Researchers show a graphene-based sensor can detect SARS-CoV-2
Researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have successfully used graphene — one of the strongest, thinnest known materials — to detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus in laboratory experiments. The researchers say the discovery could be a breakthrough in coronavirus detection, with potential applications in the fight against COVID-19 and its variants.
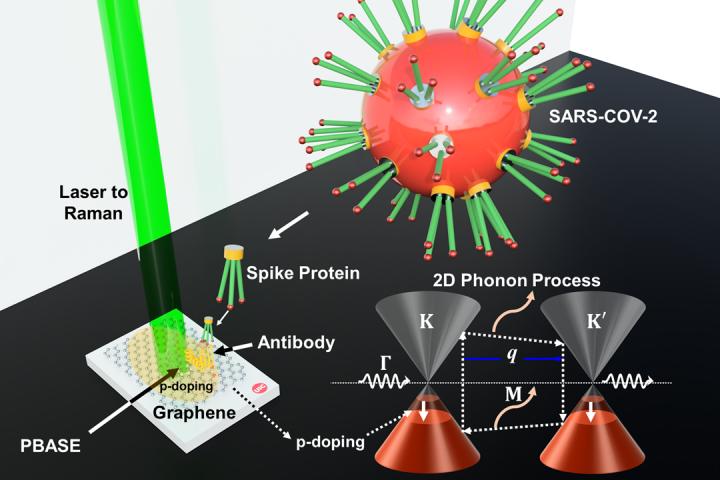
In experiments, researchers combined sheets of graphene, which are more than 1,000 times thinner than a postage stamp, with an antibody designed to target the infamous spike protein on the coronavirus. They then measured the atomic-level vibrations of these graphene sheets when exposed to COVID-positive and COVID-negative samples in artificial saliva. These sheets were also tested in the presence of other coronaviruses, like Middle East respiratory syndrome, or MERS-CoV.
The UIC researchers found that the vibrations of the antibody-coupled graphene sheet changed when treated with a COVID-positive sample, but not when treated with a COVID-negative sample or with other coronaviruses. Vibrational changes, measured with a device called a Raman spectrometer, were evident in under five minutes.
Their findings are published in the journal ACS Nano.
“We have been developing graphene sensors for many years. In the past, we have built detectors for cancer cells and ALS. It is hard to imagine a more pressing application than to help stem the spread of the current pandemic,” said Vikas Berry, professor and head of chemical engineering at the UIC College of Engineering and senior author of the paper. “There is a clear need in society for better ways to quickly and accurately detect COVID and its variants, and this research has the potential to make a real difference. The modified sensor is highly sensitive and selective for COVID, and it is fast and inexpensive.”
“This project has been an amazingly novel response to the need and demand for detection of viruses, quickly and accurately,” said study co-author Garrett Lindemann, a researcher with Carbon Advanced Materials and Products, or CAMP. “The development of this technology as a clinical testing device has many advantages over the currently deployed and used tests.”
Berry says that graphene — which has been called a “wonder material” — has unique properties that make it highly versatile, making this type of sensor possible.
Graphene is a single-atom-thick material made up of carbon. Carbon atoms are bound by chemical bonds whose elasticity and movement can produce resonant vibrations, also known as phonons, which can be very accurately measured. When a molecule like a SARS-CoV-2 molecule interacts with graphene, it changes these resonant vibrations in a very specific and quantifiable way.
“Graphene is just one atom thick, so a molecule on its surface is relatively enormous and can produce a specific change in its electronic energy,” Berry said. “In this experiment, we modified graphene with an antibody and, in essence, calibrated it to react only with the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Using this method, graphene could similarly be used to detect COVID-19 variants.”
###
The researchers say the potential applications for a graphene atomic-level sensor — from detecting COVID to ALS to cancer — continue to expand.
A provisional patent has been submitted based on this work.
Additional co-authors of the paper include Ngoc Hoang Lan Nguyen and Sungjoon Kim of UIC. The work has been funded by Ramaco Carbon and their affiliate CAMP, and partly by the Office of Naval Research.
Media Contact
Jackie Carey
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.