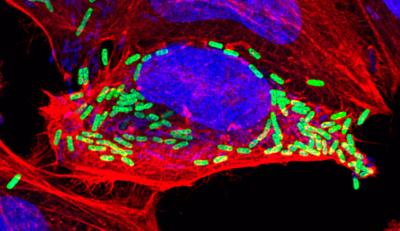
Credit: Hamid Kashkar, University of Cologne
Certain bacteria can override a defence mechanism of the immune system, so called programmed cell death, through inhibition of death effector molecules by their outer membranes components. Shigella bacteria, which cause diarrhoea, use lipopolysaccharides (LPS) on their surface to block the effector caspases. Lipopolysaccharides are a component of the bacterial outer membrane. This strategy enables the bacteria to multiply within the cell. This is the result of a study conducted by the molecular immunologist Professor Hamid Kashkar and his team in the institute for Medical Microbiology and Immunology at the CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Aging Research at the University of Cologne. The article ‘Cytosolic Gram-negative bacteria prevent apoptosis by inhibition of effector caspases through LPS’ by Günther et al. appeared in the current issue of Nature Microbiology.
Various bacterial pathogens can escape our immune system by staying and multiplying within our body cells (intracellularly). The intracellular propagation of pathogens later leads to cell breakdown and the release of microorganisms that infect neighbouring cells, spread and cause tissue damage and infectious disease.
However, the body has a response to this bacterial strategy: programmed cell death, or apoptosis, reacts to cellular stress situations during infections and causes quick suicide of the infected cells.
Due to this rapid self-destruction programme of our body cells, pathogens cannot multiply – the immune system successfully eliminates them.
Scientists have observed in the past that pathogens can effectively block apoptosis, allowing them to reproduce and spread intracellularly. However, the molecular mechanism responsible for how these bacteria ‘outsmarted’ the immune system was largely unknown.
Kashkar lab has now showed that the pathogen that causes shigellosis (Shigella), a typical cause of acute inflammatory diarrhoea, blocks apoptosis by efficiently blocking certain enzymes, so-called caspases, which act as engines that initiate apoptosis.
The biologists showed that lipopolysaccharides bind and block the caspase. Bacteria without complete LPS, on the other hand, spark apoptosis, which blocks them from reproducing intracellularly. They are successfully eliminated by the immune system and thus no longer able to cause infectious diseases. Kashkar lab’s work has thus deciphered an important bacterial strategy to prevent the rapid death of the host cell and establish a niche to spread.
###
Media Contact
Hamid Kashkar
[email protected]
49-221-478-84091
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




