Credit: Uvinduni Premadasa/ORNL, US Dept. of Energy
Climate – Predicting fire risk
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a method that uses machine learning to predict seasonal fire risk in Africa, where half of the world’s wildfire-related carbon emissions originate.
Their approach draws on data about underlying environmental drivers such as ocean temperatures and land surface changes in addition to more commonly used atmospheric and socioeconomic indicators. The method allows scientists to gain a deeper understanding of the relative importance of different variables such as soil moisture and leaf area.
“We found that oceanic and terrestrial dynamics are the most critical factors influencing the accuracy of seasonal fire prediction for these vulnerable ecosystems,” said ORNL’s Jiafu Mao. “Disturbances like fire can have a lasting impact on regional environments and global carbon cycling.”
The scientists’ computational framework could be applied to other regions or generalized to assess global fire risk and inform fire management practices that address environmental and safety concerns.
Media contact: Kim Askey, 865.576.2841, [email protected]
Image: https:/
Caption: Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a method that uses machine learning to predict seasonal fire risk in Africa, which contains about 70% of the global burned area, shown in red. Credit: NASA
Batteries – Solid state stability check
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists seeking the source of charge loss in lithium-ion batteries demonstrated that coupling a thin-film cathode with a solid electrolyte is a rapid way to determine the root cause.
In a study, researchers prepared a lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide cathode as dense, thin-films free from binders and additives. The cathode’s charging and discharging cycles were compared in cells with a standard liquid electrolyte versus a sputtered-deposited solid electrolyte. The capacity of both cells faded quickly and, within a few cycles, the cathode showed physical instability.
Further analysis confirmed that resistance at the cathode interface with the liquid electrolyte grows with cycling leading to charge capacity loss while the solid electrolyte was stable.
“Charge loss was related to the inherent structural instability of the cathode’s crystalline structure, a key finding for designing high capacity, high voltage cathodes in solid state batteries,” ORNL’s Gabriel Veith said.
Media Contact: Jennifer Burke, 865.414.6835, [email protected]
Image: https:/
Caption: ORNL researchers coupled a thin-film cathode with a solid electrolyte to rapidly determine the cause of charge loss in higher voltage lithium-ion batteries, a key finding for designing high capacity, high voltage cathodes in solid-state batteries. Credit: Nathan Phillip/ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
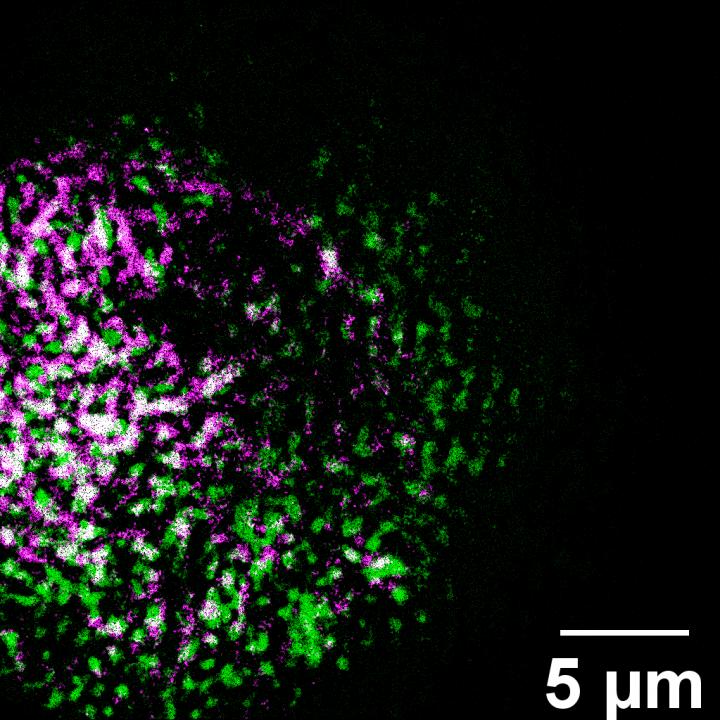
Microscopy – Images in a flash
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have built a novel microscope that provides a “chemical lens” for viewing biological systems including cell membranes and biofilms. The tool could advance the understanding of complex biological interactions, such as those between microbes and plants.
The noninvasive instrument, detailed in Optics Letters, allows researchers to capture images using ultrashort laser pulses. These intense pulses illuminate large areas of a sample, generating colors of light that allow detection of different chemical species. The approach quickly produces images over a wide field of view with chemical details.
“Because you’re getting the whole image all in the same shot, you’re able to study changes in space and in time,” ORNL’s Benjamin Doughty said.
Unlike common bioimaging techniques that can destroy or disturb samples, this label-free tool can be used on unaltered, living cells. The microscope is made with commonly available components, which may accelerate its implementation.
Media Contact: Abby Bower, 865.323.9943, [email protected]
Image: https:/
Caption: A novel ORNL microscope captured an image of lily pollen, which is colorized to show the distribution of two molecular groups. The instrument quickly shows chemical details. Credit: Uvinduni Premadasa/ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
Image: https:/
Caption: An image of lily pollen, captured using bright-field microscopy developed by ORNL, reveals only the presence of material without information about its composition. Credit: Uvinduni Premadasa/ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
###
Media Contact
Sara Shoemaker
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




