Credit: Genevieve Martin/Oak Ridge National Laboratory, US Dept. of Energy
Buildings–Pushing the envelope
An online tool developed by researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory provides architects and engineers a fast and efficient way to assess the performance of a building’s envelope design before construction begins. The Building Science Advisor allows builders to evaluate the moisture durability of the envelope, or exterior, of residential buildings. “Most building envelope issues are associated with moisture problems,” ORNL’s Andre Desjarlais said. “With BSA, we’re guiding builders through the design process by identifying features that impact durability.” The tool helps builders make better-informed decisions for energy efficiency through two pathways–expert or educational. “The expert pathway gives builders the ability to input construction plan information uninterrupted, and the educational path guides users through each step of the material selection process, providing feedback so that the user can adjust plans in real-time,” he said. The BSA will be expanded to include roofing systems, retrofits and commercial envelopes evaluation. [Contact: Jennifer Burke, (865) 576-3212; [email protected]]
Image: https:/
Caption: ORNL’s online tool provides builders a fast and efficient way to assess the performance of a building’s envelope design before construction begins. Credit: Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Dept. of Energy
Neutrons–Mastering magnetism
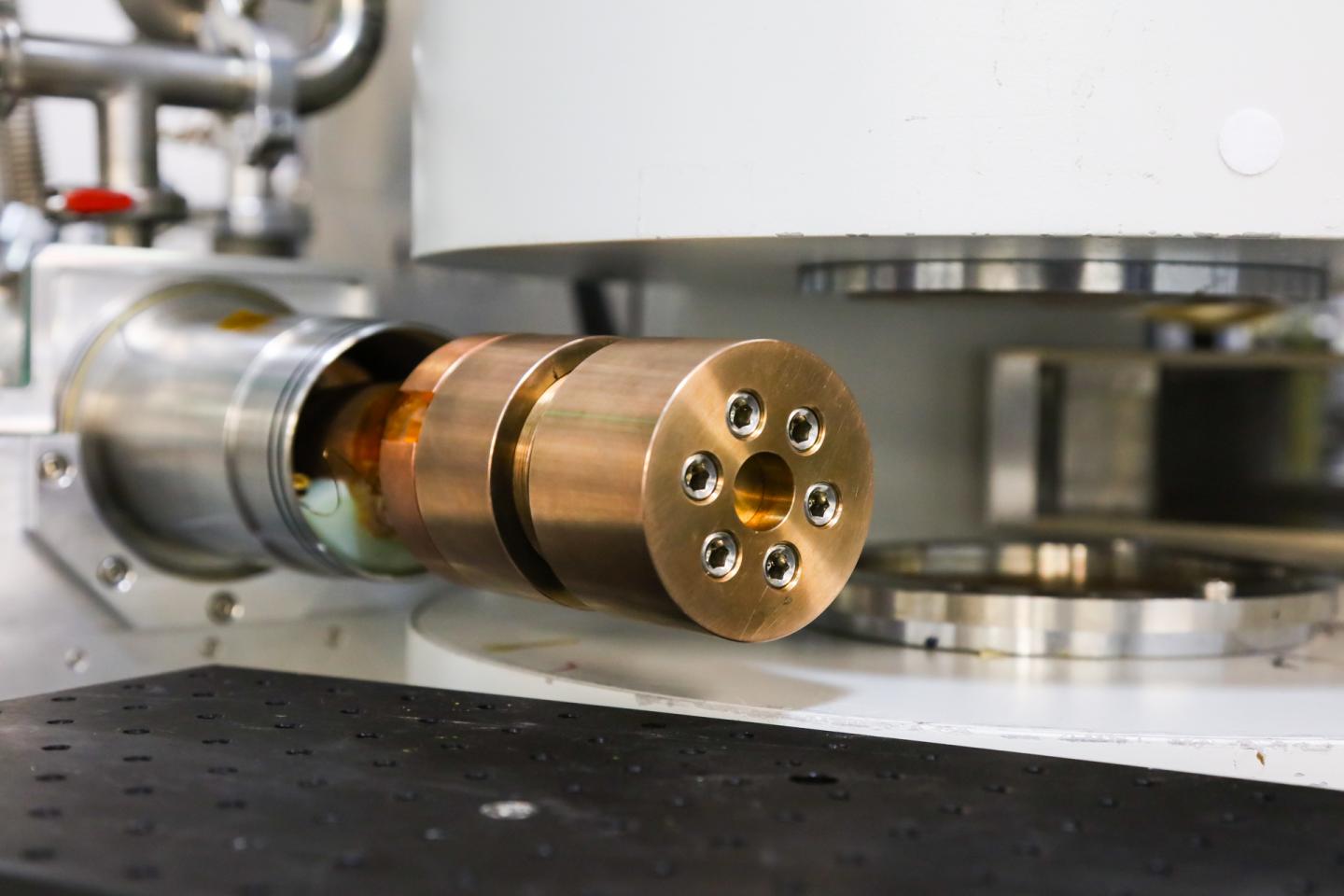
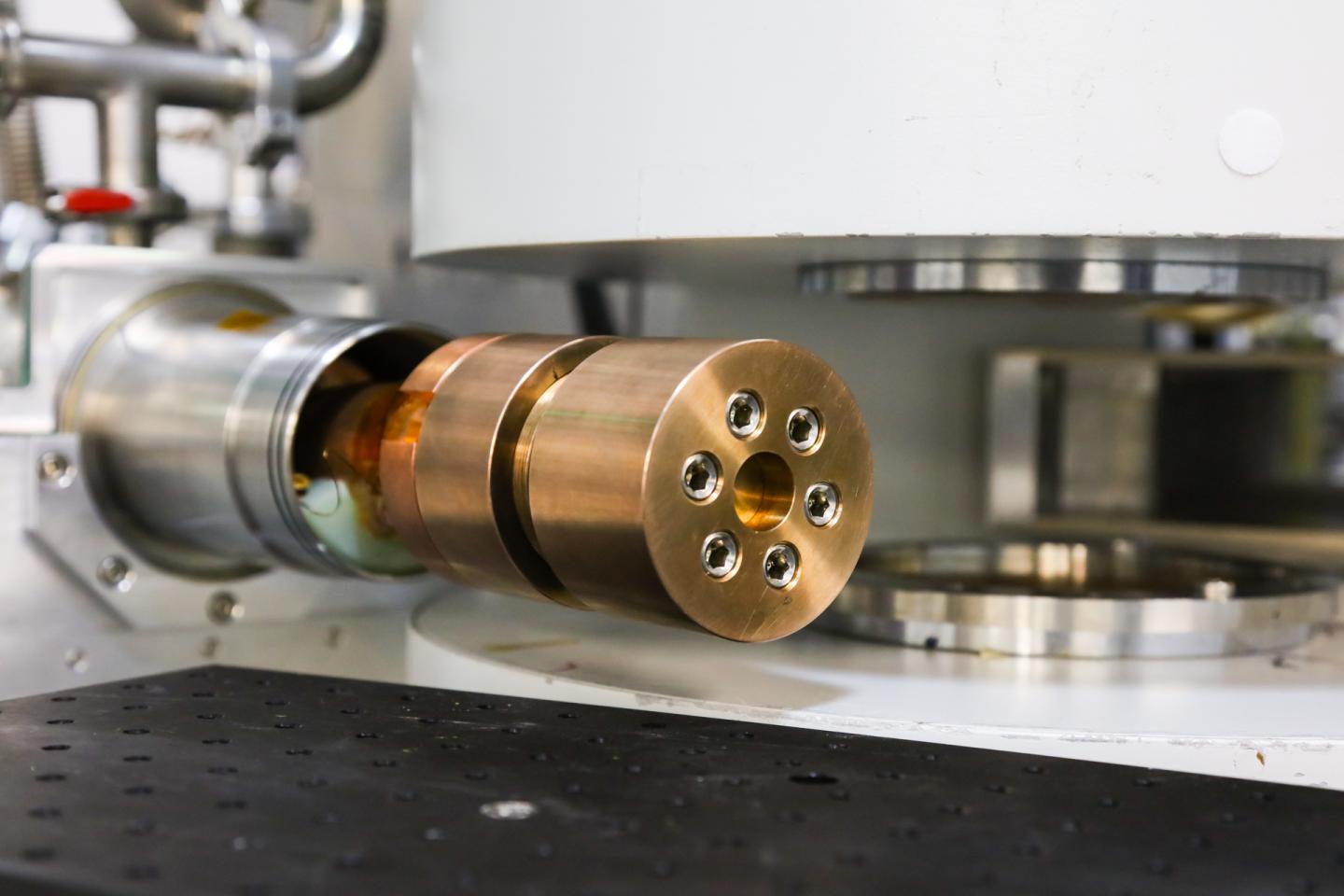
Researchers have pioneered a new technique using pressure to manipulate magnetism in thin film materials used to enhance performance in electronic devices. They used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source to explore the spacial density of atoms and observe how magnetism in a lanthanum-cobalt-oxide film changed with applied pressure. “We developed a novel method to identify the critical role that strain has on the magnetism of films and their interfaces,” said ORNL’s Michael R. Fitzsimmons. “This allows us to study magnetism in thin films without having to compare a lot of differently grown samples.” The new technique, described in Physical Review Letters, will enable novel studies into complex correlations between magnetism and pressure involving a broad class of thin films in a wide range of applications. The thin film materials were developed at ORNL, and complementary measurements were made at Argonne National Laboratory’s Advanced Photon Source.–Gage Taylor [Contact: Jeremy Rumsey, (865) 576-2038; [email protected]]
Image: https:/
Caption: Researchers developed a one-of-a-kind, high-pressure cell and used it on the Magnetism Reflectometer beamline at ORNL’s Spallation Neutron Source to study the spatially confined magnetism in a lanthanum-cobalt-oxide thin film. Credit: Genevieve Martin/Oak Ridge National Laboratory, U.S. Dept. of Energy
Quantum–Squeezed light cuts noise
Oak Ridge National Laboratory physicists studying quantum sensing, which could impact a wide range of potential applications from airport security scanning to gravitational wave measurements, have outlined in ACS Photonics the dramatic advances in the field. “Quantum-enhanced microscopes are particularly exciting,” ORNL’s Ben Lawrie said. “These quantum sensors can ‘squeeze’ the uncertainty in optical measurements, reducing the uncertainty in one variable while increasing the uncertainty elsewhere.” Squeezed light refers to a quantum state where the statistical noise that occurs in ordinary light is greatly reduced. Squeezed atomic force microscopes, or AFMs, could operate hundreds of times faster than current microscopes while providing a nanoscale description of high-speed electronic interactions in materials. This enhancement is enabled by removing a requirement in most AFMs that the microscope operate at a single frequency. Future sensing technologies that harness quantum properties could be deployed as new quantum-enabled devices or as “plug-ins” for existing sensors. [Contact: Sara Shoemaker, (865) 576-9219; [email protected]]
Image: https:/
Caption: Certain quantum sensors use a “squeezed” state of light to greatly reduce statistical noise that occurs in ordinary light. Credit: Reprinted with permission from B. J. Lawrie, et al., “Quantum Sensing with Squeezed Light.” ACS Photonics. Copyright 2019. American Chemical Society.
###
Media Contact
Sara Shoemaker
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.