Combining biopsy strategies allowed doctors to find up to 33% more cancers
Credit: UCLA Health
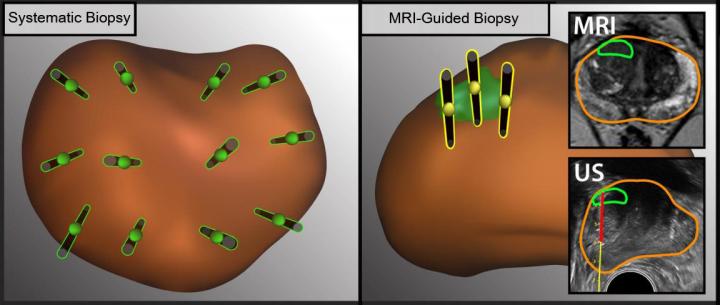
Each year, 1 million men in the U.S. undergo biopsies to determine whether they have prostate cancer. The biopsy procedure traditionally has been guided by ultrasound imaging, but this method cannot clearly display the location of tumors in the prostate gland.
A multidisciplinary team of UCLA physicians has found that a new method, which includes biopsy guided by magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, can be used together with the traditional method to increase the rate of prostate cancer detection.
Ultrasound has been used to visualize the prostate in order to take a representative sampling of tissue to biopsy. The introduction of MRI has allowed doctors to see specific lesions in the prostate and only take tissue samples from those spots. But the two sampling methods often aren’t used in combination.
In the three-year study, published in JAMA Surgery, a strategy combining both sampling methods led to the detection of up to 33 percent more cancers than standard methods. According to senior author Dr. Leonard Marks, the findings could help lead to an important change in how prostate biopsies are performed.
“Our research suggests that the different biopsy methods identify different tumors,” said Marks, who holds the Jean B. deKernion Chair in the department of urology at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. “To maximize our ability to identify prostate cancer, we need to take advantage of all the information we can. Our cancer detection rate, while using different methods in tandem, surpasses that from using either method alone. In this case, one plus one equals three.”
The study is the first to directly compare the different biopsy sampling methods in the same group of men. Previous research demonstrated the advantages of MRI-guided biopsy, but exactly how to employ the new technology has not been clear. This trial establishes that lesion-targeted and systematic sampling are both required to maximize the accuracy of prostate biopsy.
In the past decade, MRI-guided biopsy methods, which are more targeted because they can precisely show the locations of lesions in the prostate, have been used more commonly. However, some tumors are not visible as lesions on MRIs, so such cancers may not be detected.
In the 300-person study, 248 men had a prostate lesion visible on MRI. By using all available biopsy information and methods together, the researchers detected cancer in 70 percent of those men. An additional 52 men in the trial had no lesion visible on MRI, yet 15 percent of those men were found to have cancer via the traditional ultrasound method, confirming that MRI does not identify all tumors.
“Men being assessed for prostate cancer should first receive an MRI before biopsy,” said Marks, who is a member of the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center. “When there’s a lesion on MRI, physicians should take systematic and targeted biopsies together for the best chance at finding cancer. Even if the MRI is negative for lesions, men at risk — including those with elevated levels of prostate-specific antigen, a prostate nodule, or family history — should still receive a traditional, systematic biopsy.”
Identifying the precise location of cancerous tissue in the prostate is especially important as treatments become increasingly targeted. While the surgical removal of the entire gland, known as prostatectomy, is a common method of treatment, emerging treatments like focal therapy aim to eliminate only cancerous tissue in the gland while sparing healthy tissue.
“Improving our ability to see the location of cancer in the prostate in real time opens up the door for treatment innovations,” Marks said. “If we can identify the location of tumors and put biopsy needles directly into them, why not find a way to destroy the tumor on the spot?”
###
Dr. Fuad Elkhoury, a resident physician in the department of urology at the Geffen School, is the study’s first author. Other authors include Dr. Ely Felker of the department of radiology; Lorna Kwan of the department of urology; Dr. Anthony Sisk of the department of pathology; Merdie Delfin of the department of urology; and Shyam Natarajan of the departments of urology and bioengineering.
In addition to a grant from the National Cancer Institute, funding for the study came from the Jean Perkins Foundation, the Kent Kresa Family Foundation and the Steven C. Gordon Family Foundation. Marks is a co-founder of Avenda Health Inc., a biomedical device company aiming to treat prostate tumors with a laser device.
Media Contact
Ryan Hatoum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




