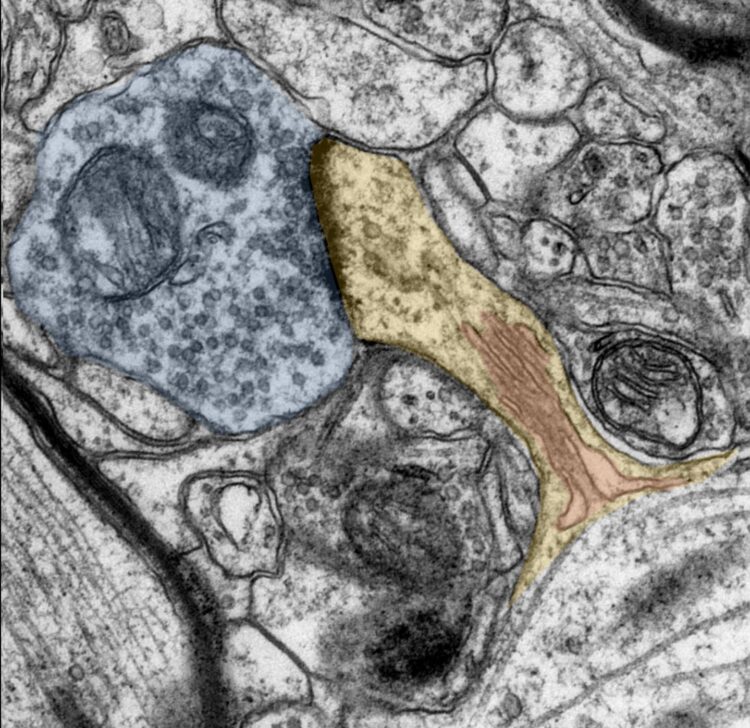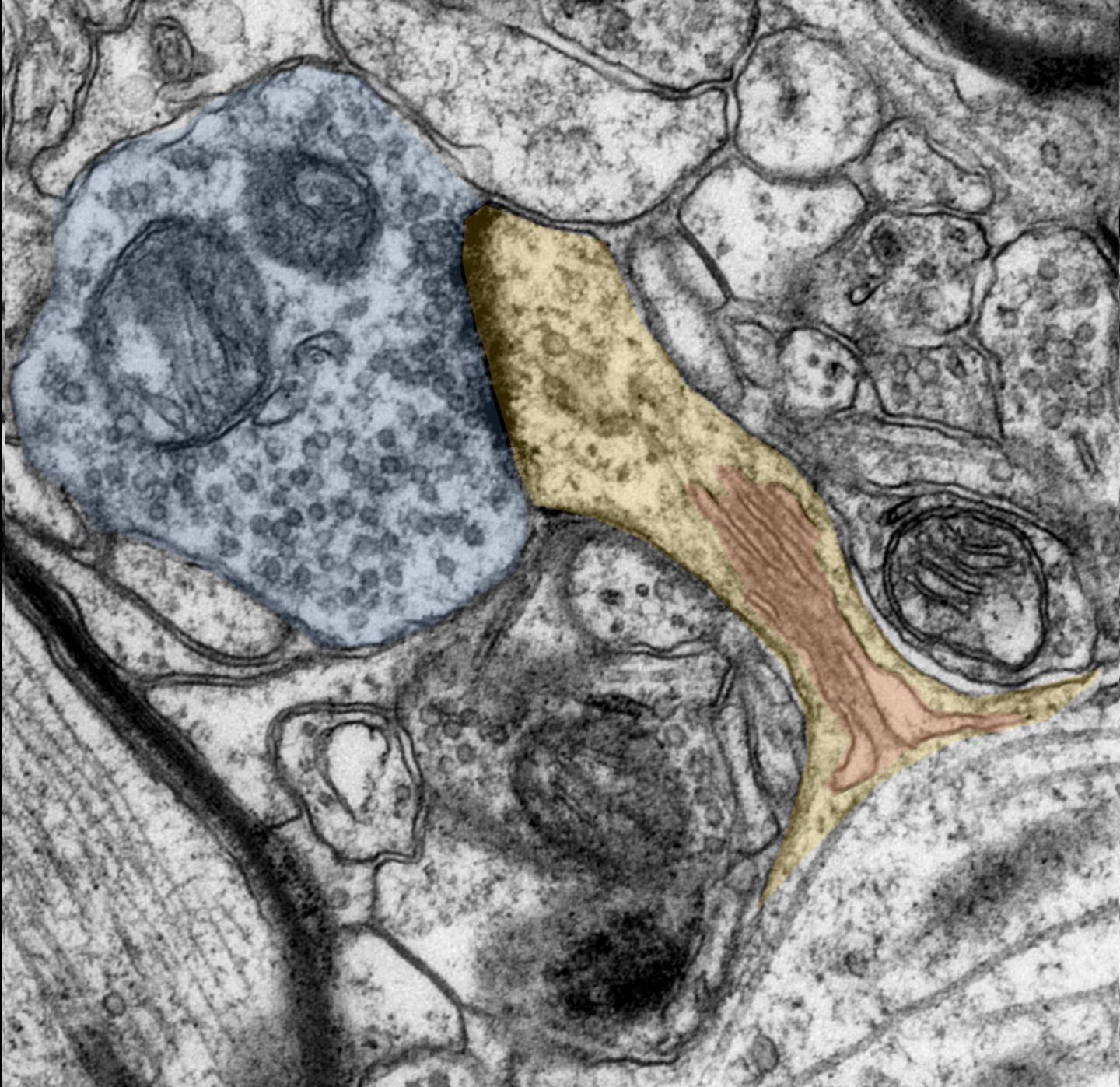
Credit: Source: Andreas Vlachos
Neuroscientists agree that a person’s brain is constantly changing, rewiring itself and adapting to environmental stimuli. This is how humans learn new things and create memories. This adaptability and malleability is called plasticity. “Physicians have long suspected that remodeling processes also take place in humans at the contact points between nerve cells, i.e. directly at the synapses. Until now, however, such a coordinated adaptation of structure and function could only be demonstrated in animal experiments,” says Prof. Dr. Andreas Vlachos from the Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology at the University of Freiburg. But now Vlachos, together with Prof. Dr. Jürgen Beck, head of the Department of Neurosurgery at the University Medical Center Freiburg, has provided experimental evidence for synaptic plasticity in humans. In addition to Vlachos and Beck, the research team consists of Dr. Maximilian Lenz, Pia Kruse and Amelie Eichler from the University of Freiburg, Dr. Jakob Strähle from the University Medical Center Freiburg and colleagues from Goethe University Frankfurt. The results were presented in the scientific journal eLife.
In the experiments, the team investigated whether so-called dendritic spines change when exposed to a vitamin A derivative called retionic acid. Dendritic spines are the parts of the synapse that receive, process and transmit signals during communication between neurons. As such, they play a crucial role in brain plasticity and are constantly adapting to everyday experience. For example, learning can change the number and shape of dendritic spines. However, a transformation in the number or shape of the spines is also found in diseases such as depression or dementia.
The research shows that retinoic acid not only increases the size of dendritic spines, but also strengthens their ability to transmit signals between neurons. “We have concluded from our results that retinoic acids are important messengers for synaptic plasticity in the human brain. Thus, this finding contributes to the identification of key mechanisms of synaptic plasticity in the human brain and could support the development of new therapeutic strategies for brain diseases, such as depression,” says Vlachos.
To experimentally demonstrate that synaptic plasticity also exists in humans, the researchers use tiny samples of human cerebral cortex, which must be compulsorily removed during neurosurgical procedures for therapeutic reasons. The removed brain tissue was then treated with retinoic acid before functional and structural properties of neurons were analyzed using electrophysiological and microscopic techniques.
###
A popular scientific summary of the results is also published on the eLife Journal website.
Popular scientific summary:
https:/
Media Contact
Prof. Dr. Andreas Vlachos
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.