Credit: UAB
Magnetic materials are ubiquitous in modern society, present in nearly all the technological devices we use every day. In particular, personal electronics like smartphones/watches, tablets, and desktop computers all rely on magnetic material to store information. Information in modern devices is stored in long chains of 1’s and 0’s, in the binary number system used as the language of computers.
« If you imagine a bar magnet, the same that many of us played with as a kid (and perhaps still do), you may recall that they were labeled with a “north” side and a “south” side (or had two different colors on each end). If two magnets were brought next to each other, the same sides would repel, and the opposite sides would attract – two distinct halves which can be easily identified. In this way, a “1” and a “0” can be assigned to a magnet’s orientation, so that a long chain of magnets can be arranged in a computer to store data », explains ICREA researcher at the UAB Jordi Sort, one of the research coordinators.
Currently, changing the orientation of a magnet (essentially writing or rewriting data) in electronics has relied on using current, the same current needed to power the outlets in your house and charge your phone. But therein lies a problem: when you run current through a material, the material heats up. This heat is a form of energy that is lost to the environment, essentially wasted. The demand to store more and more data increases each year, and necessitates creating smaller and smaller devices, which exponentially worsens this heating effect, leading to huge energy losses. It is no surprise, then, that government and private research has turned to developing new, energy-efficient materials and technologies to solve this issue.
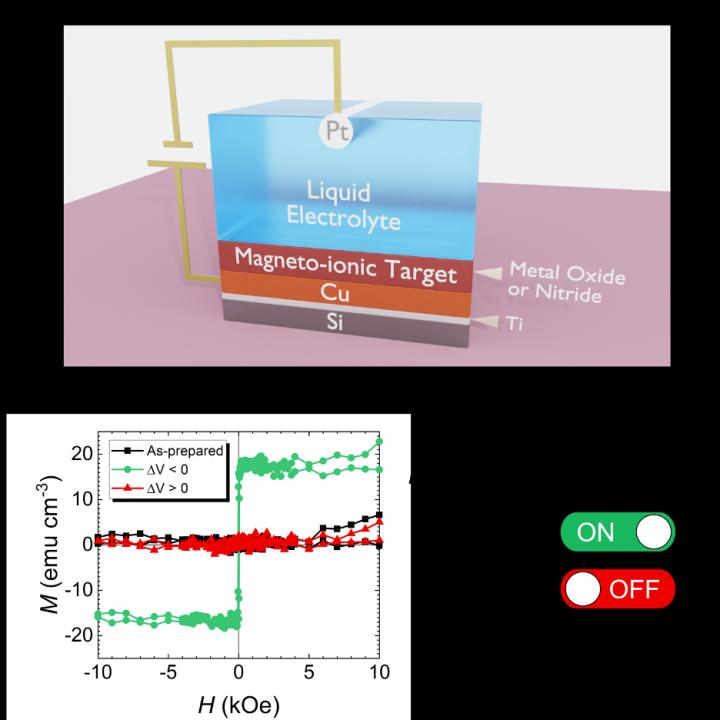
One possible solution to this problem is to use magnetic materials which can rely on voltage to reorient magnetic material, studied in a field of research called voltage-controlled magnetism, using voltage in place of current to significantly reduce the energy needed to alter the magnetic orientation. There are several approaches, but a promising and popular research branch in the field explores magneto-ionics, where non-magnetic atoms are moved in and out of a magnetic material using voltage, and so altering its magnetic properties.
A recent collaborative study between the UAB, Georgetown University, HZDR Dresden, CNM’s Madrid and Barcelona, University of Grenoble, and ICN2, and published in the journal Nature Communications has shown that it is possible to switch magnetism ON and OFF in metals containing nitrogen (that is, to generate or remove all magnetic features of this material) with voltage. One simple analogy would be that we are able to increase or completely remove the strength with which a magnet attracts to, for example, the door of a fridge, simply by connecting it to a battery and applying a certain voltage polarity. In this project, cobalt-nitride is shown to be non-magnetic on its own, but when nitrogen is removed with voltage, it forms a cobalt-rich structure which is magnetic (and vice versa). This process is shown to be repeatable and durable, suggesting that such a system is a promising means to write and store data in a cyclable manner. Interestingly, it is also shown to require less energy and it is faster than systems using alternative non-magnetic atoms, such as oxygen, elevating the possible energy savings.
###
Media Contact
Jordi Sort
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




