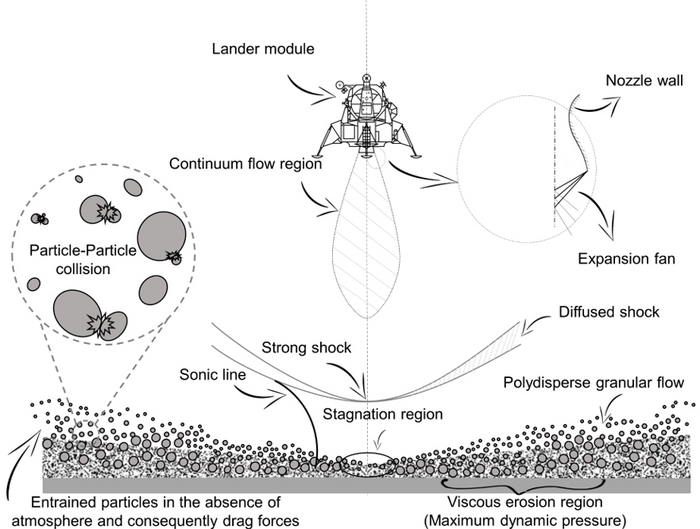
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – When a lander descends toward the moon – or a rocky planet, asteroid, or comet – the exhaust plume of the rocket interacts with the surface, causing erosion and kicking up regolith particles. The resulting blanket of dusty debris can create a dangerous brownout effect, limiting visibility and potentially damaging the spacecraft or nearby equipment.
Credit: Reproduced with permission from A. Rahimi, O. Ejtehadi, K.H. Lee, R.S. Myong, Acta Astronautica, 175 (2020) 308-326. ©2018 Elsevier.
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – When a lander descends toward the moon – or a rocky planet, asteroid, or comet – the exhaust plume of the rocket interacts with the surface, causing erosion and kicking up regolith particles. The resulting blanket of dusty debris can create a dangerous brownout effect, limiting visibility and potentially damaging the spacecraft or nearby equipment.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Chungnam National University, the University of Edinburgh, Gyeongsang National University, and the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information developed a model to describe the interaction between a rocket plume and the surface of a planetary body in near-vacuum conditions. The results can be used to evaluate the safety and feasibility of a proposed landing site and to optimize the design of spacecraft and rocket engines for planetary landings.
“Understanding the interaction between the rocket plume and the surface is important for the safety and success of space missions in terms of contamination and erosion, landing accuracy, planetary protection, and engineering design, as well as for scientific understanding and future exploration,” said author Byoung Jae Kim of Chungnam National University.
The computational framework takes in information about the rocket, its engines, and the surface composition and topography, as well as the atmospheric conditions and gravitational forces at the landing site.
By considering the interaction of the gas with solid particles as a system of equations, the simulation estimates the shape and size of the plume, the temperature and pressure of the plume and surface, and the amount of material eroded or displaced. It does so in a way that is more computationally efficient than previous methods.
“Our tool can simulate the plume surface interaction problem at the fundamental level (e.g., scour pattern formation and development of erosion models) and for practical engineering applications (e.g., predicting particle trajectories to avoid damage to the lander and previously established sites and planning descend/ascend scenarios),” said Kim.
In the model, small regolith particles reached high altitudes and caused severe brownout effects during ascent and descent. In contrast, larger particles with increased bed height led to a more favorable brownout status.
“The insights gained from this study of the effects of different parameters on plume-surface interaction can inform the development of more effective and efficient landing technologies,” said Kim. “The study also sheds light on the festooned scour patterns that can be observed on planetary surfaces, which can provide valuable information for future scientific investigations of planetary bodies.”
The researchers plan to improve the capabilities of the framework to include more complex physics, such as chemical reactions and solid particle collisions. They believe the model can be applied to other physics scenarios including needle-free drug delivery systems.
###
The article “Full continuum approach for simulating plume-surface interaction in planetary landings” is authored by Omid Ejtehadi, Rho Shin Myong, Ilyoup Sohn, and Byoung Jae Kim. It will appear in Physics of Fluids on April 25, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0143398). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0143398.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
###
Journal
Physics of Fluids
DOI
10.1063/5.0143398
Article Title
Full continuum approach for simulating plume-surface interaction in planetary landings
Article Publication Date
25-Apr-2023




