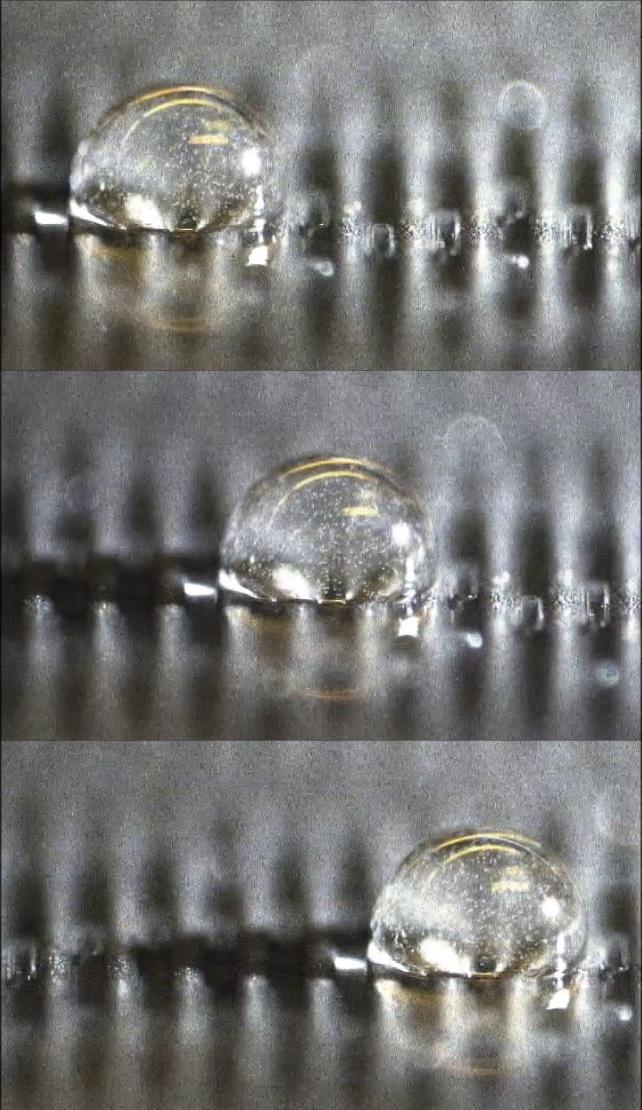
Credit: De Jong et al., Sci. Adv. 2019;5: eaaw0914
Self-cleaning surfaces and laboratories on a chip become even more efficient if we are able to control individual droplets. University of Groningen professor Patrick Onck, together with colleagues from Eindhoven University of Technology, have shown that this is possible by using a technique named mechanowetting. ‘We have come up with a way of transporting droplets by using transverse surface waves. This even works on inclined or vertical surfaces’. The research was published in Science Advances on 14 June.
The idea of mechanowetting is basically very simple: put a droplet on a transverse surface wave, and the droplet will move with the wave. ‘One of the properties of water droplets is that they always try to stay on top of a wave. If that top runs ahead, the droplet will run with it’, Onck explains. It is possible to move the droplets by using mechanical deformation to create surface waves. ‘The remarkable thing about this is that it also works on inclined or vertical surfaces: drops can even move upwards against gravity.’
Theory and practice
Edwin de Jong, PhD candidate in Onck’s group and first author of the paper, tested the concept of mechanowetting by means of a computer model. ‘When it seemed to work in theory, our colleagues from Eindhoven University of Technology devised an experiment to test it. Our model turned out to be right: in practice, the drops moved exactly as we had imagined.’
Lab-on-a-chip
One of the applications of mechanowetting is in lab-on-a-chip systems, complete laboratories the size of a credit card, which are used to analyze biological fluids such as blood or saliva. This allows the samples to be tested outside the lab, e.g. directly at the bedside, with a much faster response rate. ‘If we are able to direct each drop separately, it is possible to perform a lot of different tests at high speed with a very small volume of fluid’, says Onck. Transporting droplets separately was already possible by means of electrowetting. ‘Electrowetting is able to transport droplets by applying electric fields. However, these fields can change the biochemical properties of the sample, and that is something you don’t want when doing blood tests.’
Light waves
In the meantime, Onck’s group is exploring new possibilities. ‘We have performed computer simulations that show that mechanowetting also works by using light-responsive materials to create waves. Light is especially interesting because of its precision and its ability to control the movement of drops remotely.’ In addition to lab-on-a-chip systems, mechanowetting has several other interesting applications, such as self-cleaning surfaces, where water droplets actively absorb and remove the dirt. It also offers opportunities for harvesting moisture from the air, by collecting dew drops for use as drinking water.
###
Reference: De Jong, E., Wang, Y., Toonder, J. M. J. den, Onck, P. R. (2019). Climbing droplets driven by mechanowetting on transverse waves. Science Advances 14 June 2019.
Media Contact
Rene Fransen
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




