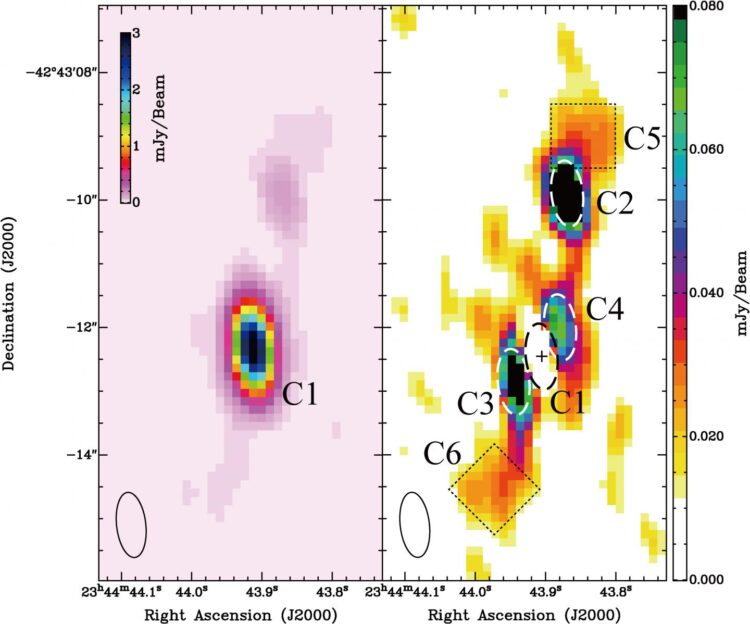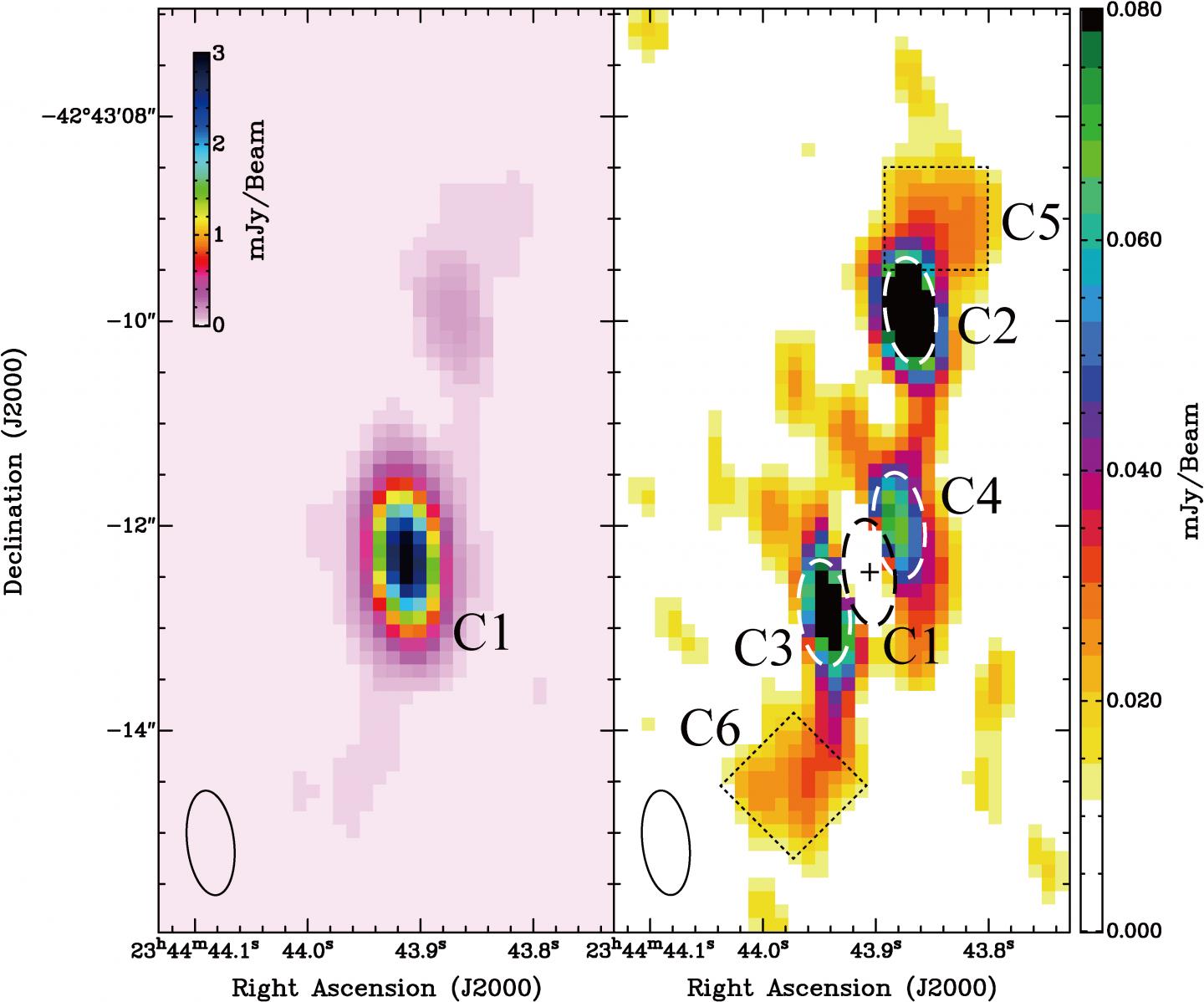
Credit: Akahori et al.
Radio astronomers have detected jets of hot gas blasted out by a black hole in the galaxy at the heart of the Phoenix Galaxy Cluster, located 5.9 billion light-years away in the constellation Phoenix. This is an important result for understanding the coevolution of galaxies, gas, and black holes in galaxy clusters.
Galaxies are not distributed randomly in space. Through mutual gravitational attraction, galaxies gather together to form collections known as clusters. The space between galaxies is not entirely empty. There is very dilute gas throughout a cluster which can be detected by X-ray observations.
If this intra-cluster gas cooled, it would condense under its own gravity to form stars at the center of the cluster. However, cooled gas and stars are not usually observed in the hearts of nearby clusters, indicating that some mechanism must be heating the intra-cluster gas and preventing star formation. One potential candidate for the heat source is jets of high-speed gas accelerated by a super-massive black hole in the central galaxy.
The Phoenix Cluster is unusual in that it does show signs of dense cooled gas and massive star formation around the central galaxy. This raises the question, “does the central galaxy have black hole jets as well?”
A team led by Takaya Akahori at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan used the Australia Telescope Compact Array (ATCA) to search for black hole jets in the Phoenix Galaxy Cluster with the highest resolution to date. They detected matching structures extending out from opposite sides of the central galaxy. Comparing with observations of the region taken from the Chandra X-ray Observatory archive data shows that the structures detected by ATCA correspond to cavities of less dense gas, indicating that they are a pair of bipolar jets emitted by a black hole in the galaxy. Therefore, the team discovered the first example, in which intra-cluster gas cooling and black hole jets coexist, in the distant Universe.
Further details of the galaxy and jets could be elucidated through higher-resolution observations with next generation observational facilities, such as the Square Kilometre Array scheduled to start observations in the late 2020s.
###
These results appeared as Akahori, Takuya et al. “Discovery of Radio Jets in the Phoenix galaxy cluster center” in the August 2020 issue of Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan.
Media Contact
Dr. Hitoshi Yamaoka
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.