. The work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health.
Media Contact
Anne DeLotto Baier
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.