This article by Dr. Navin B. Patel et al. is published in Current Computer-Aided Drug Design Volume 14 , Issue 4 , 2018
Credit: Bentham Science Publishers, Navin B. Patel
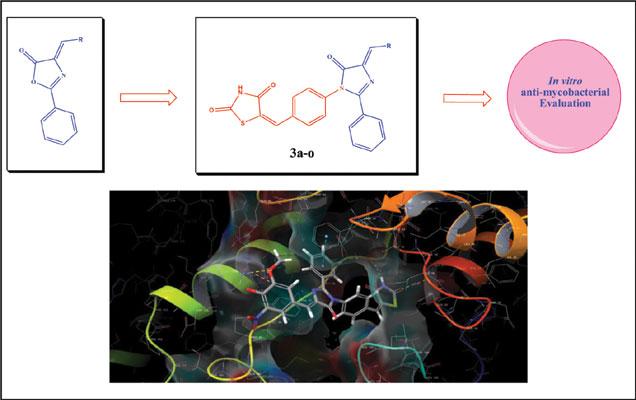
Researchers from the Department of Chemistry, Veer Narmad South Gujarat University, India have designed and synthesized azole scaffolds (a series of A series of (E)-5-(4-((Z)-4-substitutedbenzylidene-2-thienylmethylene-5-oxo- 2-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-1-yl) benzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-diones). Analysis of ligand-protein interactions was also conducted using molecular docking studies with (InhA) Enoyl-ACP reductase of the type II fatty acid synthase (FAS-II) system along with an investigation of the ADME properties of the scaffolds for use in oral medicine.
In vitro antimycobacterial activity was carried out against the M. tuberculosis H37Rv strain using Lowenstein-Jensen medium and antimicrobial activity against two gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus, S. pyogenes), two gram-negative bacteria (E. coli, P. aeruginosa) and three fungal species (C. albicans, A. niger, A. clavatus) using the broth microdilution method. In silico molecular docking studies were carried out using Glide (grid-based ligand docking) program incorporated in the Schrödinger molecular modeling package by Maestro 11.0 and ADME properties of synthesized compounds was performed using DruLito software.
Patel et al’s investigations revealed 6 compounds that exhibited promising antimicrobial activity and 1 compound (labelled 3n) which showed very good antimycobacterial activity along with Gilde docking score (-8.864) and with the one violation in Lipinski’s rule of five.
The researchers note that this is a preliminary result which gives directions for improving pharmaceutical derivatives for the treatment of tuberculosis. This article is Open Access. To obtain the article please visit http://www.
###
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




