A Kanazawa University researcher proposes a novel cosmological model to study thermodynamics on the horizon of the universe
Credit: Kanazawa University
Kanazawa, Japan – The expansion of the Universe has occupied the minds of astronomers and astrophysicists for decades. Among the cosmological models that have been suggested over the years, Lambda cold dark matter (LCDM) models are the simplest models that can provide elegant explanations of the properties of the Universe, e.g., the accelerated expansion of the late Universe and structural formations. However, the LCDM model suffers from several theoretical difficulties, such as the cosmological constant problem. To resolve these difficulties, alternative thermodynamic scenarios have recently been proposed that extend the concept of black hole thermodynamics.
“Previous research implies that a certain type of universe will behave like an ordinary macroscopic system. The expansion of the Universe is considered likely to be related to thermodynamics on its horizon, based on the holographic principle,” explains the study’s author, Kanazawa University’s Nobuyoshi Komatsu.
“I considered a cosmological model with a power-law term, assuming application of the holographic equipartition law. The power-law term is proportional to Hα, where H is the Hubble parameter and α is considered to be a free parameter (α may be related to the entanglement of the quantum fields close to the horizon).”
“I used the proposed model to study the thermodynamic properties on the horizon of the Universe, focusing on the evolutions of the Bekenstein-Hawking entropy. I found that the model satisfies the second law of thermodynamics on the horizon,” says Associate Professor Komatsu.
“In addition, I used the model to examine the relaxation-like processes that occur before the last stage of the evolution of the Universe and thus enable study of the maximization of the entropy.”
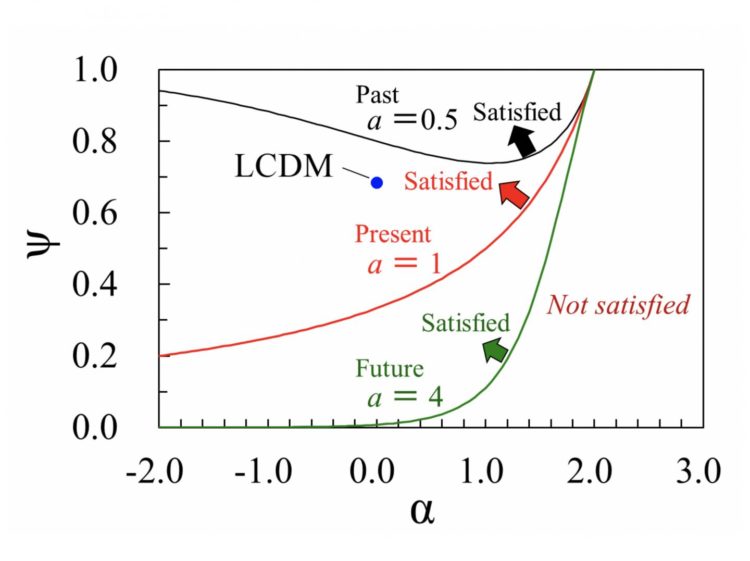
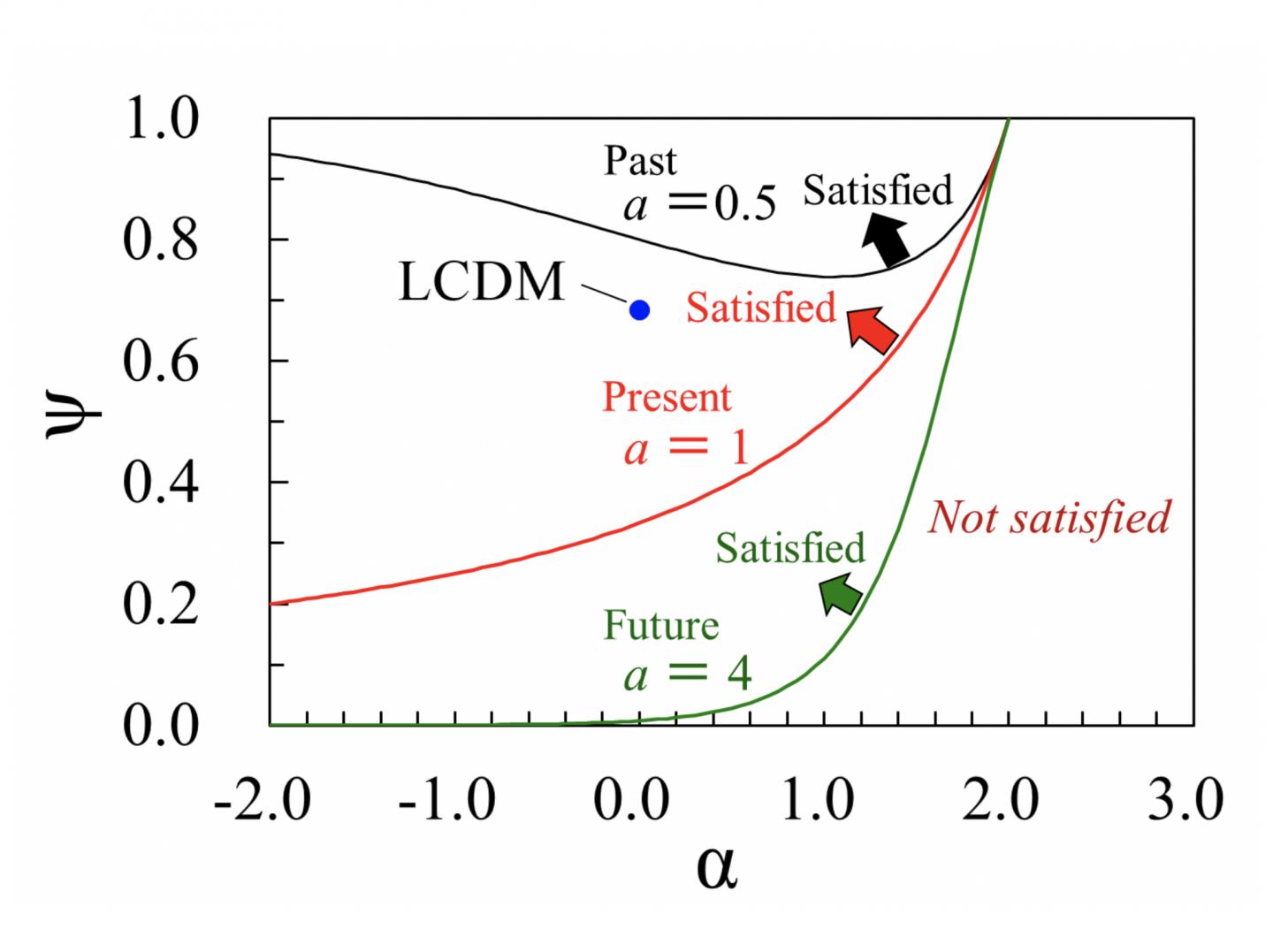
“Figure 1 shows the boundaries for maximization of the entropy in the (α, ψ) plane. Here, ψ represents a type of density parameter for the effective dark energy. The upper side of each boundary corresponds to the region that satisfies the conditions for maximization of the entropy. For example, the point for the fine-tuned LCDM model is found to satisfy the conditions for maximization of the entropy at the present time. In addition, the region close to this point also satisfies the conditions for maximization of the entropy, both at the present time and in the future. Cosmological models in this region are likely to be favored from a thermodynamics viewpoint,” says Associate Professor Komatsu.
In addition to the reported results of the study, it is hoped that the developed model will serve to enable discussion and analysis of the wide range of currently available cosmological models from a thermodynamics perspective.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
81-762-645-076
Related Journal Article
http://dx.