This article by Dr. Felix-Martin Werner and Prof. Rafael Coveñas is published in Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2021
Credit: Dr. Felix-Martin Werner, Dr. Rafael Coveñas
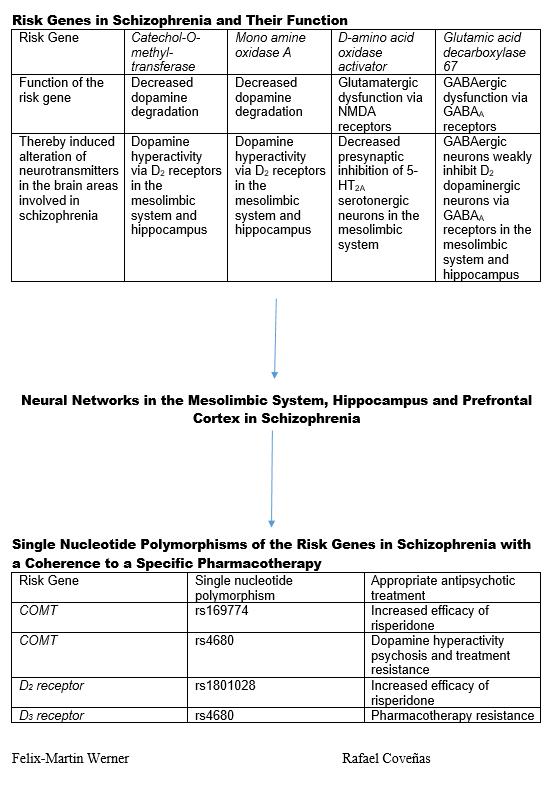
Dr. Felix-Martin Werner, working at the Euro Academy Pößneck in Germany and Prof. Rafael Coveñas, working at the Institute of Neurosciences of Castilla and León, Salamanca in Spain, have been working on neurological and psychiatric disease for over ten years. In their most recent review, published in Current Pharmaceutical Design (Bentham Science Publishers) Werner and Coveñas cover information about the risk genes in schizophrenia and explain the importance of examining their single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP’s). In schizophrenia, 260 risk genes have been discovered, and an association between single SNPs and the clinical efficacy of a specific antipsychotic drug has been established. Among the risk genes in schizophrenia, the COMT, MAO A/B, GAD 67, DAOA, dysbindin-1 and neuregulin-1 genes are described, and their functions can be represented by an updated neural network model of the ventral tegmental area, hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. The COMT and MAO A/B genes encode a decreased dopamine degradation. As a consequence, dopamine hyperactivity via D2 receptors occurs in the hippocampus and ventral tegemental area. The GAD 67 gene encodes a GABA dysfunction. Consequently, GABAergic neurons weakly inhibit D2 dopaminergic neurons in the hippocampus and ventral tegmental area via GABAA receptors. The DAOA gene encodes a glutamatergic dysfunction. This leads to a weak presynaptic inhibition of 5-HT2A serotonergic neurons in the hippocampus and ventral tegmental area via NMDA receptors. Dysbindin-1 and neuregulin-1 genes encode as well a glutamatergic dysfunction. The most important SNPs, which show an association with a specific pharmacotherapy, are mentioned. The SNP rs169774 of the COMT gene and the SNP rs1801028 of the D2 receptor gene are linked with an increased efficacy of the antipsychotic drug risperidone. The SNP of the COMT and D2 receptor genes are related with a dopamine hyperactivity psychosis and treatment resistance. Patients suffering both hyperactivity and resistance could be treated with the antipsychotic drug clozapine in combination with the novel antipsychotic drug cariprazine. This drug combination improves the PANSS total score in treatment-resistant schizophrenic patients. “By examining in a cohort of schizophrenic patients the SNPs of the risk genes, it will be possible to differentiate patients with a good response to a specific antipsychotic drug from those with treatment resistance,” notes Dr. Werner.
###
For more information please visit: https:/
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




