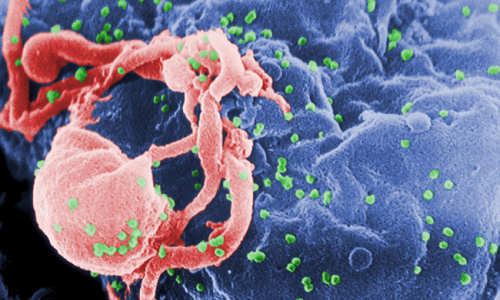
In a remarkable new advance against the virus that causes AIDS, scientists from The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have announced the creation of a novel drug candidate that is so potent and universally effective, it might work as part of an unconventional vaccine.
The research, which involved scientists from more than a dozen research institutions, was published February 18 online ahead of print by the prestigious journal Nature.
The study shows that the new drug candidate blocks every strain of HIV-1, HIV-2 and SIV (simian immunodeficiency virus) that has been isolated from humans or rhesus macaques, including the hardest-to-stop variants. It also protects against much-higher doses of virus than occur in most human transmission and does so for at least eight months after injection.
“Our compound is the broadest and most potent entry inhibitor described so far,” said Michael Farzan, a professor on TSRI’s Florida campus who led the effort. “Unlike antibodies, which fail to neutralize a large fraction of HIV-1 strains, our protein has been effective against all strains tested, raising the possibility it could offer an effective HIV vaccine alternative.”
Blocking a Second Site
When HIV infects a cell, it targets the CD4 lymphocyte, an integral part of the body’s immune system. HIV fuses with the cell and inserts its own genetic material—in this case, single-stranded RNA—and transforms the host cell into a HIV manufacturing site.
The new study builds on previous discoveries by the Farzan laboratory, which show that a co-receptor called CCR5 contains unusual modifications in its critical HIV-binding region, and that proteins based on this region can be used to prevent infection.
With this knowledge, Farzan and his team developed the new drug candidate so that it binds to two sites on the surface of the virus simultaneously, preventing entry of HIV into the host cell. “When antibodies try to mimic the receptor, they touch a lot of other parts of the viral envelope that HIV can change with ease,” said TSRI Research Associate Matthew Gardner, the first author of the study with Lisa M. Kattenhorn of Harvard Medical School. “We’ve developed a direct mimic of the receptors without providing many avenues that the virus can use to escape, so we catch every virus thus far.”
The team also leveraged preexisting technology in designing a delivery vehicle—an engineered adeno-associated virus, a small, relatively innocuous virus that causes no disease. Once injected into muscle tissue, like HIV itself, the vehicle turns those cells into “factories” that could produce enough of the new protective protein to last for years, perhaps decades, Farzan said.
Data from the new study showed the drug candidate binds to the envelope of HIV-1 more potently than the best broadly neutralizing antibodies against the virus. Also, when macaque models were inoculated with the drug candidate, they were protected from multiple challenges by SIV.
“This is the culmination of more than a decade’s worth of work on the biochemistry of how HIV enters cells,” Farzan said. “When we did our original work on CCR5, people thought it was interesting, but no one saw the therapeutic potential. That potential is starting to be realized.”
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by The Scripps Research Institute.