Credit: ZHANG Wei and LI Shengying
Mycophenolic acid (MPA), discovered in 1893, was the first natural antibiotic to be isolated and crystallized in human history. Today, this fungal metabolite has been developed into multiple first-line immunosuppressive drugs to control immunologic rejection during organ transplantation and treat various autoimmune diseases.
However, the biogenesis of such an old and important molecule was an unsolved mystery for more than a century.
Recently, scientists from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences cracked this intriguing black box by fully elucidating the biosynthetic pathway of MPA. The results were published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS).
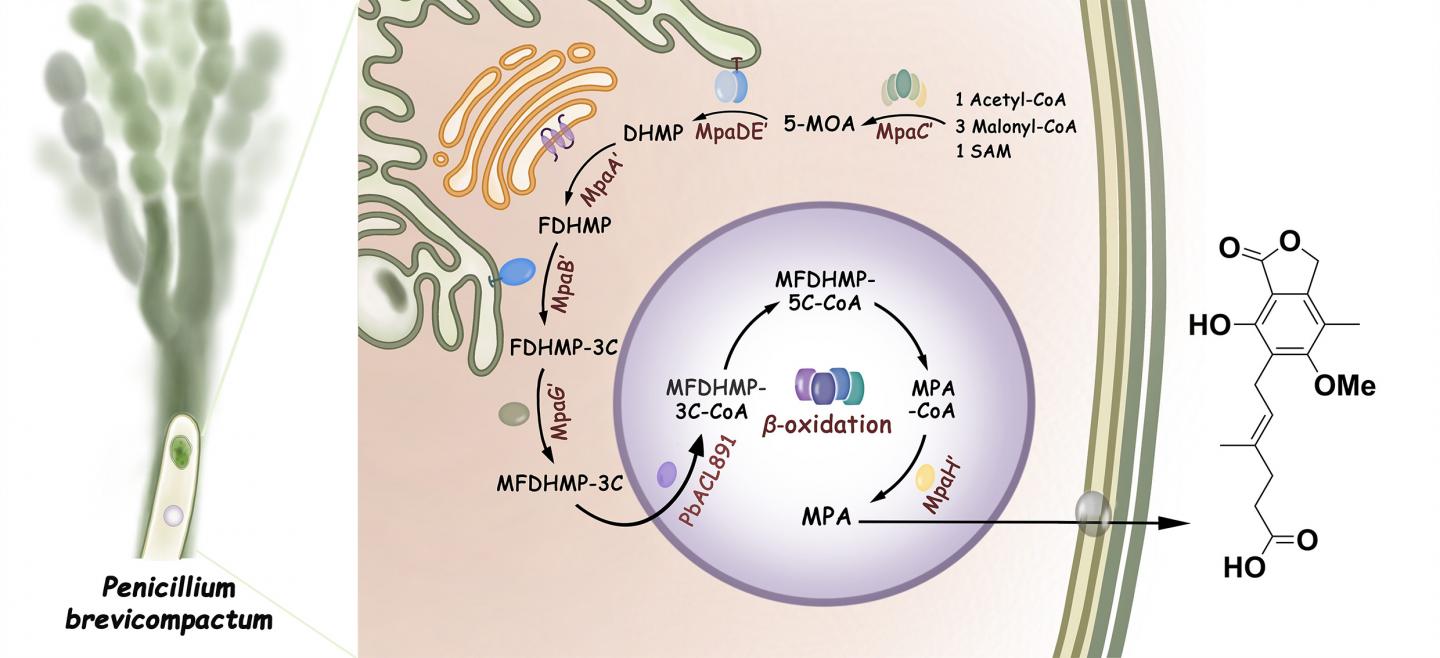
The researchers revealed that MPA biogenesis requires very unique cooperation between biosynthetic enzymes and β-oxidation catabolic machinery.
Interestingly, the involved enzymes were observed to be compartmentalized in different organelles including cytoplasm, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, and peroxisomes.
In this pathway, the oxygenase MpaB’, which is intriguingly homologous to a latex-clearing enzyme, was identified as the long-sought key enzyme responsible for oxidative cleavage of the farnesyl side chain that is structurally similar to rubber.
The resultant carboxylic acid intermediate allows it to be recognized by the fungal β-oxidation machinery located in the peroxisomes. The following successive β-oxidation chain-shortening process is elegantly gated by the peroxisomal acyl-CoA hydrolase MpaH’, thus leading to efficient and specific production of MPA.
The scientists concluded that compartmentalized biosynthesis is likely a very important characteristic of natural product biosynthesis in higher organisms such as fungi and plants.
They hope their work will prompt more research on this phenomenon since there is only very limited knowledge about the subcellular localization of fungal biosynthetic enzymes and their involvement in product formation and intermediate trafficking.
The researchers also hope the insights gained from this study will encourage industrial strain improvements that would lower the cost of this popular immunosuppressive drug as well as novel drug development based on MPA structural derivatization. “Ultimately, we wish that millions of patients will benefit from this basic research,” said LI Shengying, corresponding author of the study.
###
Media Contact
CHENG Jing
[email protected]
Original Source
http://english.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




