Inspired by the way plants grow toward light sources, a phenomenon known as phototropism, bioengineers from the University of California, Berkeley have created a hydrogel that could be manipulated by light.
The new hydrogel, described earlier this month in the journal Nano Letters, could have future applications in the emerging field of soft robotics, which takes a cue from squishy creatures in nature, like starfish, squids and octopuses, to create flexible components.
“Shape-changing gels such as ours could have applications for drug delivery and tissue engineering,” said study principal investigator Seung-Wuk Lee, associated professor of bioengineering.
Researchers combined synthetic, elastic proteins with sheets of graphene, one-atom thick carbon sheets that stack to form graphite. Graphite is the same material used in pencil lead. The graphene sheets generate heat when exposed to near infrared light. That heat affects the synthetic proteins, which absorb water when cooled and release it when hot.
The two materials together formed the nanocomposite biopolymer, or hydrogel, which was designed so that one side was more porous than the other. The side that was more porous allowed a faster absorption and release of water than the other side.
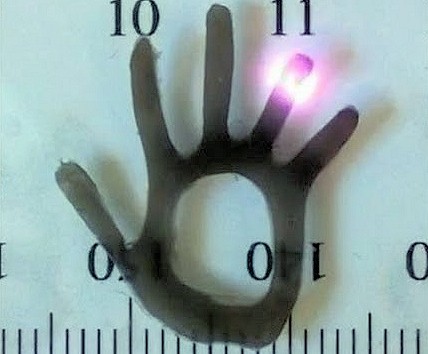
“By combining these materials, we were able to mimic the way plant cells expand and shrink in response to light in a much more precisely controlled manner,” said Lee. “Because the gels shrank unevenly, the material bent when the light hit it. We used these bending motions to demonstrate a hand-shaped hydrogel that exhibited joint-like articulation when exposed to light.”
Other study authors are Eddie Wang and Malav Desai, both graduate students in bioengineering.
Story Source:
The above story is reprinted from materials provided by News Berkeley University, Sarah Yang.