Russian researchers announced the development of a combined action drug based on ionizing radiation and bacterial toxin.
Credit: Evgeny Pchelkin
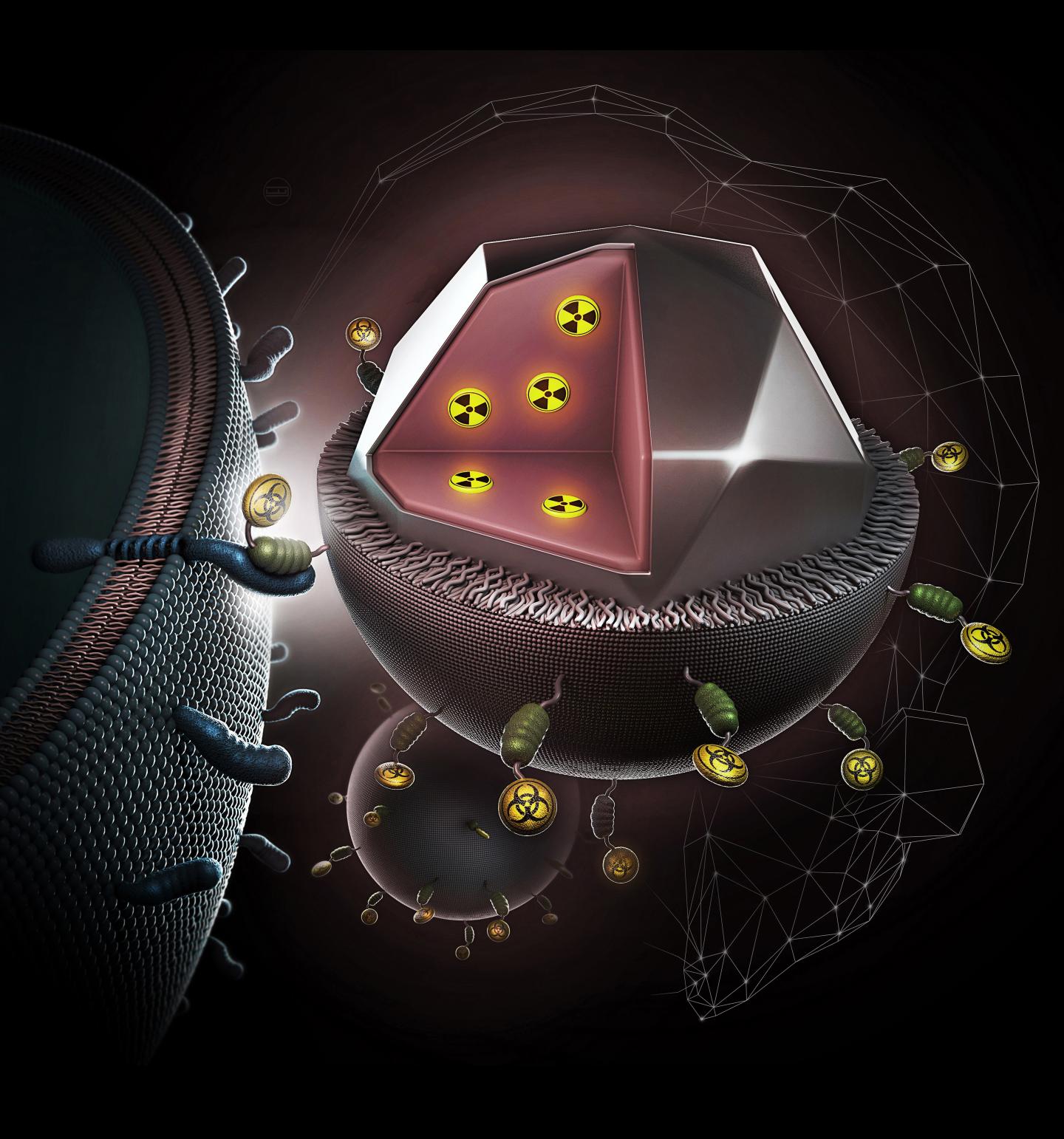
Russian researchers announced the development of a combined action drug based on ionizing radiation and bacterial toxin. Their total effect appeared to be 2,200 times stronger compared to that exerted by the radiation and toxin, separately. The drug affects tumor cells selectively providing better diagnostics and treatment of malignant tumors. These advances were reported in an article published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Chemotherapy is widely used for treatment of cancerous diseases. However, it is associated with severe side effects (hair loss, nausea, loss of appetite, oedema, anemia, memory disorders, and so on) as the drugs affect the body in total and are accumulated throughout normal tissues. Moreover, the chemotherapy often requires repeated drug administration to overcome tumor propensity to relapse. A perfect anti-cancer drug should provide a powerful impact to all tumor cells at once to prevent their recovery.
The combined therapy proposed and realised by the Russian scientists appeared to be successful. “Just like modern armies deploy tanks, foot troops, and artillery, we also fight tumors using several mechanisms at once: ionising radiation and a strong toxin of bacterial origin,” says Andrey Zvyagin, head of the Department of Biomedical Engineering at the Institute of Molecular Medicine, Sechenov University.
The drug developed by the scientists consists of a nanoparticles, as the core, with embedded radiopharmaceutical agent (a source of ionising beta-radiation), and a highly toxic toxin derived from bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The nanosized drug core is decorated with polymer to render the nanocomplex water miscible and biologically amiable and coupled with biological molecules, which represent the toxin fused with a targeting biomolecule by genetic engineering methods. The radiopharmaceutical agent is well secluded inside the nanoparticle and guarantees its side-effect-free targeted action to tumor cells. Blood vessels that feed the tumor have pores through which the drug enters the tumor from the blood flow. The targeting biomolecule binds itself with cancer cells causing them to accumulate in the primary and metastatic tumors. The radiopharmaceutical agent is able to affect the cells both in immediate proximity to the nanoparticles and up to 1 cm from them, providing for efficient therapy of considerable tumor masses. The toxin blocks the synthesis of proteins in the cells preventing them from restoration and dissemination.
The new drug was tested both on cells and laboratory animals: breast cancer (the most widely spread type of cancer in women) was grafted on a laboratory mouse, and after that the tested drug was administered to it. In experiments on cells, the effect of the combination was 2,200 times stronger than the effect from the separate use of its components. The efficiency of combined therapy was confirmed by experiments on laboratory mice. The drug not only treats, but also facilitates visualisation of the tumors, which makes it a diagnostical tool. The area of medicine that combines diagnostics and treatment is called theranostics.
###
The work was carried out together with scientists from N.I. Lobachevsky State University of Nizhny Novgorod, Shemyakin-Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, a company “Amplituda Science and Technology Center”, and other research groups. The whole work, from the idea to the publishing of the article, was carried out in Russia.
Media Contact
Nataliya Rusanova
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




