Credit: Hosono, Karato, Makino & Saitoh
New Haven, Conn. – For more than a century, scientists have squabbled over how the Earth’s moon formed. But researchers at Yale and in Japan say they may have the answer.
Many theorists believe a Mars-sized object slammed into the early Earth, and material dislodged from that collision formed the basis of the moon. When this idea was tested in computer simulations, it turned out that the moon would be made primarily from the impacting object. Yet the opposite is true; we know from analyzing rocks brought back from Apollo missions that the moon consists mainly of material from Earth.
A new study published April 29 in Nature Geoscience, co-authored by Yale geophysicist Shun-ichiro Karato, offers an explanation.
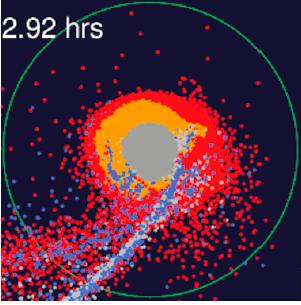
The key, Karato says, is that the early, proto-Earth — about 50 million years after the formation of the Sun — was covered by a sea of hot magma, while the impacting object was likely made of solid material. Karato and his collaborators set out to test a new model, based on the collision of a proto-Earth covered with an ocean of magma and a solid impacting object.
The model showed that after the collision, the magma is heated much more than solids from the impacting object. The magma then expands in volume and goes into orbit to form the moon, the researchers say. This explains why there is much more Earth material in the moon’s makeup. Previous models did not account for the different degree of heating between the proto-Earth silicate and the impactor.
“In our model, about 80% of the moon is made of proto-Earth materials,” said Karato, who has conducted extensive research on the chemical properties of proto-Earth magma. “In most of the previous models, about 80% of the moon is made of the impactor. This is a big difference.”
Karato said the new model confirms previous theories about how the moon formed, without the need to propose unconventional collision conditions — something theorists have had to do until now.
For the study, Karato led the research into the compression of molten silicate. A group from the Tokyo Institute of Technology and the RIKEN Center for Computational Science developed a computational model to predict how material from the collision became the moon.
###
The first author of the study is Natsuki Hosono of RIKEN. Additional co-authors are Junichiro Makino and Takayuki Saitoh.
Media Contact
Jim Shelton
[email protected]




