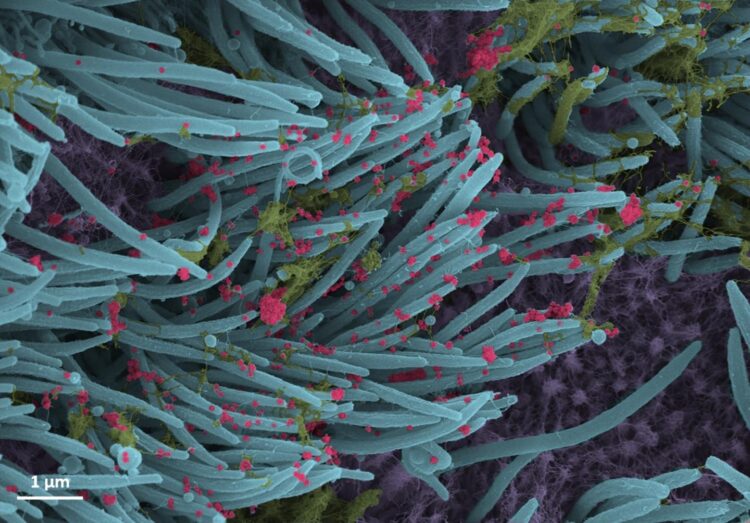
The UNC School of Medicine lab of Camille Ehre, PhD, generated high-powered microscopic images showing startlingly high SARS-CoV-2 viral loads on human respiratory surfaces, ready to spread infection in infected individuals and to others
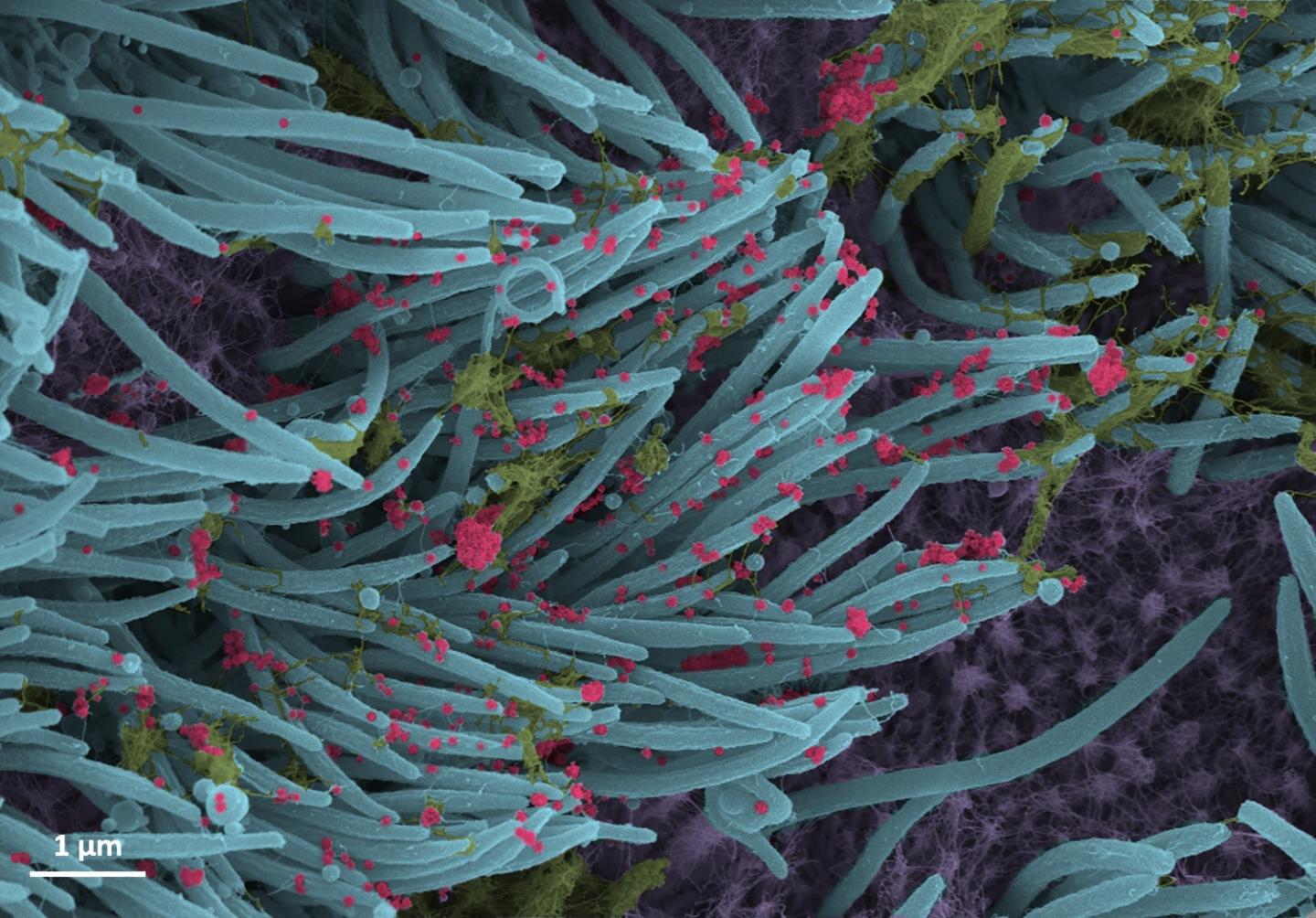
Credit: Ehre Lab, UNC School of Medicine
The UNC School of Medicine laboratory of Camille Ehre, PhD, Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, produced striking images in respiratory tract cultures of the infectious form of the SARS-CoV-2 virus produced by infected respiratory epithelial cells. The New England Journal of Medicine featured this work in its “Images in Medicine” section.
Ehre, a member of the UNC Marsico Lung Institute and the UNC Children’s Research Institute, captured these images to illustrate how intense the SARS-CoV-2 infection of the airways can be in very graphic and easily understood images. Her lab conducted this research in collaboration with the labs of Ralph Baric, PhD, the William R. Kenan Distinguished Professor of Epidemiology at the UNC Gillings School of Public Health, who holds a joint faculty appointment at the UNC Department of Microbiology and Immunology, and Richard Boucher, MD, the James C. Moeser Eminent Distinguished Professor of Medicine and Director of the Marsico Lung Institute at the UNC School of Medicine.
In a laboratory setting, the researchers inoculated the SARS-Co-V-2 virus into human bronchial epithelial cells, which were then examined 96 hours later using scanning electron microscopy.
The images, re-colorized by UNC medical student Cameron Morrison, show infected ciliated cells with strands of mucus (yellow) attached to cilia tips (blue). Cilia are the hair-like structures on the surface of airway epithelial cells that transport mucus (and trapped viruses) from the lung. A higher power magnification image shows the structure and density of SARS-CoV-2 virions (red) produced by human airway epithelia. Virions are the complete, infectious form of the virus released onto respiratory surfaces by infected host cells.
This imaging research helps illustrate the incredibly high number of virions produced and released per cell inside the human respiratory system. The large viral burden is a source for spread of infection to multiple organs of an infected individual and likely mediates the high frequency of COVID-19 transmission to others. These images make a strong case for the use of masks by infected and uninfected individuals to limit SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
###
The images can be viewed here:
https:/
The National Institutes of Health and the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation funded this research.
Media Contact
Mark Derewicz
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.