Scientists from the University of Granada are the first to develop magnetic bacteria that, as part of food intake, help to diagnose digestive diseases like stomach cancer
BioNanoMed network presentation with Dr. Pau Bruguera (Biokit), Dr. Montserrat Vendrell (Biocat) and Dr. Josep Samitier (IBEC).
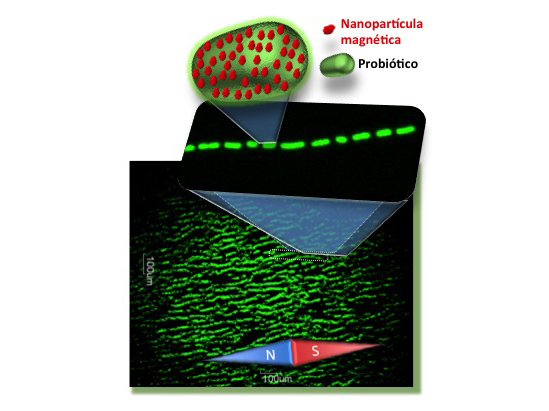
Researchers have incorporated magnetic particles into probiotic bacteria like those found in many foodstuffs. These “magnetic probiotics” behave like some natural magnetic bacteria but are difficult to obtain in large quantities and have never been used in humans.
Scientists from the University of Granada have successfully created magnetic bacteria that could be added to foodstuffs and could, after ingestion, help diagnose diseases of the digestive system like stomach cancer. These important findings constitute the first use of a food as a natural drug and aid in diagnosing an illness, anywhere in the world.
The researchers—members of Bionanomet, the Metallic Bionanoparticle research group of the Department of Inorganic Chemistry and the Institute of Biotechnology of the University of Granada—have conducted this research in collaboration with BIOSEARCH SA, a private company. Their results have been published in the latest issue of Advanced Functional Materials.
To design these magnetic bacteria, the researchers looked to Nature. They tried to copy magnetobacteria, which naturally produce very limited numbers of internal magnets that, essentially, provide them with a means of orienting themselves as if they possessed an internal compass.
Artificial magnetic bacteria are probiotic bacteria surrounded by thousands of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. The bacteria are living magnets that align with an external magnetic field. So, in Medicine, they may have many applications as magnetic drugs.
Biomedical applications
These artificial magnetic bacteria could have biomedical applications in magnetic resonance imaging—to facilitate diagnosis—or in heating malign cells through magnetic hypothermia and, thus, curing diseases like cancer.
This new technology—patented by BIOSEARCH SA—is still only in an experimental phase but it will facilitate the use of these probiotic bacteria, common in food, to diagnose and treat tumours and as an edible iron supplement.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by University of Granada.