Credit: Kanazawa University
[Background]
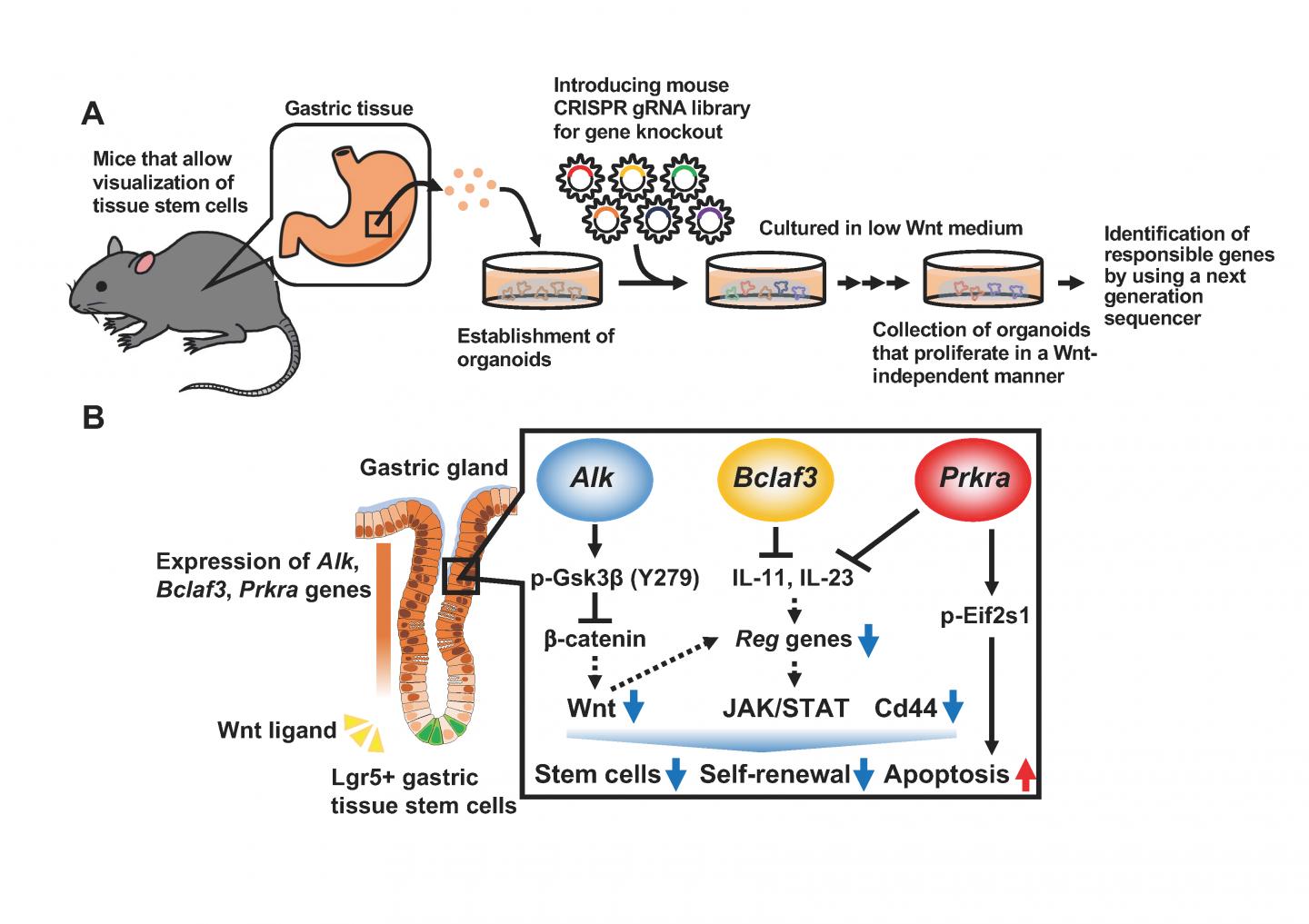
The human body consists of about 60 trillion cells that are renewed day by day to maintain homeostasis of body tissues. In particular, cells of the digestive tract are renewed completely within several weeks thanks to vigorous proliferation where tissue stem cells of every tissue play critical roles in supplying those cells. Tissue stem cells play essential roles in various phenomena such as histogenesis and recovery from damage by producing differentiated cells while dividing. They do this by producing identical cells (self-renewal) or by differentiating into other types of cells. The research team led by Profs. Murakami and Barker of the Cancer Research Institute, Kanazawa University revealed the presence of gastric tissue stem cells expressing the Lgr5 gene*1), a tissue stem cell marker at the gastric gland base in the gastric tissue, the stemness*2) of which could be suppressed by Wnt signaling*3) (Leushacke M. et al., Nat. Cell Biol., 2017). However, due to the technical difficulty of further detailed in vivo verification, most of the molecular mechanisms related to tissue stem cells regulated by Wnt signaling remained a mystery.
[Results]
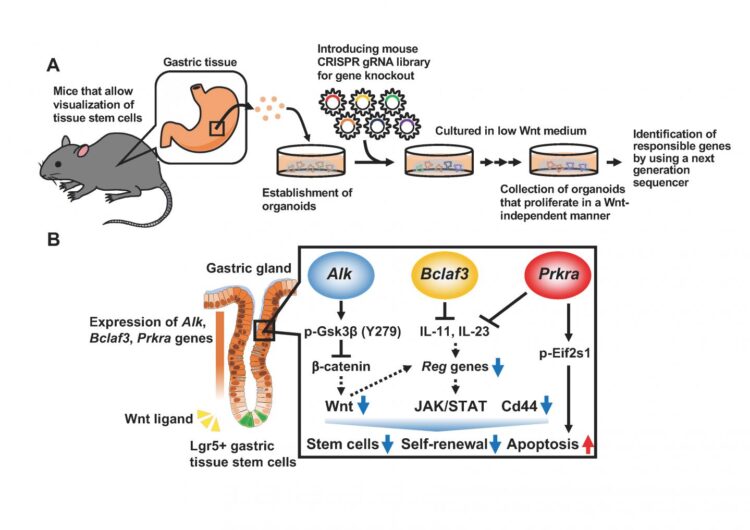
The research team investigated the intracellular molecular mechanisms for Wnt signaling-dependent regulation of proliferation and self-renewal of gastric tissue stem cells by using organoids*4) established from mice. These enabled visualization of Lgr5+ gastric tissue stem cells. Further, screening using Genome-Scale CRISPR Knock-Out (GeCKO)*5), which can arbitrarily produce loss-of-function of various genes, allowed the elucidation of molecular mechanisms regulating the Wnt signaling-dependence of gastric tissue stem cells. The team revealed that loss-of-function of Alk, Bclaf3 and Prkra genes induced Wnt signaling-independent proliferation of the organoids. Because these genes are expressed in differentiated cells of mouse gastric tissues but not in stem cells, the team postulated that these genes might negatively regulate the stemness of tissue cells. Further analyses have revealed that Alk suppresses Wnt signaling by phosphorylating Gsk3β, one of the regulatory factors of Wnt signaling. Further, Bclaf3 and Prkra regulate the expression of Reg family genes, which are essential for proliferation of gastric tissue stem cells, by inhibiting expression of epithelial interleukins 11 and 23*6). From these results, Alk, Bclaf3 and Prkra have been identified as the genes that determine the stemness of gastric tissue stem cells.
[Future Prospects]
The present study has elucidated previously unknown molecular mechanisms regulating the self-renewal and differentiation of tissue stem cells, which play roles in tissue homeostasis and recovery from damage. Similar molecular mechanisms may exist and function in other tissue stem cells, since Wnt signaling is widely activated in various stem cells regardless of their developmental stages. It is expected that treatments for tissue damage, not only of the digestive tract but also in liver, kidney and pancreas, should become possible if regulation of the self-renewal and differentiation of stem cells via the regulatory mechanisms described above could be verified in other tissues. The results of the present study provide new insights and technical approaches in stem cell research and are expected to stimulate innovation in the field of regenerative medicine and cancer treatment in the future.
###
[Glossary]
*1) Lgr5 gene
The gene coding leucine-rich orphan G-protein-coupled receptor5. It is one of the target genes of Wnt signaling that regulates the determination of cell fate and is a marker gene of epithelial stem cells that are necessary for the homeostasis of digestive tract tissues and for the recovery from damage. In recent years, expression of this gene is known in a wide range of epithelial tissues of kidney, lung, liver, uterus, etc. It is also reported as a stem cell marker of colorectal cancers in addition to normal epithelial stem cells.
*2) Stemness
Stemness refers to the property of being able to proliferate by cell division while, at the same time, maintaining the ability to differentiate into a variety of cells that form tissues.
*3) Wnt signaling
The signaling pathway activated by Wnt protein. Wnt signaling plays important roles in a wide variety of cell processes of ontogeny such as cell fate, proliferation and migration. Mutations of genes associated with Wnt signaling pathway are involved in various hereditary and spontaneously-emerging cancers.
*4) Organoid
Organoid refers to an ex vivo three-dimensional cell culture body that possesses structure and functions mimicking those of real tissues and organs. Since an organoid mimicking in vivo properties of a tissue or an organ can be maintained and observed, it is expected that organoids can be used for applications such as screening drug candidates, toxicity tests, pathophysiological research of diseases, etc.
*5) GeCKO screening method
This method can randomly knock out genes by introducing into a cell a diluted mixture of guide RNAs (gRNA) corresponding to all the genes. Thereafter, a cell population having the phenotype of interest is recovered and the knocked out genes responsible for inducing the phenotype of interest can be identified using a next generation sequencer.
*6) Interleukin
A bioactive substance produced by immune cells such as lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages for the regulation of intercellular immune responses. Interleukin 11 and 23 are secreted also from gastric epithelial cells.
Media Contact
Ayako Honda
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.