Oncotarget Volume 11, Issue 27 published ‘Correction of the NSE concentration in hemolyzed serum samples improves its diagnostic accuracy in small-cell lung cancer’ by Genet et al. which reported that this study aimed to develop a hemolysis correction
Credit: Correspondence to – Daan van de Kerkhof – [email protected]
Oncotarget Volume 11, Issue 27 published “Correction of the NSE concentration in hemolyzed serum samples improves its diagnostic accuracy in small-cell lung cancer” by Genet et al. which reported that this study aimed to develop a hemolysis correction equation and evaluate its role in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) diagnostics.
A hemolysis correction equation was obtained by analyzing the relationship between the measured Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) concentration and the degree of hemolysis.
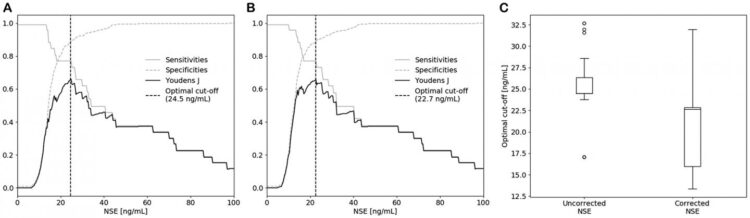
Correction of the measured NSE concentration in patients suspected of lung cancer caused an increase in AUC and a significantly lower cut-off value for SCLC detection when compared to uncorrected results.
Therefore, a hemolysis correction equation should be used to correct falsely elevated NSE concentrations.
Application of the equation illustrates the importance of hemolysis correction in SCLC diagnostics and questions the correctness of the currently used diagnostic cut-off value.
Dr. Daan van de Kerkhof from The Catharina Hospital Eindhoven as well as The Máxima Medical Center said, “Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) is a dimeric metalloenzyme which functions as a cell specific isoenzyme of the glycolytic enzyme enolase.”
Furthermore, improved discrimination of the two main lung cancer subtypes, SCLC and non-small cell lung cancer was achieved when applying a diagnostic cut-off value of 25 ng/mL NSE or analyzing multiple protein tumor markers such as NSE and progastrin-releasing peptide at the same time.
Considering the use of NSE in lung cancer diagnostics and the medical actions that may follow, accurate and reliable quantification of NSE is of main importance.
However, previous studies evaluating the prognostic value of NSE in lung cancer diagnostics did not apply exclusion criteria or did not include the effect of hemolysis on the measured NSE concentration as such, while other factors that could influence serum tumor marker concentrations were addressed.
Therefore, this study aimed to develop, validate and apply a hemolysis correction equation that nullifies the effect of hemolysis on NSE quantification in samples of adult patients.
Using this equation, the effect of hemolysis correction on the NSE cut-off value in SCLC diagnostics was evaluated and the maximum acceptable degree of hemolysis for reliable correction was established.
“The effect of hemolysis correction on the NSE cut-off value in SCLC diagnostics was evaluated and the maximum acceptable degree of hemolysis for reliable correction was established.”
The Kerkhof Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Paper, “this study demonstrates that a hemolysis correction equation improves diagnostic accuracy of serum NSE concentrations in patients suspected of lung cancer. A hemolysis correction equation is therefore suggested to be incorporated in NSE-based clinical decision making, bearing in mind that results of samples with an H-index above 30 μmol/L should not be reported to clinicians.“
###
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI – https:/
Full text – https:/
Correspondence to – Daan van de Kerkhof – [email protected].
Keywords –
small-cell lung cancer,
protein tumor markers,
neuron-specific enolase,
hemolysis correction equation
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a weekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https:/
SoundCloud – https:/
Facebook – https:/
Twitter – https:/
LinkedIn – https:/
Pinterest – https:/
Reddit – https:/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit http://www.
Media Contact
[email protected]
18009220957×105
Media Contact
Ryan James Jessup
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.