Rutgers innovation may help guide treatment of Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s diseases
Credit: Letao Yang, KiBum Lee, Jin-Ho Lee and Sy-Tsong (Dean) Chueng
A Rutgers-led team has created better biosensor technology that may help lead to safe stem cell therapies for treating Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and other neurological disorders.
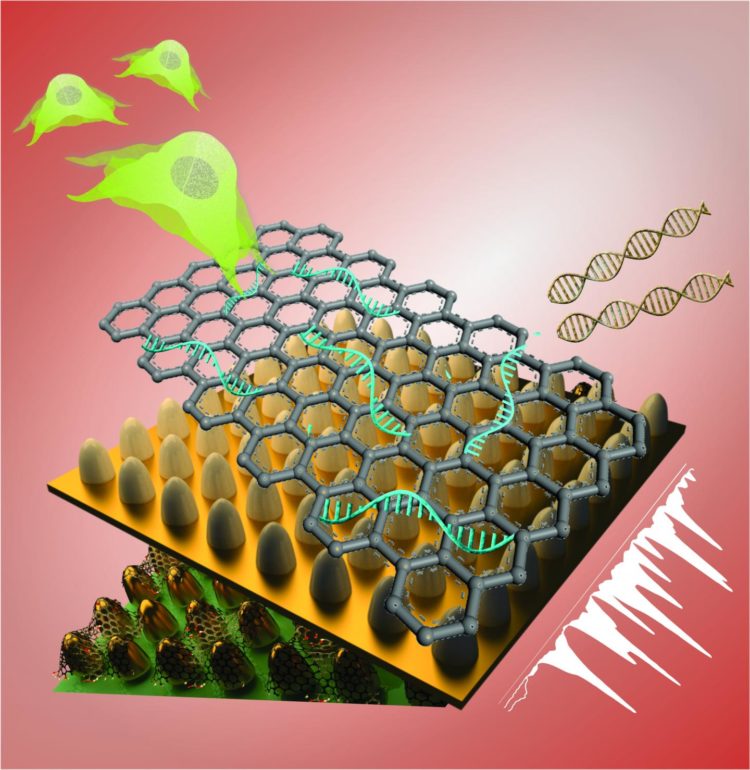
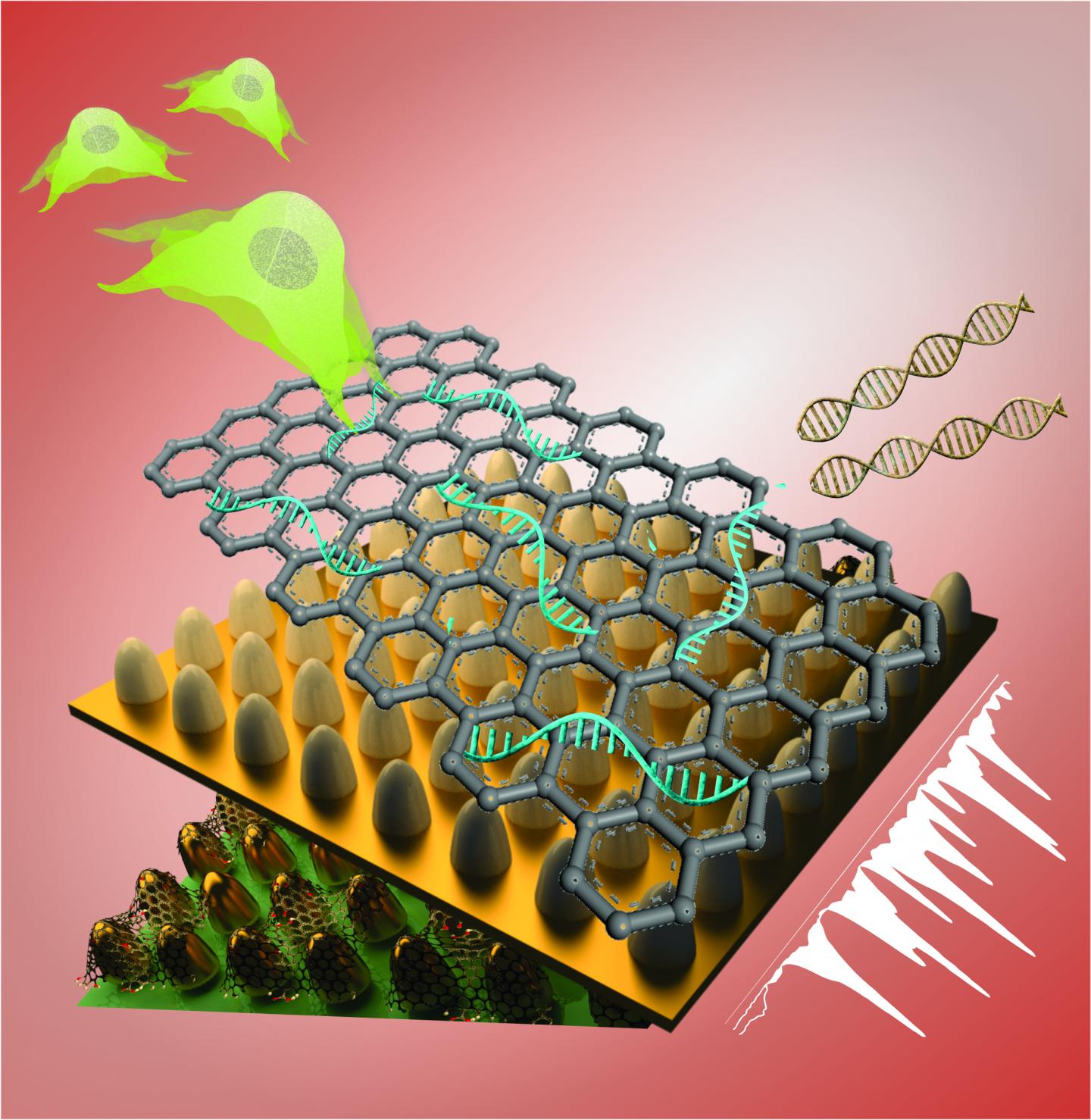
The technology, which features a unique graphene and gold-based platform and high-tech imaging, monitors the fate of stem cells by detecting genetic material (RNA) involved in turning such cells into brain cells (neurons), according to a study in the journal Nano Letters.
Stem cells can become many different types of cells. As a result, stem cell therapy shows promise for regenerative treatment of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, stroke and spinal cord injury, with diseased cells needing replacement or repair. But characterizing stem cells and controlling their fate must be resolved before they could be used in treatments. The formation of tumors and uncontrolled transformation of stem cells remain key barriers.
“A critical challenge is ensuring high sensitivity and accuracy in detecting biomarkers – indicators such as modified genes or proteins – within the complex stem cell microenvironment,” said senior author KiBum Lee, a professor in the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology in the School of Arts and Sciences at Rutgers University-New Brunswick. “Our technology, which took four years to develop, has demonstrated great potential for analyzing a variety of interactions in stem cells.”
The team’s unique biosensing platform consists of an array of ultrathin graphene layers and gold nanostructures. The platform, combined with high-tech imaging (Raman spectroscopy), detects genes and characterizes different kinds of stem cells with greater reliability, selectivity and sensitivity than today’s biosensors.
The team believes the technology can benefit a range of applications. By developing simple, rapid and accurate sensing platforms, Lee’s group aims to facilitate treatment of neurological disorders through stem cell therapy.
Stem cells may become a renewable source of replacement cells and tissues to treat diseases including macular degeneration, spinal cord injury, stroke, burns, heart disease, diabetes, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, according to the National Institutes of Health.
###
The study’s co-lead authors are Letao Yang and Jin-Ho Lee, postdoctoral researchers in Lee’s group. Rutgers co-authors include doctoral students Christopher Rathnam and Yannan Hou. A scientist at Sogang University in South Korea contributed to the study.
Media Contact
Todd Bates
[email protected]
848-932-0550
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.