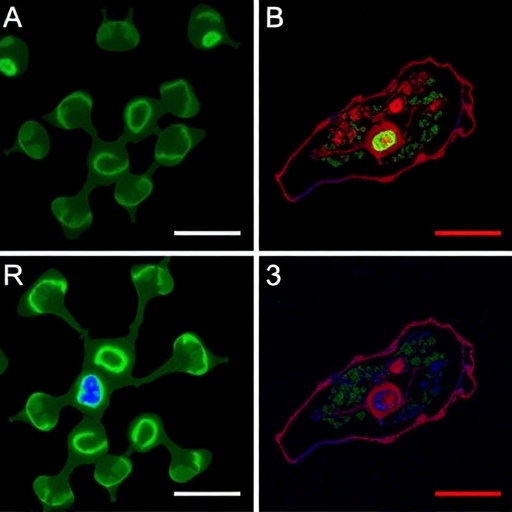
Credit: Lindsay France/Cornell University
ITHACA, N.Y. – By discovering the culprit behind decreased blood flow in the brain of people with Alzheimer’s, biomedical engineers at Cornell University have made possible promising new therapies for the disease.
You know that dizzy feeling you get when, after lying down for an extended period, you stand up a little too quickly?
That feeling is caused by a sudden reduction of blood flow to the brain, a reduction of around 30 percent. Now imagine living every minute of every day with that level of decreased blood flow.
People with Alzheimer’s disease don’t have to imagine it. The existence of cerebral blood flow reduction in Alzheimer’s patients has been known for decades, but the exact correlation to impaired cognitive function is less understood.
“People probably adapt to the decreased blood flow, so that they don’t feel dizzy all of the time, but there’s clear evidence that it impacts cognitive function,” said Chris Schaffer, associate professor of biomedical engineering at Cornell University.
A new study from the joint lab of Schaffer and associate professor Nozomi Nishimura, offers an explanation for this dramatic blood flow decrease: white blood cells stuck to the inside of capillaries, the smallest blood vessels in the brain. And while only a small percentage of capillaries experience this blockage, each stalled vessel leads to decreased blood flow in multiple downstream vessels, magnifying the impact on overall brain blood flow.
Their paper, “Neutrophil Adhesion in Brain Capillaries Reduces Cortical Blood Flow and Impairs Memory Function in Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Models,” published in Nature Neuroscience.
The paper’s co-lead authors are Jean Cruz-Hernandez, Ph.D., now a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard Medical School, and Oliver Bracko, a research associate in the Schaffer-Nishimura Lab.
The paper, Schaffer said, is the culmination of approximately a decade of study, data gathering and analysis. It began with a study in which Nishimura was attempting to put clots into the vasculatures of Alzheimer’s mouse brains to see their effect.
“It turns out that … the blockages we were trying to induce were already in there,” she said. “It sort of turned the research around – this is a phenomenon that was already happening.”
Recent studies suggest that brain blood flow deficits are one of the earliest detectable symptoms of dementia.
“What we’ve done is identify the cellular mechanism that causes reduced brain blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease models, which is neutrophils [white blood cells] sticking in capillaries,” Schaffer said. “We’ve shown that when we block the cellular mechanism [that causes the stalls], we get an improved blood flow, and associated with that improved blood flow is immediate restoration of cognitive performance of spatial- and working-memory tasks.”
“Now that we know the cellular mechanism,” he said, “it’s a much narrower path to identify the drug or the therapeutic approach to treat it.”
The team has identified approximately 20 drugs, many of them already FDA approved for human use, that have potential in dementia therapy and are screening these drugs in Alzheimer’s mice now.
Schaffer said he’s “super-optimistic” that, if the same capillary-blocking mechanism is at play in humans as it is in mice, this line of research “could be a complete game-changer for people with Alzheimer’s disease.”
###
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, the Alzheimer’s Art Quilt Initiative, and the Brightfocus Foundation.
Cornell University has dedicated television and audio studios available for media interviews supporting full HD, ISDN and web-based platforms.
Media Contact
Lindsey Hadlock
[email protected]
607-269-6911
Original Source
http://news.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.