A team of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators has developed a device with the potential of shortening the time required to rapidly diagnose pathogens responsible for health-care-associated infections from a couple of days to a matter of hours. The system described in the journal Science Advances also would allow point-of-care diagnosis, as it does not require the facilities and expertise available only in hospital laboratories.
“Health-care-associated infections are a major problem that affects more than 600,000 patients each year, more than 10 percent of whom will die, and incurs more $100 billion in related costs,” says Ralph Weissleder, MD, PhD, director of the MGH Center for Systems Biology, Thrall Family Professor of Radiology at Harvard Medical School (HMS) and co-senior author of the report. “Rapid and efficient diagnosis of the pathogen is a critical first step in choosing the appropriate antibiotic regimen, and this system could provide that information in a physician’s office in less than two hours.”
While considered the gold standard for diagnosing bacterial infections, traditional culture-based diagnosis can take several days and requires specialized equipment, trained laboratory personnel and procedures that vary depending on the particular pathogen. Emerging genetic approaches that identify bacterial species by their nucleic acid sequences are powerful but still require complex equipment and workflows, restricting such testing to specialized hospital laboratories.
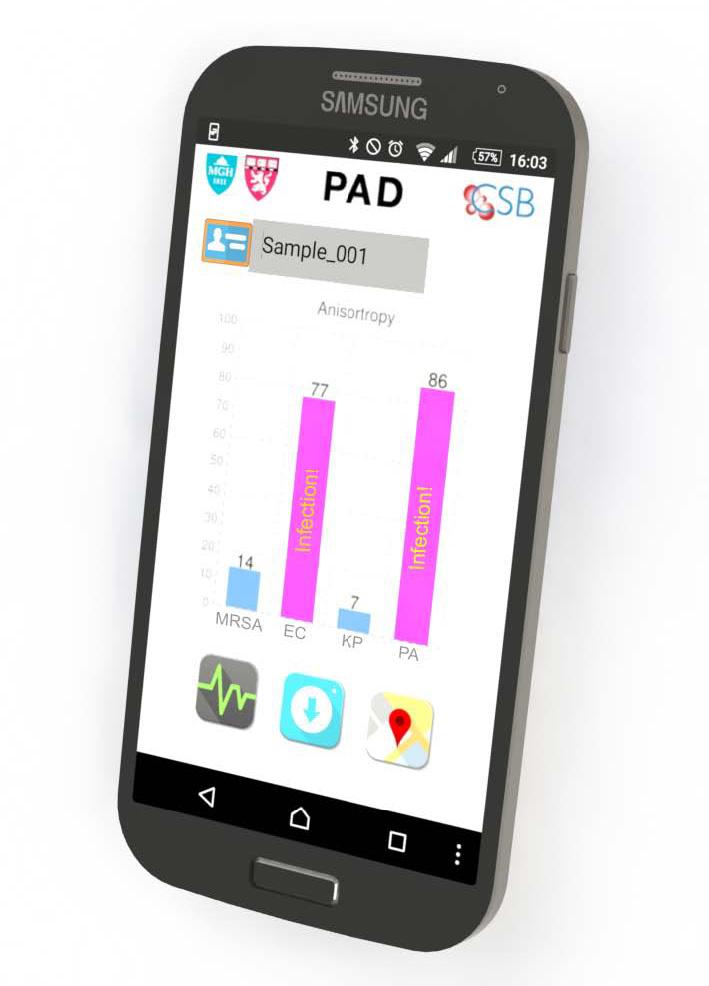
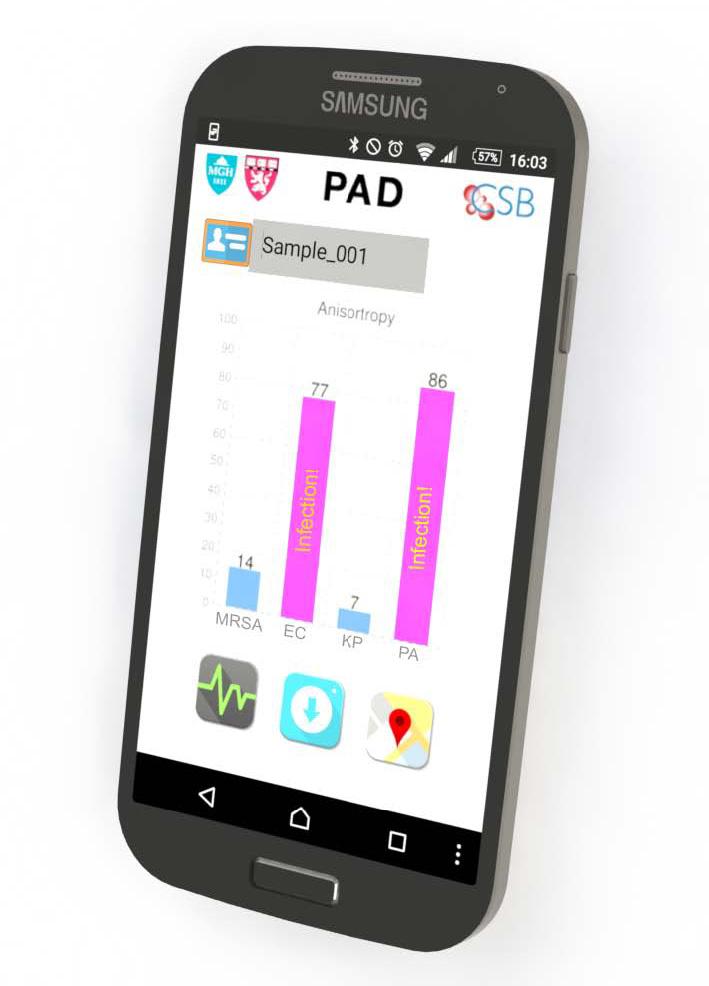
The system developed by the MGH team, dubbed PAD for Polarization Anisotropy Diagnostics, allows for accurate genetic testing in a simple device. Bacterial RNA is extracted from a sample in a small, disposable plastic cartridge. Following polymerase chain reaction amplification of the RNA, the material is loaded into a 2-cm plastic cube containing optical components that detect target RNAs based on the response to a light signal of sequence-specific detection probes. These optical cubes are placed on an electronic base station that transmits data to a smartphone or computer where the results can be displayed.
In this proof-of-principle study, the team used a prototype PAD system containing four optical cubes to test clinical samples from nine patients and compared the results with those acquired by conventional microbiology cultures. Testing for the presence of five important bacterial species — E. coli, Klebsiella, Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas, and Staph aureus — and for factors indicating the virulence and antibiotic resistance of specific strains produced identical results with both procedures. But while PAD provided results in less than two hours, the bacterial culture process took three to five days. The team has now designed probes for more than 35 bacterial species and virulence factors, and the overall cost of running the PAD assay should not exceed $2.00.
“This prototype still needs several improvements, including building a self-contained system housing all functions, further reducing the current assay time to less than one hour and expanding the panel of probes to even more pathogens and resistance factors,” says Hakho Lee, PhD, of MGH Center for Systems Biology (CSB), co-senior author of the report and an associate professor of Radiology at HMS. “But we can see three immediate applications for a system that can provide such rapid and accurate results – quickly diagnosing a patient’s infection, determining whether antibiotic-resistant bacteria are present in a group of patients, and detecting bacterial contamination of medical devices or patient environments.”
###
Ki Soo Park, PhD, and Chen-Han Huang, PhD, of the MGH-CSB are co-lead authors of the Science Advances report. Additional co-authors are Kyungheon Lee, PhD, and Cesar M. Castro, MD, MGH-CSB, and Yeong-Eun Yoo, Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials. Support for the study includes National Institutes of Health grants R01 HL113156, R01 EB004626, R01 EB010011, and T32 CA79443; and Department of Defense Ovarian Cancer Research Program award W81XWH-14-1-0279.
Contact for today (Monday, May 2): Sue McGreevey, [email protected], 617 724-2764.
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The MGH conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the United States, with an annual research budget of more than $800 million and major research centers in AIDS, cardiovascular research, cancer, computational and integrative biology, cutaneous biology, human genetics, medical imaging, neurodegenerative disorders, regenerative medicine, reproductive biology, systems biology, transplantation biology and photomedicine. In July 2015, MGH returned into the number one spot on the 2015-16 U.S. News & World Report list of “America’s Best Hospitals.”
Media Contact
McKenzie Ridings
[email protected]
617-726-0274
@MassGeneralNews
http://www.mgh.harvard.edu
The post Mass. General-developed device may provide rapid diagnosis of bacterial infections appeared first on Scienmag.