Study shows improvements to chemical sensing chip that aims to quickly and accurately identify drugs and other trace chemicals
Credit: Huaxiu Chen, University at Buffalo.
BUFFALO, N.Y. — University at Buffalo researchers are reporting an advancement of a chemical sensing chip that could lead to handheld devices that detect trace chemicals — everything from illicit drugs to pollution — as quickly as a breathalyzer identifies alcohol.
The chip, which also may have uses in food safety monitoring, anti-counterfeiting and other fields where trace chemicals are analyzed, is described in a study that appears on the cover of the Dec. 17 edition of the journal Advanced Optical Materials.
“There is a great need for portable and cost-effective chemical sensors in many areas, especially drug abuse,” says the study’s lead author Qiaoqiang Gan, PhD, professor of electrical engineering in the UB School of Engineering and Applied Sciences.
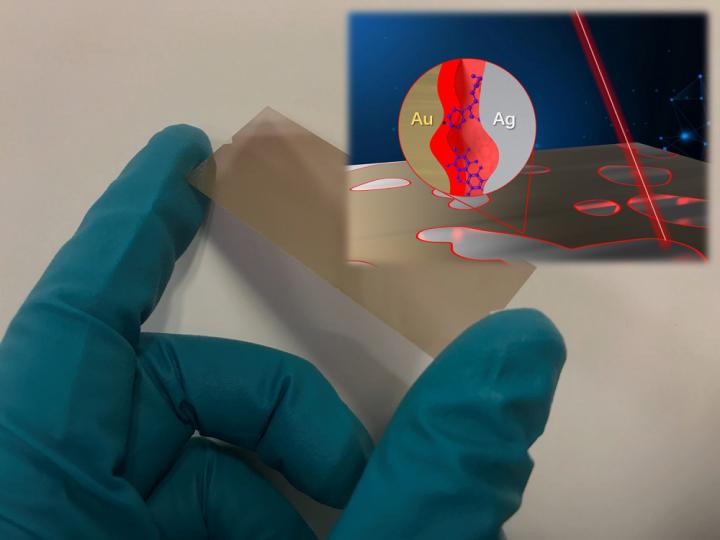
The work builds upon previous research Gan’s lab led that involved creating a chip that traps light at the edges of gold and silver nanoparticles.
When biological or chemical molecules land on the chip’s surface, some of the captured light interacts with the molecules and is “scattered” into light of new energies. This effect occurs in recognizable patterns that act as fingerprints of chemical or biological molecules, revealing information about what compounds are present.
Because all chemicals have unique light-scattering signatures, the technology could eventually be integrated into a handheld device for detecting drugs in blood, breath, urine and other biological samples. It could also be incorporated into other devices to identify chemicals in the air or from water, as well as other surfaces.
The sensing method is called surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS).
While effective, the chip the Gan group previously created wasn’t uniform in its design. Because the gold and silver was spaced unevenly, it could make scattered molecules difficult to identify, especially if they appeared on different locations of the chip.
Gan and a team of researchers — featuring members of his lab at UB, and researchers from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology in China, and King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi Arabia — have been working to remedy this shortcoming.
The team used four molecules (BZT, 4-MBA, BPT, and TPT), each with different lengths, in the fabrication process to control the size of the gaps in between the gold and silver nanoparticles. The updated fabrication process is based upon two techniques, atomic layer deposition and self-assembled monolayers, as opposed to the more common and expensive method for SERS chips, electron-beam lithography.
The result is a SERS chip with unprecedented uniformity that is relatively inexpensive to produce. More importantly, it approaches quantum-limit sensing capabilities, says Gan, which was a challenge for conventional SERS chips
“We think the chip will have many uses in addition to handheld drug detection devices,” says the first author of this work, Nan Zhang, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in Gan’s lab. “For example, it could be used to assess air and water pollution or the safety of food. It could be useful in the security and defense sectors, and it has tremendous potential in health care.”
###
The work was supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation.
Media Contact
Cory Nealon
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




