New mechanism highlights risks of circadian disruption and supports timed cancer treatment
Credit: Amita Sehgal
Disrupting normal circadian rhythms promotes tumor growth and suppresses the effects of a tumor-fighting drug, according to a new study publishing April 30 in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Yool Lee, Amita Sehgal, and colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania. The results provide mechanistic support for “chronotherapy,” the delivery of cancer drugs timed to the endogenous circadian rhythm.
Circadian rhythms regulate many aspects of physiology from the organismic to the subcellular levels. Disruption of circadian rhythms, whether through jet travel, shift work, or sleep disturbances, is a known risk factor for several types of cancer. In animal models, hormonally induced circadian disruption promotes tumor growth, but the underlying mechanism or mechanisms have not been clear.
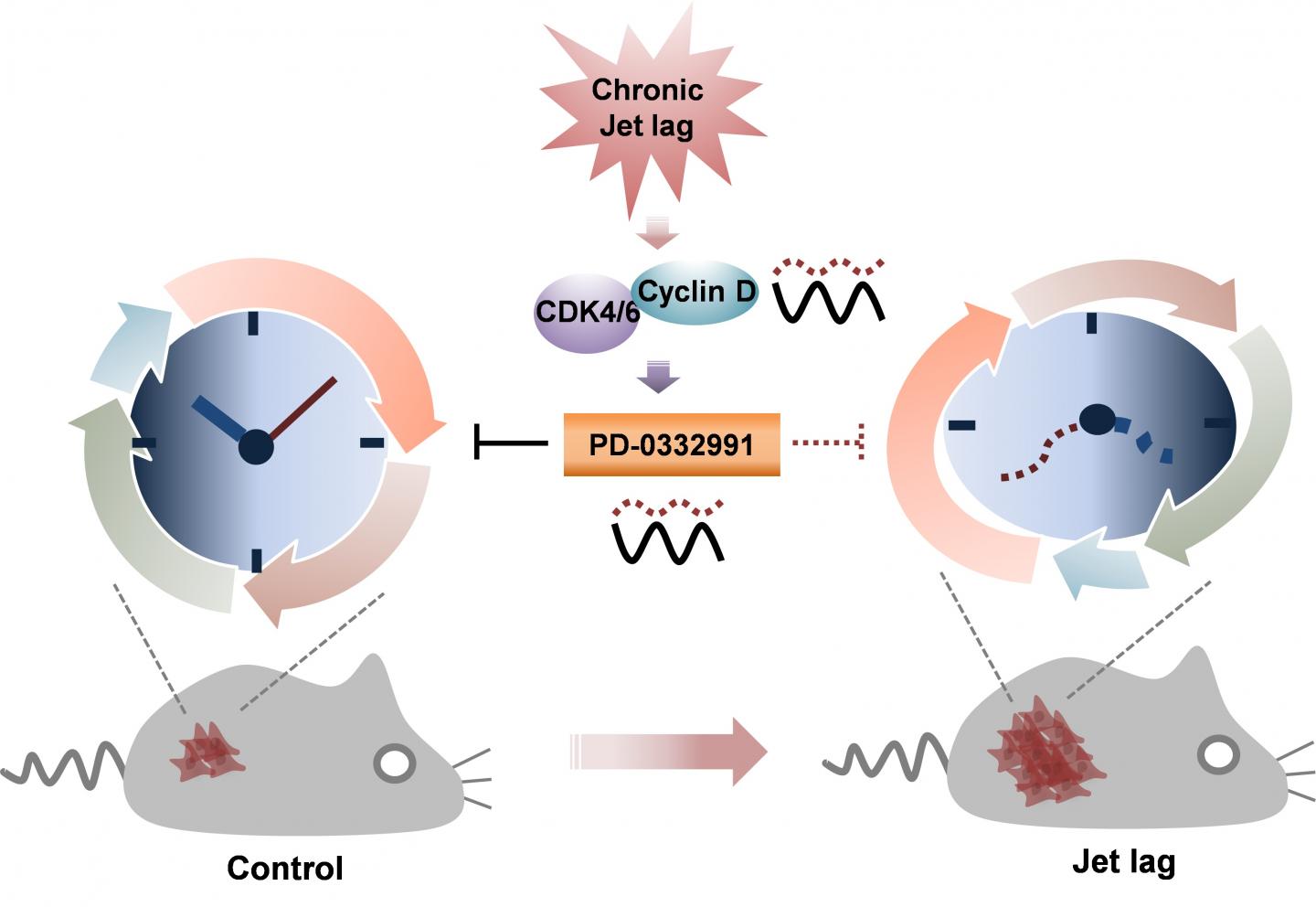
To uncover potential mechanisms, the authors used the hormone dexamethasone to chronically advance daily rhythms in cultured cells. They found that treatment altered expression of multiple genes, especially those involved in regulating the cell cycle. Circadian rhythm disruption increased cell proliferation, an effect that could be traced to increased expression of a cell-cycle control protein called cyclin D1. Cyclin D1, in turn, activated cyclin D-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6), a protein that switched the cell from growing larger to synthesizing new DNA, a step that ultimately leads to cell division.
Because tumor growth is linked so tightly to cell division, many cancer treatments seek to arrest progression through the cell cycle. The authors found that the tumor-fighting ability of one such drug, called PD-0332991, which inhibits CDK4/6 activity, varies with time-of-day such that treatment in the morning is more effective than treatment at night. Efficacy of PD-0332991 was reduced in both cells and mice when their circadian rhythms were disrupted.
“We suggest that chronic disruption of the normal circadian rhythm tips the balance between tumor-suppressive and tumor-progressive gene expression to favor tumor growth,” Sehgal said. “Better understanding the molecular effects of jet lag, shift work, and other sources of chronic disruption may lead to strategies to minimize the increased cancer risk associated with these behaviors, and to better treatment strategies, including timing delivery of cancer therapy for maximum benefit.”
###
Peer-reviewed / Experimental Study / Cells
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Biology: http://journals.
Citation: Lee Y, Lahens NF, Zhang S, Bedont J, Field JM, Sehgal A (2019) G1/S cell cycle regulators mediate effects of circadian dysregulation on tumor growth and provide targets for timed anticancer treatment. PLoS Biol 17(4): e3000228. https:/
Funding: This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (R37-NS-048471) and Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) to A.S. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Media Contact
Amita Sehgal
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




