Chaperones keep the tumor suppressor protein p53 in check
Credit: G. Agam / LMU & V. Dahiya / TUM
The anti-tumor protein p53 can decide on the life or death of a cell: If it detects damage in the cell’s genome, the protein pushes the cell to suicide. New research conducted at Technical University of Munich (TUM) shows that this inborn cancer prevention only works when special proteins, known as chaperones, allow it to take place.
A cancer therapy without side-effects, that specifically attacks only tumor cells: still a dream for doctors and patients alike. But nature has long since developed exactly this kind of focused anti-tumor program. Each of our cells is equipped with it: When serious damage to the genome is detected, the cell destroys itself, thus preventing the growth of the tumor. A research team in Munich has now decoded the complex regulatory mechanism, which involves a number of different proteins.
“We’ve known for some time that such a regulatory mechanism exists, and that the tumor suppressor protein p53 plays a key role. What was not known before was the role played by molecular chaperones in regulating the cellular machinery,” explains Prof. Johannes Buchner, who holds the TUM Professorship for Biotechnology.
A closer look at the molecular machine
The chaperones, as they are called in biotechnology, are proteins that make sure that other proteins fold properly and thus remain functional. In their laboratory the researchers demonstrated that two groups of these “escort” proteins, Hsp70 and Hsp40 as well as Hsp90, control the function of the tumor suppressor protein p53 by influencing its three-dimensional structure.
The biochemists investigated what happens in the test tube upon adding the chaperones Hsp40 and Hsp70 to a solution containing p53. p53 lost its ability to bind to DNA, meaning that its biological activity also ceased.
Fluorescence reveals the structure
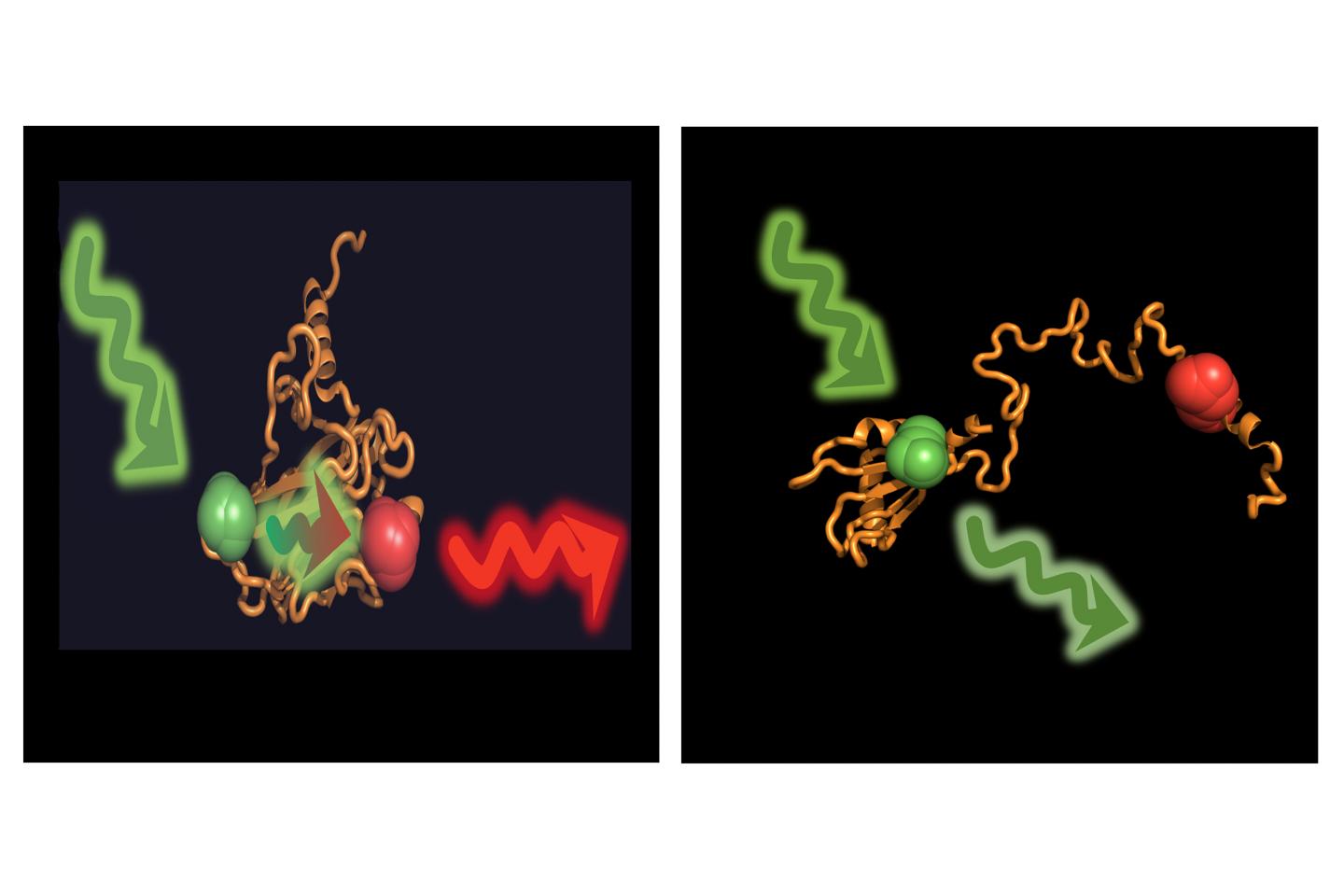
But what makes all this work? To answer this question, the scientists marked p53 with fluorescent dyes, making it possible for them to monitor the structure of individual p53 molecules. In isolation, p53 alone is folded; under the influence of Hsp40 and Hsp70 it is completely unfolded, consuming energy in the process. The opposite effect was observed when the chaperone Hsp90 was added: It put the unfolded p53 back into its active, folded form.
“We were very surprised by this enormous impact of the chaperones,” Buchner recalls. “Here the cell has an extremely complex regulatory mechanism which the chaperones use to keep the tumor suppressor protein in line.”
As long as these molecular escorts are available, p53 stays unfolded and biologically inactive. But if the cell comes under pressure and the chaperones have to keep the peace at another location, p53 folds, binds to the DNA and, when necessary, triggers the cellular suicide.
According to Buchner, an understanding of this molecular interaction could in the future help to better understand the role of proteins and to find new points of attack for cancer therapies.
###
The structure of p53 was investigated using Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET). The procedure is based on the concept that when the protein labeled with the donor dye is excited by light, it triggers the acceptor dye molecules, at a distance of only a few nanometers, to emit light thereby revealing structural changes in a protein. Working together with a team led by Prof. Don Lamb at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, the researchers were thus able to measure individual p53 molecules and to observe how these molecules change their structure under the influence of Hsp40 and Hsp70 or Hsp90.
The research was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) (SFB 1035, the Clusters of Excellence Nanosystems Initiative Munich (NIM) and Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CiPSM)). The lead author was supported with an Alexander von Humboldt Foundation postdoctoral fellowship.
Publication:
Vinay Dahiya, Ganesh Agam, Jannis Lawatscheck, Daniel Andreas Rutz, Don C. Lamb, Johannes Buchner: Coordinated conformational processing of the tumor suppressor protein p53 by the Hsp70 and Hsp90 chaperone machineries, Molecular Cell, April 23, 2019, DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.03.026
Media Contact
Dr. Andreas Battenberg
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




