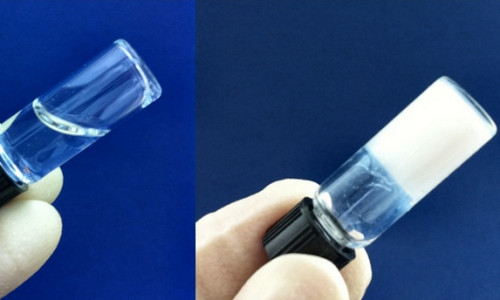
Rice University bioengineers have developed a hydrogel scaffold for craniofacial bone tissue regeneration that starts as a liquid, solidifies into a gel in the body and liquefies again for removal.
The material developed in the Rice lab of bioengineer Antonios Mikos is a soluble liquid at room temperature that can be injected to the point of need. At body temperature, the material turns instantly into a gel to help direct the formation of new bone to replace that damaged by injury or disease.
The gel conforms to irregular three-dimensional spaces and provides a platform for functional and aesthetic tissue regeneration. It is intended as an alternative to prefabricated implantable scaffolds.
The invention is the subject of a new paper that appeared online this week in the American Chemical Society journal Biomacromolecules.
Lead author Tiffany Vo, a fourth-year doctoral graduate student in the Mikos lab, earned a Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research for her work on the project.
“This new platform technology leverages injectable, thermally responsive, chemically crosslinkable and bioresorbable hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications,” Mikos said. “It enables the formation of scaffolds locally and the delivery of growth factors and stem cells into defects of complex anatomical shapes with minimal surgical intervention.”
Thermosensitive technologies are not new to the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, Mikos said. What makes the poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), or PNiPAAm, scaffold promising is that its chemical cross-linking technology allows the researchers to eliminate gel shrinkage without reducing swelling; this improves its stability so that it serves as an effective delivery vehicle for growth factors and stem cell populations.
Once sufficient quality and quantity of bone tissue have regenerated to fill the defected site, the hydrogel scaffold can be transitioned back into a liquid state and released naturally.
As part of the project, the researchers will test the hydrogel’s enhanced seeding capabilities and ability to promote cellular attachment, crosstalk and proliferation toward greater bone formation. The knowledge will improve the understanding of biomaterial-based therapies for minimally invasive tissue regeneration as viable clinical alternatives.
“The results demonstrate the ability to encapsulate stem cell populations with temperature-sensitive gelling scaffolds for injectable cell delivery with enormous implications for the development of novel therapeutics for craniofacial bone regeneration,” Mikos said.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by Rice University, Mike Williams.