Credit: NASA/NRL
When NASA’s Aqua satellite passed over the Northwestern Pacific Ocean, water vapor data provided information about the intensity of Tropical Cyclone Phanfone. In the Philippines, the storm is known locally as Ursula.
Tropical Depression 30W formed early on Dec. 22 and strengthened into a tropical storm. By 4 a.m. EST (0900 UTC), the storm was renamed Phanfone.
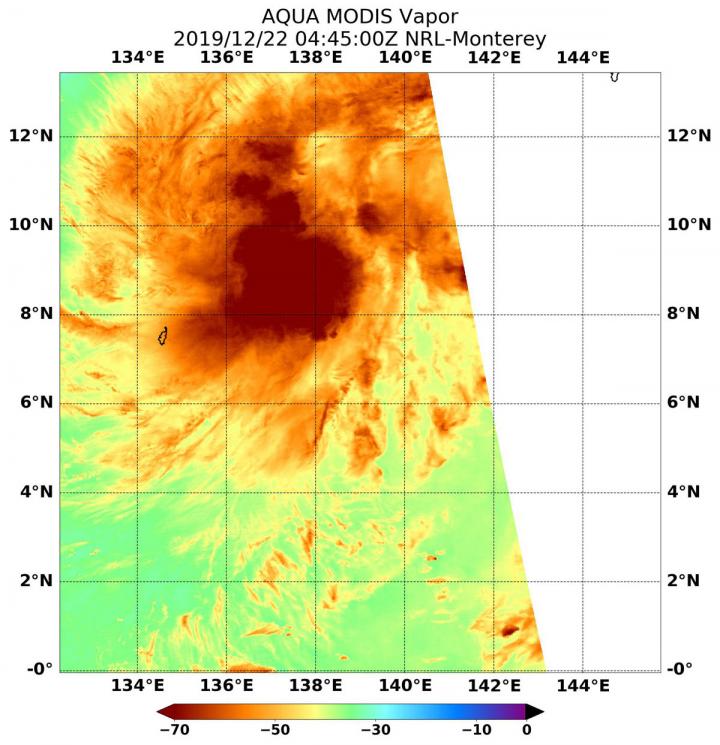
NASA’s Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone on Dec. 22 at 0445 UTC (Dec. 21 at 11:45 p.m. EST) and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument gathered water vapor content and temperature information. The MODIS image showed highest concentrations of water vapor and coldest cloud top temperatures were around the center of circulation.
MODIS data also showed coldest cloud top temperatures were as cold as or colder than minus 70 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 56.6 degrees Celsius) in those storms. Storms with cloud top temperatures that cold have the capability to produce heavy rainfall.
Water vapor analysis of tropical cyclones tells forecasters how much potential a storm has to develop. Water vapor releases latent heat as it condenses into liquid. That liquid becomes clouds and thunderstorms that make up a tropical cyclone. Temperature is important when trying to understand how strong storms can be. The higher the cloud tops, the colder and the stronger the storms.
On Dec. 23 at 4 a.m. EST (0900 UTC), Tropical Storm Phanfone (Philippines designation Ursula) was located near latitude 9.8 degrees north and longitude 132.2 degrees east, about 717 nautical miles east-southeast of Manila, Philippines. Phanfone is moving to the west-northwest and had maximum sustained winds near 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph).
On Dec. 23 at 10 a.m. EST (1500 UTC), the GMI or Microwave Imager sensor aboard NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s Global Precipitation Measurement mission or GPM core satellite, showed an eye was developing in Phanfone’s center.
Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center expect Phanfone will move west-northwest toward and through the central Philippine archipelago and the Visayas and Mindanao regions on Dec. 24 and 25.
NASA’s Aqua satellite is one in a fleet of NASA satellites that provide data for hurricane research.
Typhoons and hurricanes are the most powerful weather event on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
###
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




