The future of selection decisions and breeding programs are examined in a review in the Journal of Dairy Science®
Credit: Journal of Dairy Science
Philadelphia, March 31, 2021 – In an article appearing in the Journal of Dairy Science®, scientists from the United States Department of Agriculture and the Council on Dairy Cattle Breeding provide an insightful review of how US dairy industry breeding selection objectives are established, as well as detail opportunities and obstacles related to new technologies for documenting animal performance.
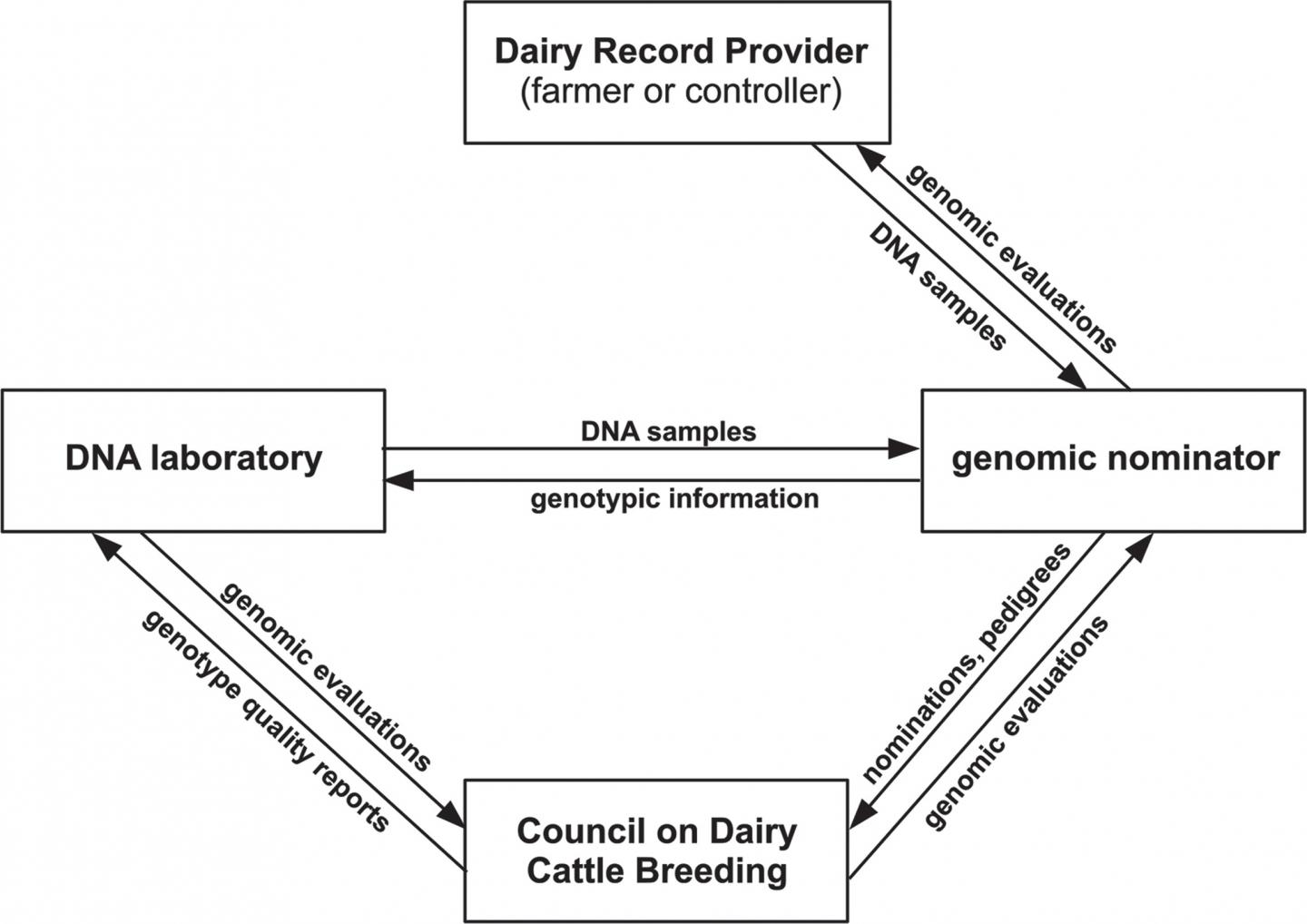
Genetic selection has been an extremely efficacious tool for the long-term enhancement of livestock populations, and the implementation of genomic selection has doubled the rate of gain in dairy cattle. Data captured through the national dairy herd improvement program are used to calculate genomic evaluations for comparing and ranking animals for selection. Over time, most of the focus on the selection indices used to rank bulls and cows on their genetic merit has changed from yield traits to fertility, health, and fitness traits.
Today, most breeding stock are selected and marketed using the net merit dollars (NM$) selection index, which progressed from two traits in 1926 (milk and fat yield) to a mix of 36 individual traits following the most recent update three years ago. Updates to the index depend upon the estimation of a variety of values, and it can be challenging to reach an agreement among stakeholders on what should be included in the index at each review and how those traits should be weighted. Phenotypes for some of the new traits are difficult or costly to measure or depend upon changes to on-farm practices that have not been widely implemented. There is also a need to collect more comprehensive data about the environment in which animals perform, including information about feeding, housing, milking systems, and infectious and parasitic load.
“The rate of change is rapid, and farmers need objective sources of information more than ever before,” said first author John B. Cole, PhD, affiliated with the Animal Genomics and Improvement Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture, Beltsville, MD, USA, at the time the review was accepted for publication. “The best way for the industry to meet the needs of the dairy producers, who drive the whole system, is to treat genetic evaluations as a shared good for the benefit of all.”
The number of traits evaluated continues to increase, and is mind-boggling to many, which indicates that new approaches to classify and express traits may be necessary.
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.