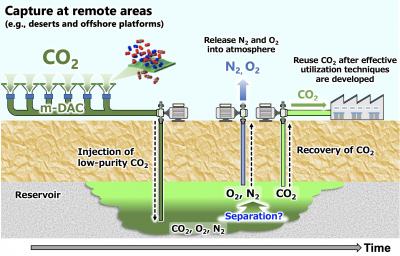
Fukuoka, Japan – The global threat of ongoing climate change has one principal cause: carbon that was buried underground in the form of fossil fuels is being removed and released into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2). One promising approach to addressing this problem is carbon capture and storage: using technology to take CO2 out of the atmosphere to return it underground.
In a new study published in Greenhouse Gases Science and Technology, researchers from Kyushu University and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan, investigated geological storage of low-purity CO2 mixed with nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), produced by direct air capture (DAC) using membrane-based technology.
According to Professor Tsuji, “Because of the ubiquity of ambient air, direct air capture has the potential to become a ubiquitous means of carbon capture and storage that can be implemented in many remote areas, such as deserts and offshore platforms. This is important both for reducing transportation costs and ensuring social acceptance.”
###
The article, “Geological storage of CO2-N2-O2 mixtures produced by membrane-based direct air capture (DAC),” is published in Greenhouse Gases Science and Technology at DOI: https:/
Media Contact
Tomoya Koga
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.